교육 정보
- 교육 명: 경기미래기술학교 AI 교육
- 교육 기간: 2023.05.08 ~ 2023.10.31
- 오늘의 커리큘럼:
머신러닝
(7/17 ~ 7/28)- 강사: 이현주, 이애리 강사님
- 강의 계획:
1. 머신러닝
Ensemble
보팅(Voting)
-
서로 다른 여러 모델을 사용하여 하나의 데이터를 분류하고 각 모델에서 도출된 결과를 통해 최종 결과를 결정
- 하드보팅 : 각 모델의 최종 결과를 기준으로 다수결로 결정
- 소프트 보팅: 각 모델의 class 별 확률을 토대로 전체 확률을 계산하여 결정
-
without voting
#SVM
from sklearn.svm import SVC
svm_model = SVC(probability=True, random_state=42)
svm_model.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred = svm_model.predict(X_test)
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, accuracy_score, classification_report
cm = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred)
print(cm)
sns.heatmap(cm, annot=True)
plt.show()
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
print(f'{accuracy = :.4f}')
print(classification_report(y_test, y_pred))
# ROC
from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score, roc_curve, auc
phat = svm_model.predict_proba(X_test)[: ,1]
fpr, tpr, threshold = roc_curve(y_test, phat)
plt.plot(fpr, tpr)
plt.xlabel('false positive rate')
plt.ylabel('true positive rate')
plt.show()
print(f'{auc(fpr, tpr) = }')
#
# 결과
accuracy = 0.8701
precision recall f1-score support
0 0.87 1.00 0.93 354
1 1.00 0.02 0.04 54
accuracy 0.87 408
macro avg 0.93 0.51 0.48 408
weighted avg 0.89 0.87 0.81 408
auc(fpr, tpr) = 0.7959301109018623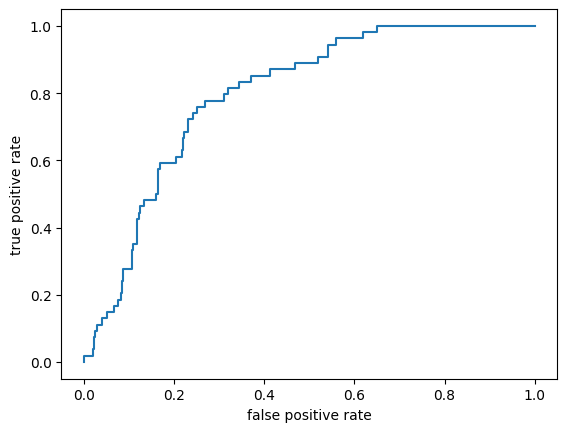
- soft voting
# soft (RandomForestClassifier, SVC, LogisticRegression)
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier, VotingClassifier
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
#모델 생성 및 학습
rfClf = RandomForestClassifier(random_state=42)
svmClf = SVC(probability=True, random_state=42)
logClf = LogisticRegression(random_state=42)
clf = VotingClassifier(estimators=[('rf', rfClf), ('svm', svmClf), ('log', logClf)], voting='soft')
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
#평가
clf_pred = clf.predict(X_test)
cm = confusion_matrix(y_test, clf_pred)
print(cm)
sns.heatmap(cm, annot=True)
plt.show()
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, clf_pred)
print(f'{accuracy = :.4f}')
print(classification_report(y_test, clf_pred))
#ROC 커브 그리기 AUC 출력
phat = clf.predict_proba(X_test)[: ,1]
fpr, tpr, threshold = roc_curve(y_test, phat)
plt.plot(fpr, tpr)
plt.xlabel('false positive rate')
plt.ylabel('true positive rate')
plt.show()
print(f'{auc(fpr, tpr) = }')
#
# 결과
accuracy = 0.8676
precision recall f1-score support
0 0.87 0.99 0.93 354
1 0.50 0.04 0.07 54
accuracy 0.87 408
macro avg 0.69 0.52 0.50 408
weighted avg 0.82 0.87 0.81 408
auc(fpr, tpr) = 0.9008683825068005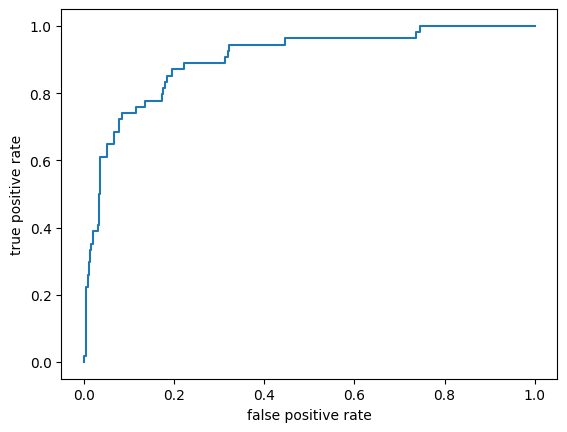
- hard voting
# hard (RandomForestClassifier, SVC, LogisticRegression)
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier, VotingClassifier
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
#모델 생성 및 학습
rfClf = RandomForestClassifier(random_state=42)
svmClf = SVC(random_state=42)
logClf = LogisticRegression(random_state=42)
clf = VotingClassifier(estimators=[('rf', rfClf), ('svm', svmClf), ('log', logClf)], voting='hard')
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
#평가
clf_pred = clf.predict(X_test)
cm = confusion_matrix(y_test, clf_pred)
print(cm)
sns.heatmap(cm, annot=True)
plt.show()
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, clf_pred)
print(f'{accuracy = :.4f}')
print(classification_report(y_test, clf_pred))
# hard에서는 확률이 없어서 roc 안나옴
#
# 결과
accuracy = 0.8873
precision recall f1-score support
0 0.89 1.00 0.94 354
1 0.90 0.17 0.28 54
accuracy 0.89 408
macro avg 0.89 0.58 0.61 408
weighted avg 0.89 0.89 0.85 408배깅(Bagging)
-
같은 종류의 모델을 여러번 사용해서 결과를 예측 (train 데이터의 중복 가능)
-
대표적인 배깅: RandomForest
-
without bagging
# 단일 로지스틱 회귀
logReg = LogisticRegression(random_state=0)
logReg.fit(X_train, y_train)
log_pred = logReg.predict(X_test)
# confusion matrix
cm = confusion_matrix(y_test, log_pred)
print(cm)
sns.heatmap(cm, annot=True)
plt.show()
# accuracy
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, log_pred)
print(f'{accuracy = :.4f}')
# report
print(classification_report(y_test, log_pred))
#
# 결과
accuracy = 0.8946
precision recall f1-score support
0 0.90 0.99 0.94 354
1 0.76 0.30 0.43 54
accuracy 0.89 408
macro avg 0.83 0.64 0.68 408
weighted avg 0.88 0.89 0.87 408
- Bagging with LogisticRegression
from sklearn.ensemble import BaggingClassifier
bagClf = BaggingClassifier(LogisticRegression(random_state=0),
n_estimators=1000,
oob_score=True,
random_state=0)
bagClf.fit(X_train, y_train)
bag_pred = bagClf.predict(X_test)
#
# 결과
# confusion matrix
cm = confusion_matrix(y_test, bag_pred)
print(f'{cm = }')
# accuracy
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, bag_pred)
print(f'{accuracy = :.4f}')
# report
report = classification_report(y_test, bag_pred)
print('report\n', report)
# ROC & AUC
phat = bagClf.predict_proba(X_test)[: ,1]
fpr, tpr, threshold = roc_curve(y_test, phat)
plt.plot(fpr, tpr)
plt.xlabel('false positive rate')
plt.ylabel('true positive rate')
plt.show()
print(f'{auc(fpr, tpr) = }')
#
# 결과
cm = array([[348, 6],
[ 39, 15]])
accuracy = 0.8897
report
precision recall f1-score support
0 0.90 0.98 0.94 354
1 0.71 0.28 0.40 54
accuracy 0.89 408
macro avg 0.81 0.63 0.67 408
weighted avg 0.87 0.89 0.87 408
auc(fpr, tpr) = 0.8886796400920695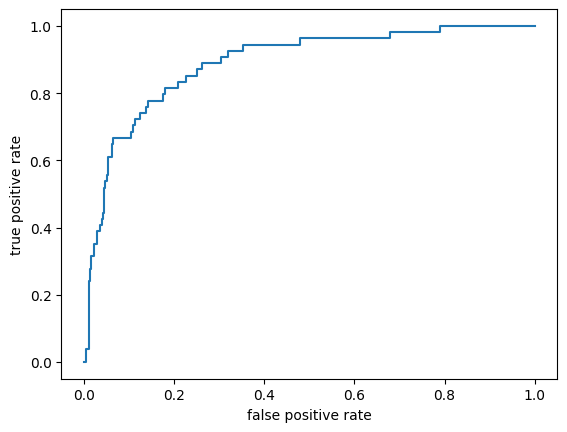
- Random Forest (그 자체로 bagging 기법)
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
rfm = RandomForestClassifier()
rfm.fit(X_train, y_train)
rfm_pred = rfm.predict(X_test)
# confusion matrix
cm = confusion_matrix(y_test, rfm_pred)
print(f'{cm = }')
# accuracy
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, rfm_pred)
print(f'{accuracy = :.4f}')
# report
report = classification_report(y_test, rfm_pred)
print('report\n', report)
# ROC & AUC
phat = rfm.predict_proba(X_test)[: ,1]
fpr, tpr, threshold = roc_curve(y_test, phat)
plt.plot(fpr, tpr)
plt.xlabel('false positive rate')
plt.ylabel('true positive rate')
plt.show()
print(f'{auc(fpr, tpr) = }')
#
# 결과
cm = array([[349, 5],
[ 30, 24]])
accuracy = 0.9142
report
precision recall f1-score support
0 0.92 0.99 0.95 354
1 0.83 0.44 0.58 54
accuracy 0.91 408
macro avg 0.87 0.72 0.77 408
weighted avg 0.91 0.91 0.90 408
auc(fpr, tpr) = 0.9017315337936807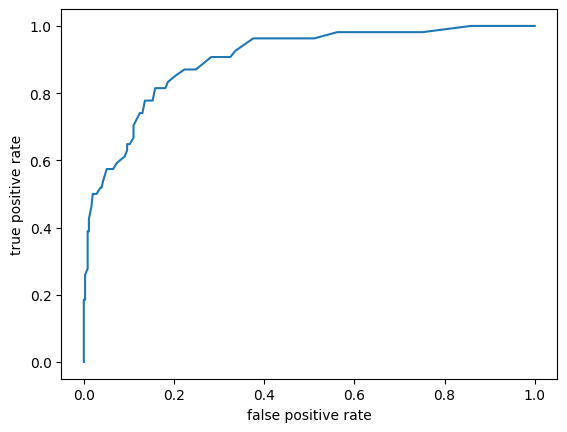
- Bagging with DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
bagClf = BaggingClassifier(DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state=0),
n_estimators=500,
oob_score=True,
random_state=0)
bagClf.fit(X_train, y_train)
bag_pred = bagClf.predict(X_test)
# confusion matrix
cm = confusion_matrix(y_test, bag_pred)
print(f'{cm = }')
# accuracy
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, bag_pred)
print(f'{accuracy = :.4f}')
# report
report = classification_report(y_test, bag_pred)
print('report\n', report)
# ROC & AUC
phat = bagClf.predict_proba(X_test)[: ,1]
fpr, tpr, threshold = roc_curve(y_test, phat)
plt.plot(fpr, tpr)
plt.xlabel('false positive rate')
plt.ylabel('true positive rate')
plt.show()
print(f'{auc(fpr, tpr) = }')
#
# 결과
cm = array([[341, 13],
[ 28, 26]])
accuracy = 0.8995
report
precision recall f1-score support
0 0.92 0.96 0.94 354
1 0.67 0.48 0.56 54
accuracy 0.90 408
macro avg 0.80 0.72 0.75 408
weighted avg 0.89 0.90 0.89 408
auc(fpr, tpr) = 0.887241054613936
부스팅(Boosting)
-
약한 학습기를 순차학습을 통해 강화시키는 알고리즘
-
step 별로 잘못 분류된 데이터에 가중치를 부여하는 방식
-
AdaBoost
from sklearn.ensemble import AdaBoostClassifier
adaClf = AdaBoostClassifier(random_state=0)
adaClf.fit(X_train, y_train)
ada_pred = adaClf.predict(X_test)
# confusion matrix
cm = confusion_matrix(y_test, ada_pred)
print(f'{cm = }')
# accuracy
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, ada_pred)
print(f'{accuracy = :.4f}')
# report
report = classification_report(y_test, ada_pred)
print('report\n', report)
#
# 결과
cm = array([[334, 20],
[ 29, 25]])
accuracy = 0.8799
report
precision recall f1-score support
0 0.92 0.94 0.93 354
1 0.56 0.46 0.51 54
accuracy 0.88 408
macro avg 0.74 0.70 0.72 408
weighted avg 0.87 0.88 0.88 408- GradientBoost
- 에이다부스트와 비슷하나 가중치 업데이트를 경사 하강법을 이용
from sklearn.ensemble import GradientBoostingClassifier
gbClf = GradientBoostingClassifier(random_state=0)
gbClf.fit(X_train, y_train)
gbClf_pred = gbClf.predict(X_test)
# confusion matrix
cm = confusion_matrix(y_test, gbClf_pred)
print(f'{cm = }')
# accuracy
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, gbClf_pred)
print(f'{accuracy = :.4f}')
# report
report = classification_report(y_test, gbClf_pred)
print('report\n', report)
#
# 결과
cm = array([[337, 17],
[ 27, 27]])
accuracy = 0.8922
report
precision recall f1-score support
0 0.93 0.95 0.94 354
1 0.61 0.50 0.55 54
accuracy 0.89 408
macro avg 0.77 0.73 0.74 408
weighted avg 0.88 0.89 0.89 408스태킹(stacking)
- 여러 알고리즘을 사용해서 얻은 예측값을 학습데이터로 사용하여 결과를 예측하는 방법
rfm = RandomForestClassifier(random_state=0)
svm = SVC(probability=True, random_state=0)
gbm = GradientBoostingClassifier(random_state=0)
# 기본 모델 학습
rfm.fit(X_train, y_train)
svm.fit(X_train, y_train)
gbm.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 기본 모델로 예측
rfm_preds_1 = rfm.predict(X_train)
svm_preds_1 = svm.predict(X_train)
gbm_preds_1 = gbm.predict(X_train)
rfm_preds_2 = rfm.predict(X_test)
svm_preds_2 = svm.predict(X_test)
gbm_preds_2 = gbm.predict(X_test)
# meta_model을 위한 새로운 train/test 데이터셋 생성
mata_train = pd.DataFrame({'RF':rfm_preds_1, 'GB': gbm_preds_1, 'SVM':svm_preds_1})
meta_test = pd.DataFrame({'RF':rfm_preds_2, 'GB': gbm_preds_2, 'SVM':svm_preds_2})
# 메타 모델 생성
meta_model = LogisticRegression()
# 메타 모델 학습
meta_model.fit(mata_train, y_train)
# 메타 모델로 예측
stack_pred = meta_model.predict(meta_test)
# confusion matrix
cm = confusion_matrix(y_test, stack_pred)
print(f'{cm = }')
# accuracy
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, stack_pred)
print(f'{accuracy = :.4f}')
# report
report = classification_report(y_test, stack_pred)
print('report\n', report)
#
# 결과
cm = array([[345, 9],
[ 30, 24]])
accuracy = 0.9044
report
precision recall f1-score support
0 0.92 0.97 0.95 354
1 0.73 0.44 0.55 54
accuracy 0.90 408
macro avg 0.82 0.71 0.75 408
weighted avg 0.89 0.90 0.89 408