Page Table Structure
페이징 테이블을 구성하는 일반적인 3가지 방식
Hierarchical Paging
logical address space를 여러개의 page table로 분할
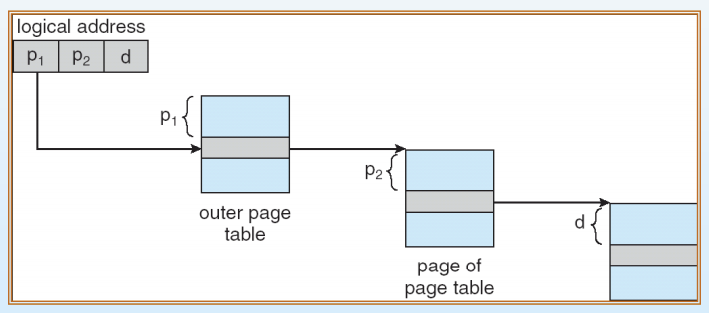
Two Level Page Table
page table 자체가 paging 되는 것을 말한다.
- 4KB page size를 가진 32-bit 기계의 logical address
- 20bit page number → 1million entries in table
- 12bit page offset (4K word in page)
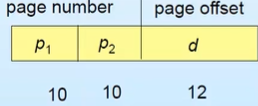
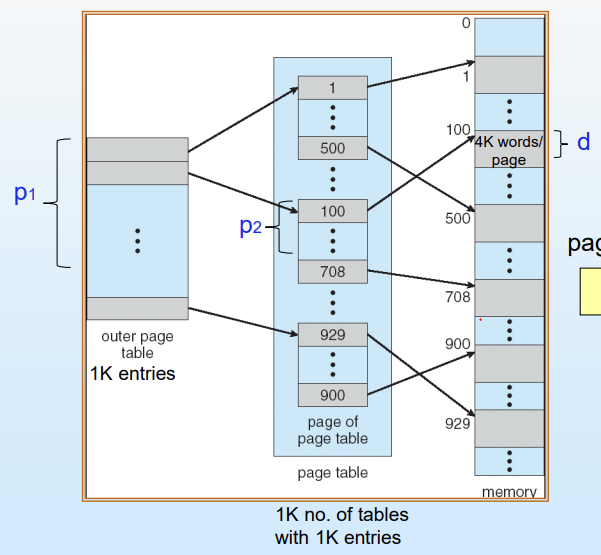
- P1: outer page table index, P2 : outer page table 내의 offset
- two level 32bit paging architecture에서의 address-translation
Hashed Page Table
-
address space > 32bit 이면 논리 주소를 hash로 사용하는 hashed page table을 사용함.
-Hash형 page table의 각 항목은 연결리스트를 가지고 있다. 이 list에는 collision을 일으켜서 해쉬되는 원소들이 연결되어 있다. -
장점: Hashed Page Table을 만들고 hash function으로 access 횟수를 많이 줄일 수 있다.
-
3가지 필드
1) virtual(=logical) page number
2) 사상되는 page frame number
3) linked list 상의 다음 원소 pointer
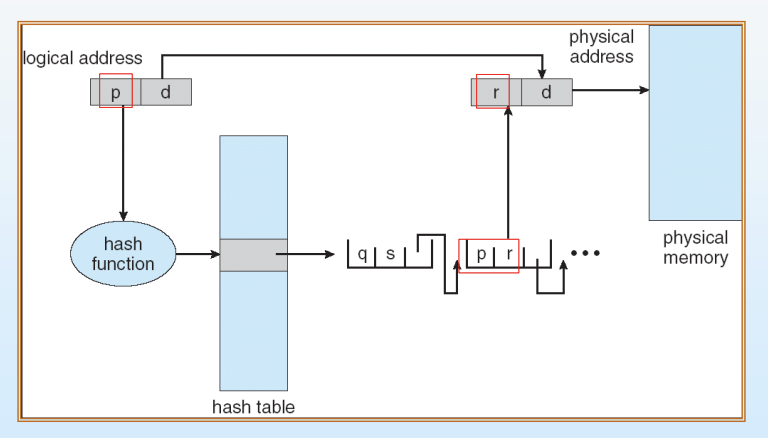
- logical address space으로부터 page number가 오면 이를 hashing한다.
- Hashed page table에서 연결 리스트를 따라가며 첫번째 원소와 page 번호를 비교한다.
- 일치하면 그에 해당하는 page frame 번호(두번째 필드)를 가져와 physical address를 얻는다. 일치하지 않으면 다음 원소로 비교(2번이랑 같은)
사실 process 하나당 page table이 존재하기에 이런 문제들이 발생했던 것. 그럼 이 frame은 어떤 프로세스의 몇 번 page인지 역으로 접근!! : Inverted page table
Inverted Page Tables
각각의 프로세스마다 페이지 테이블이 만들어지기 때문에 실제로는 다른 프로세스에서 해당 메모리에 접근하고 있음에도 불구하고 page table entry에 데이터를 가지고 있어야 하는 경우가 있다. → 단점 : page table의 크기
- 해결 : inverted page table 사용
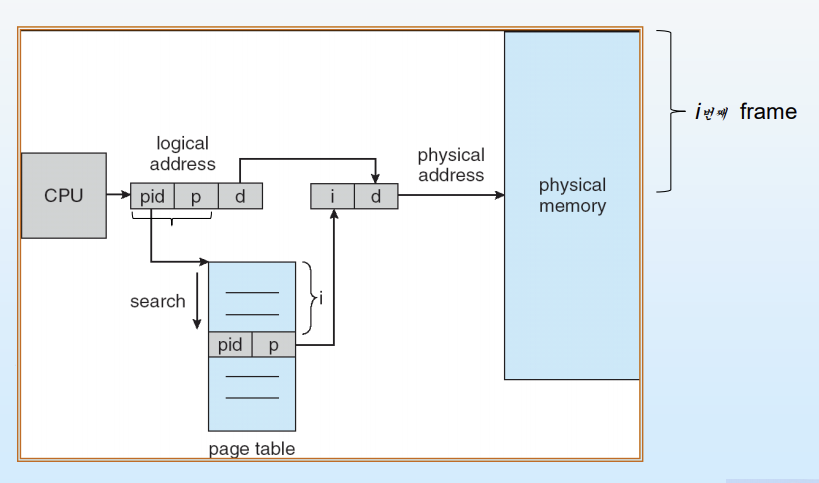
- 시스템에 page table이 한개만 존재한다.
- 각 physical memory에 하나의 page를 가진다.
- 장점 : logical page마다 각 page table를 가지는 대신 physical frame에 대응하는 항목만 table에 저장되기 때문 사용되는 memory가 감소!
- 주소 공간 ID가 필요하다. 이 ASID는 logical address가 상응하는 physical address에 대응되는 것을 보장한다.
- 단점: search시간 오래 걸림. → Hash를 이용하여 시간을 감소시키면 됨.
- logical address : <process-id, page-number, offset>으로 구성
- inverted page table 항목은 <process-id, page-number>로 구성 → process id = 주소 공간 id
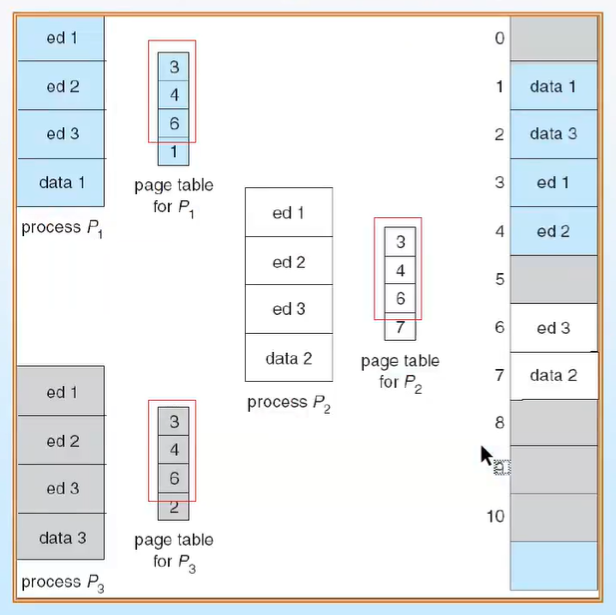
Shared Pages
- Shared code
- process 간에 공유되는 read-only(reentrant) code
- 모든 proces의 logical address space 간에서 동일한 위치에 있어야 함
- non-self-modifying code이므로 실행 중에 변하지 않는다
- 따라서 2개 이상의 프로세스가 같은 코드에서 동시에 실행된다.
- Private code and data
- 각 process는 code와 data를 private하게 보관
- private code & data에 대한 page는 logical address space의 어느 위치에나 있을 수 잇음
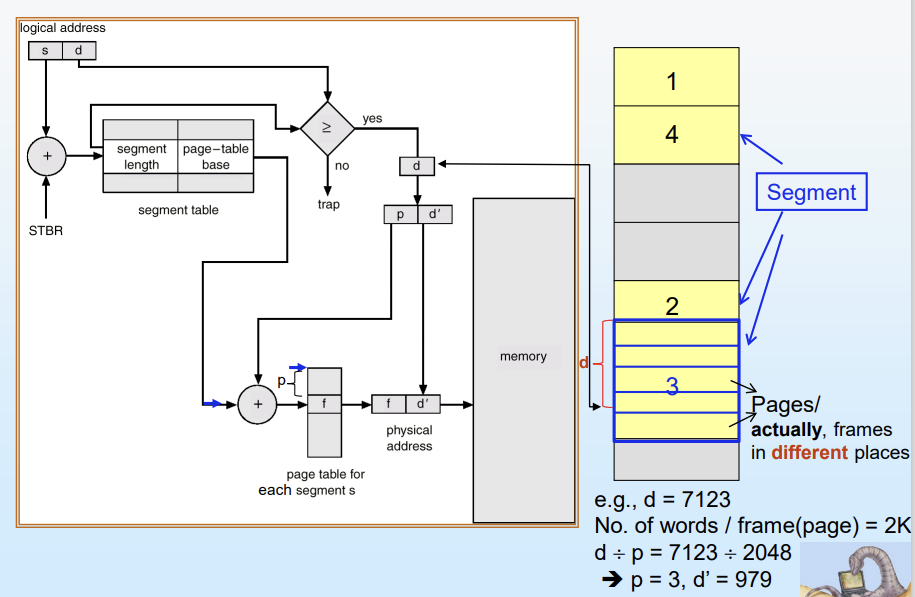
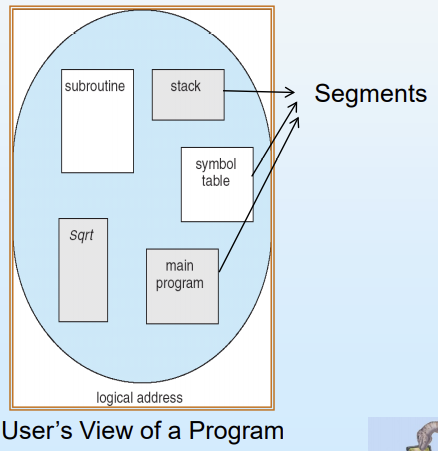
Segmentation
메모리의 user view를 그대로 지원하는 memory-management 기법
-
logical address space = segments의 집합
-
Logical address : <segement-number, offset>으로 구성
-
Segment table
- base : segment 시작 주소
- limit : segment 길이
-
Segment-table base register (STBR)에 segment table의 위치 point
-
Segment-table length register (STLR)은 program에 사용하는 segment의 개수 나타냄
s < STLR일 때, Segment number s 유효
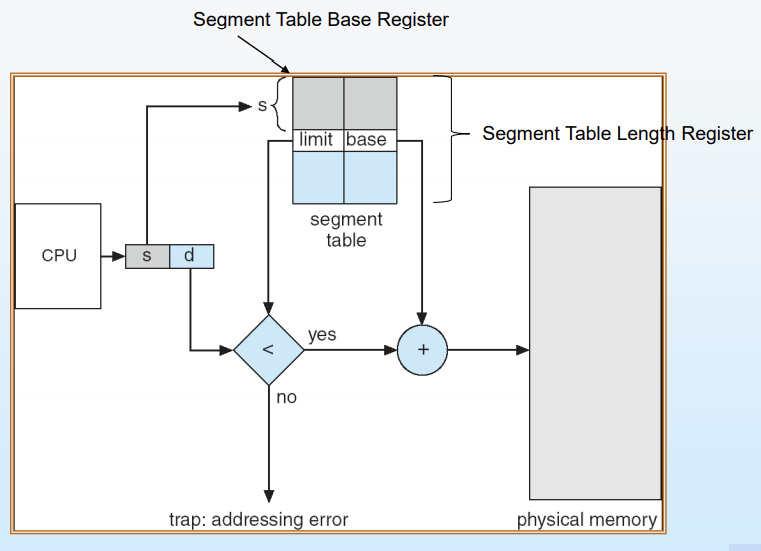
-
Relocation
- dynamic
- segment table에 의해 (base값 바꿈)
-
Sharing
- shared segments
- same segment number
-
Allocation
- first fit or best fit
- external fragmentation은 존재함
-
Protection : segment table에 bit 추가로 구현
- validation bit = 0 -> 잘못된 segment
- read/write/execute privileges(권한)
- code sharing도 segment 단위로
- dynamic storage-allocation problem이 발생 (segments 길이가 다양하기 때문)
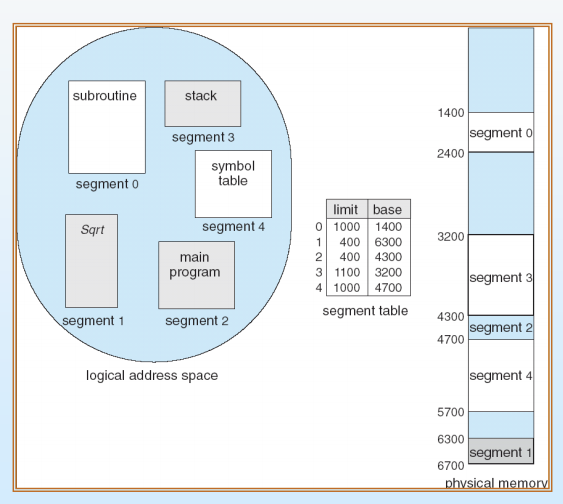
- segment sharing
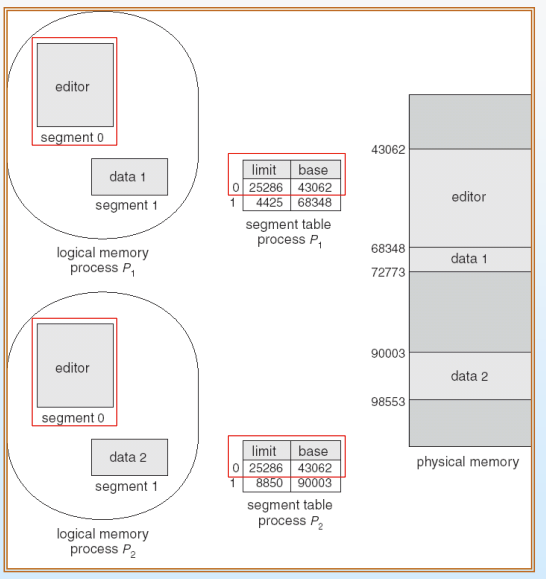
Segmentation with Paging - MULTICS
- segment를 paging하여 external fragmentation 및 long search time 문제 해결