우리는 pintos에서 hash table을 사용할 것이다.
pintos 안에는 이미 hash.c, hash.h 을 통해서 함수가 구현되어 있는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
여기서는 hash를 간단하게 정리하고 코드 정리를 하겠다.
hash table이란
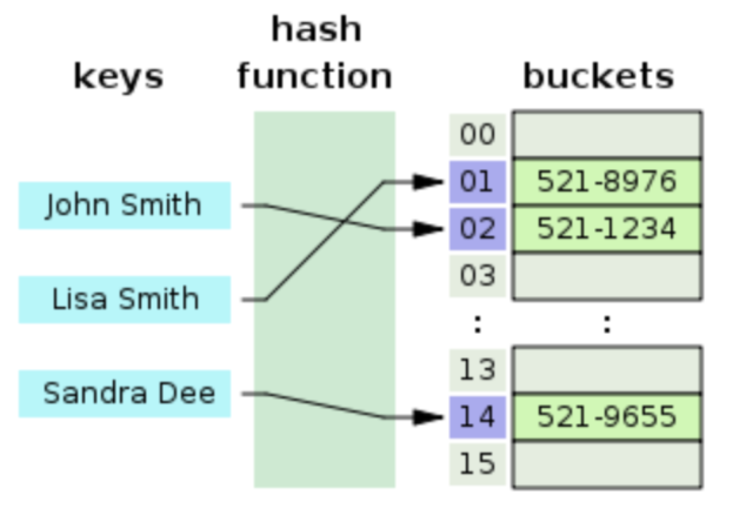
데이터를 저장하는 자료구조 중 하나이며 key, value로 묶여있기 때문에 빠른 속도로 검색할 수 있다.
hash table은 key를 이용하여 index를 생성하고 해당 index와 value를 연결한다.
(index, value) 묶인 것을 bucket 이라고 한다
평균 시간복잡도는 O(1) 이다.
hash table의 구조체는 아래와 같이 생겼다.
/* Hash table. */
struct hash {
size_t elem_cnt; /* Number of elements in table. */
size_t bucket_cnt; /* Number of buckets, a power of 2. */
struct list *buckets; /* Array of `bucket_cnt' lists. */
hash_hash_func *hash; /* Hash function. */
hash_less_func *less; /* Comparison function. */
void *aux; /* Auxiliary data for `hash' and `less'. */
};/* Hash element. */
struct hash_elem {
struct list_elem list_elem;
};실제 hash는 hash_elem이라는 struct를 사용해서 연결되게 된다.
즉 struct hash에 직접 접근하여 사용할 일은 없다. - gitbook에도 나오는 내용
(list와 유사함)
hash_entry 함수를 보면 list_entry 함수와 거의 동일하게 생겼다.
하는 역할도 비슷하다.
이런 식으로 hash의 함수를 그대로 쓸 수 있다.
#define hash_entry(HASH_ELEM, STRUCT, MEMBER) \
((STRUCT *) ((uint8_t *) &(HASH_ELEM)->list_elem \
- offsetof (STRUCT, MEMBER.list_elem)))
#define list_entry(LIST_ELEM, STRUCT, MEMBER) \
((STRUCT *) ((uint8_t *) &(LIST_ELEM)->next \
- offsetof (STRUCT, MEMBER.next)))
차이점으로는 list의 경우 compare 함수가 필요 없는 경우도 존재하였지만 (list_push_back, list_push_front etc.) hash는 필수적으로 필요하다
hash 구조체를 보면 hash를 사용하기 위해서는 hash_hash_func 과 hash_less_func은 필수이다.
hash_hash_func 은 hash_element 에 대한 hash 값을 64bit type으로 return 한다
그 안에 들어가는 func은 buffer안의 size 만큼의 byte를 hash 값으로 return 한다.
unsigned
page_hash (const struct hash_elem *p_, void *aux UNUSED) {
const struct page *p = hash_entry (p_, struct page, elem_hash);
return hash_bytes (&p->va, sizeof (p->va));
}bool
page_cmp_less (const struct hash_elem *a_, const struct hash_elem *b_,
void *aux UNUSED) {
const struct page *a = hash_entry (a_, struct page, elem_hash);
const struct page *b = hash_entry (b_, struct page, elem_hash);
return a->va < b->va;
}다음부터는 실제 코드를 보며 같이 정리하도록 하겠다.