문제 링크
문제
티어: 골드 2
**알고리즘: bfs, 해시맵
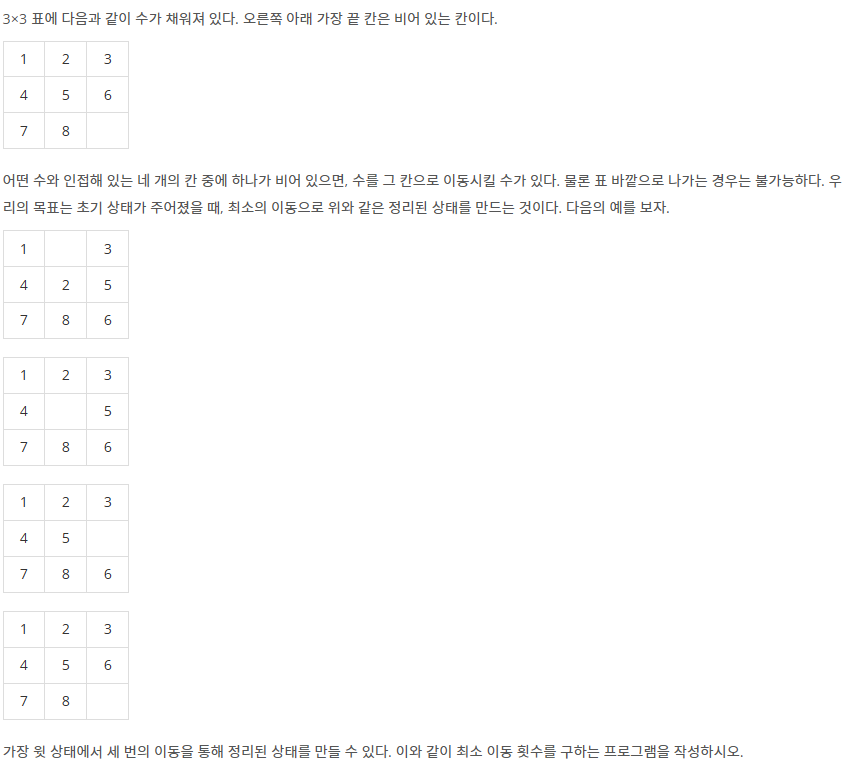
입력
세 줄에 걸쳐서 표에 채워져 있는 아홉 개의 수가 주어진다. 한 줄에 세 개의 수가 주어지며, 빈 칸은 0으로 나타낸다.
출력
첫째 줄에 최소의 이동 횟수를 출력한다. 이동이 불가능한 경우 -1을 출력한다.
풀이
target인
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 0
을 만들기 위한 최소 이동 횟수를 출력한다.
3x3 이기 때문에 모든 경우를 찾아보는 풀이를 생각할 수 있다.
각 자리에 9개의 수가 올 수 있다고 한다면 9!이기 때문에 충분히 가능하고, 절대로 9!만큼 경우의 수가 나오지도 않는다. 이보다 훨씬 경우의 수는 작을 것이다. (0이 인접해야만 움직일 수 있기 때문에 움직임이 제한되어 있기 때문)
그래서 모든 상태를 미리 만들어 놓기 보다는 HashMap을 활용해서 가능한 상태만을 체크하는 것이 메모리를 더 효율적으로 사용하는 방법이 될 것이다.
또한 상태를 체크하기 위해서는 3x3 배열을 하나의 String으로 처리한다면, 쉽게 상태를 나타낼 수 있다.
bfs를 통해서 0과 인접한 경우를 모두 탐색을 할 것인데, 이동을 했다고 했을 때 String 값이 이미 방문한 상태라면 또 방문할 이유는 없다. 최소 이동 횟수를 구해야 하기 때문이다.
그래서 bfs로 노드마다 방문할 수 있는 모든 경우를 탐색하고, 중복 처리를 한다면 쉽게 풀 수 있다.
또한 추가적으로 메모리를 절약하는 방법은 char[]이나 String을 활용하는 것이다.
int[]는 각 요소가 4byte이기 때문에 요소의 길이가 1인 상태에서는 2byte로 나타낼 수 있는 char[]이나 String을 활용하는 것이 효율적이다. (물론 int[]라고 해서 안될 것 같지는 않지만 메모리 절약이 중요한 문제인 것 같기 때문에 이 부분도 고려해 줬다.)
소스 코드
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GraphInfo {
String s;
int bInd;
GraphInfo(String s, int bInd) {
this.s = s;
this.bInd = bInd;
}
}
class TwoD {
int x, y;
TwoD(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
public class Main {
static final int[] dx = {
-1,
0,
1,
0
};
static final int[] dy = {
0,
-1,
0,
1
};
static final String target = "123456780";
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
int inputBInd = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
String str = st.nextToken();
if (str.equals("0")) {
inputBInd = convertFrom2DTo1D(j, i);
}
sb.append(str);
}
}
GraphInfo input = new GraphInfo(sb.toString(), inputBInd);
System.out.println(bfs(input));
}
static int bfs(GraphInfo input) {
Queue < GraphInfo > que = new LinkedList < > ();
HashMap < String, Boolean > visited = new HashMap < > ();
visited.put(input.s, true);
que.add(input);
int cnt = 0;
while (!que.isEmpty()) {
int sz = que.size();
for (int t = 0; t < sz; t++) {
GraphInfo node = que.poll();
if (node.s.equals(target)) {
//같다면
return cnt;
}
TwoD td = convertFrom1DTo2D(node.bInd);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nx = td.x + dx[i];
int ny = td.y + dy[i];
if ((0 <= nx && nx <= 2) && (0 <= ny && ny <= 2)) {
char[] charArr = node.s.toCharArray();
int cp = convertFrom2DTo1D(nx, ny); //바꿀 위치
char temp = charArr[cp];
charArr[cp] = '0';
charArr[node.bInd] = temp;
String newStr = new String(charArr);
if(visited.get(newStr) == null) {
//방문하지 않았다면
que.add(new GraphInfo(newStr, cp));
visited.put(newStr, true);
}
}
}
}
cnt += 1;
}
return -1;
}
static int convertFrom2DTo1D(int x, int y) {
return y * 3 + x;
}
static TwoD convertFrom1DTo2D(int ind) {
return new TwoD(ind % 3, ind / 3);
}
}