다익스트라(Dijkstra)
출발점에서 목표점까지의 최단 경로를 구하는 알고리즘
- 한 노드에서 다른 모든 노드로의 최단 경로를 구할 수 있음
- 간선에 음의 가중치가 없어야 함
- 그리디 + DP 형태
- 방문하지 않은 노드 중에서 가장 비용이 적은 노드 선택(그리디)
- 해당 노드로부터 갈 수 있는 노드들의 비용을 갱신(DP)
- 시간 복잡도 : O(ElogV)
동작 방식
A노드에서 출발해 F노드로 가는 최단 경로를 구한다.
이 때, 현재 노드에서 인접한 노드의 거리가 가장 가까운 순으로 방문한다.
distance 는 A -> N 까지 계산된 최단 거리이다.
visited 로 방문체크를 한다.
확인되지 않은 거리는 전 부 무한으로 잡는다(INF)
- 시작점에서 이웃 노드를 방문해 거리를 계산 한다.
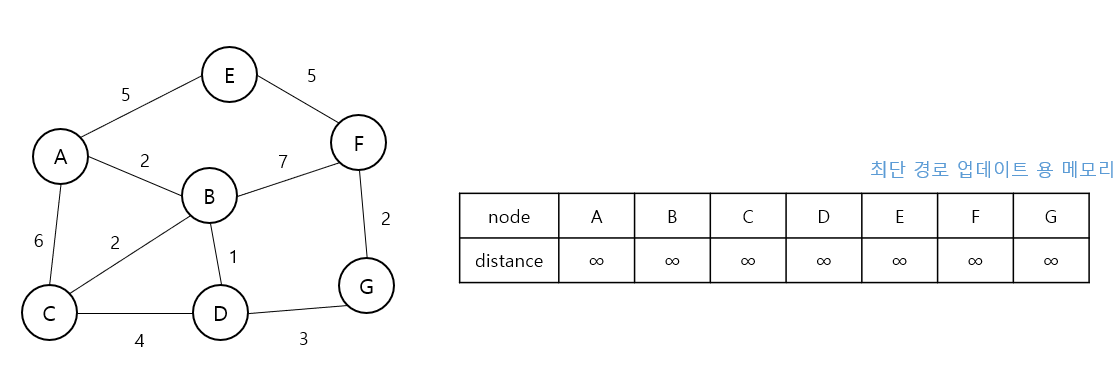
- 시작점에서 인접한 노드에서 그래프의 상태가 업데이트 된다.
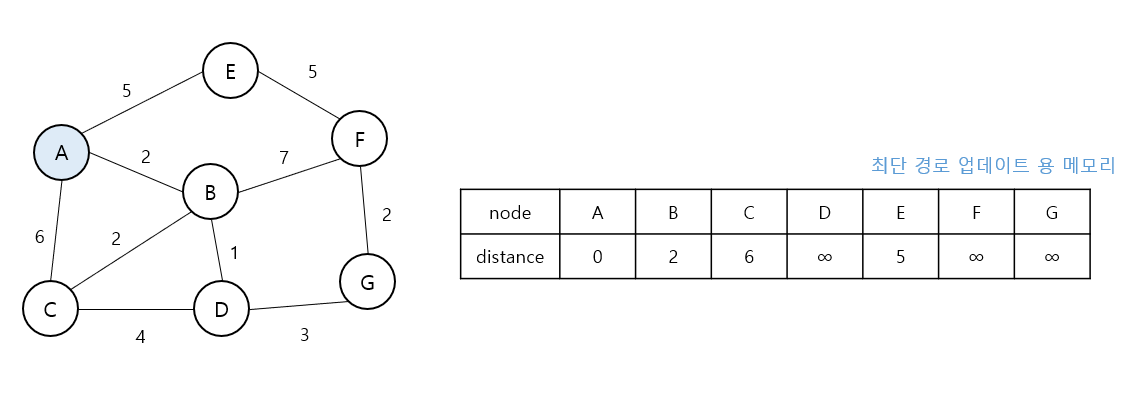
- 업데이트된 거리보다 더 빠른 경로를 발견한 경우 (distance[C] = 6 -> 4) 값을 업데이트 해준다
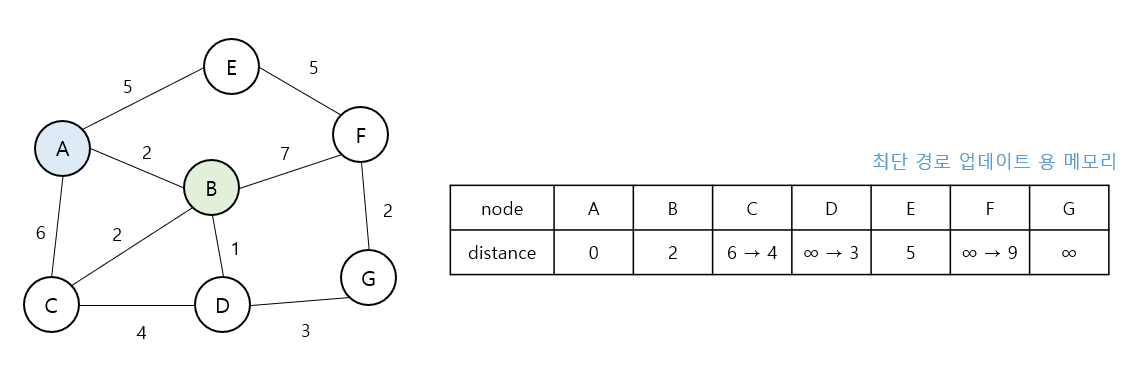
- 인접한 노드에서 그래프의 상태가 업데이트 된다.
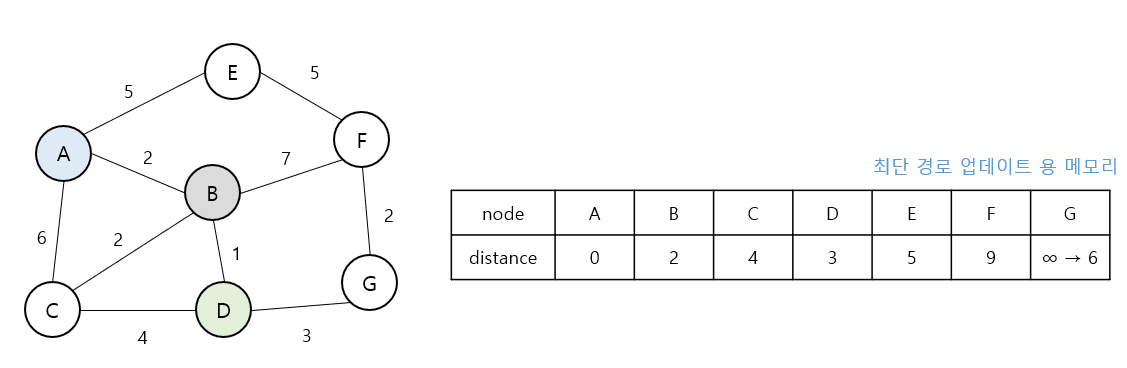
- 시작 노드에서 노드로 오는 경로가 더 느리기 때문에 업데이트 되지 않는다.
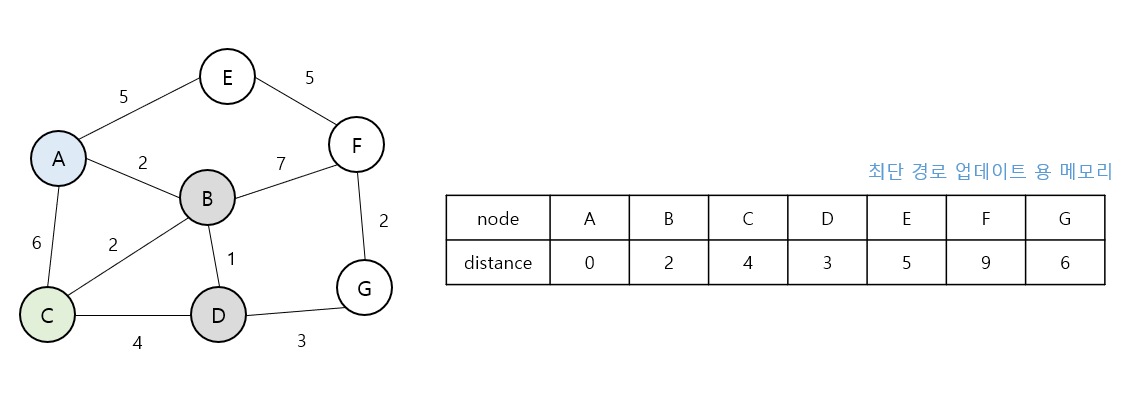
- 시작 노드에서 오는는 경로와 같기 때문에 업데이트 되지 않는다.
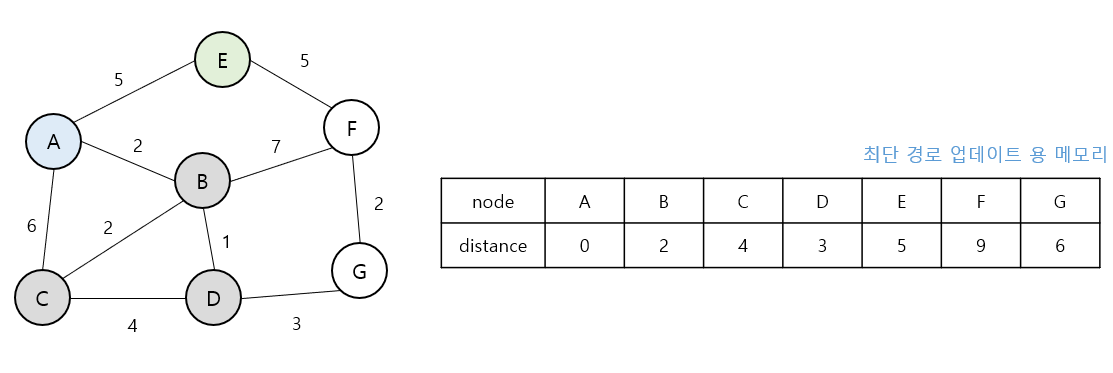
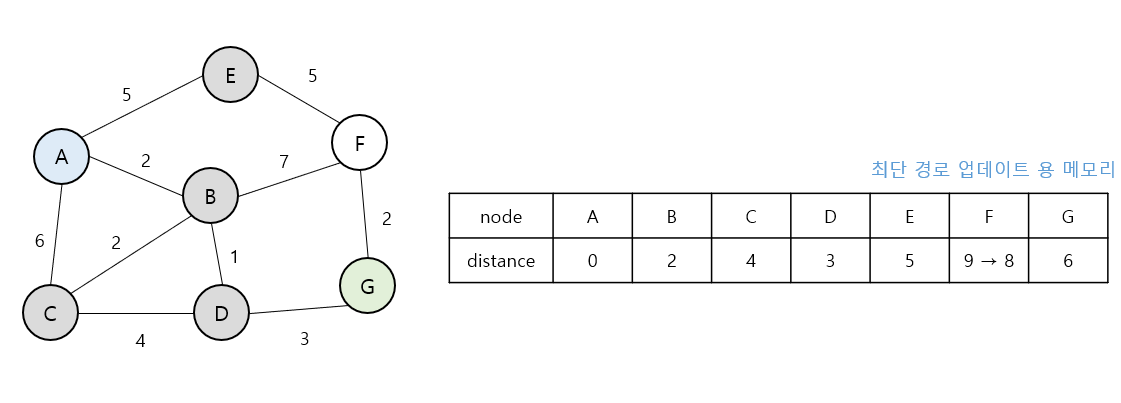
- 업데이트된 거리보다 더 빠른 경로를 발견한 경우 (distance[F] = 9 -> 8) 값을 업데이트 해준다
- 더 빠른 경로가 없기 때문에 그대로 업데이트 되지 않고 끝난다.
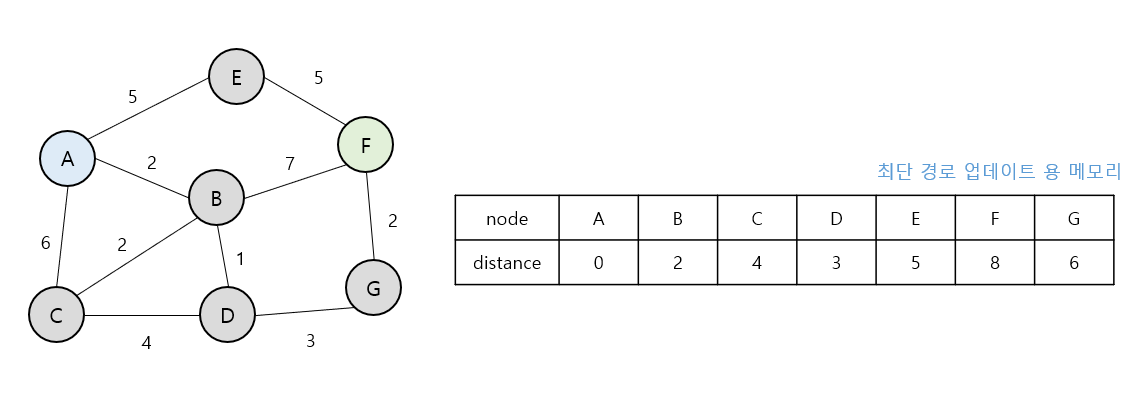
이미지 출처 : 제로베이스
구현 방법
반복문 - O(V²)
static class Node {
int to;
int weight;
public Node(int to, int weight) {
this.to = to;
this.weight = weight;
}
}
static void dijkstra(int v, int[][] data, int start) {
ArrayList<ArrayList<Node>> graph = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i <= v; i++) {
graph.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
for (int i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
graph.get(data[i][0]).add(new Node(data[i][1], data[i][2]));
}
int[] dist = new int[v + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= v; i++) {
dist[i] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
dist[start] = 0;
boolean[] visited = new boolean[v + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < v; i++) {
int minDis = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int curIdx = 0;
for (int j = 1; j <= v; j++) {
if (!visited[j] && dist[j] < minDis) {
minDis = dist[j];
curIdx = j;
}
}
visited[curIdx] = true;
for (int j = 0; j < graph.get(curIdx).size(); j++) {
Node adjNode = graph.get(curIdx).get(j);
if (dist[adjNode.to] > dist[curIdx] + adjNode.weight) {
dist[adjNode.to] = dist[curIdx] + adjNode.weight;
}
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= v; i++) {
if (dist[i] == Integer.MAX_VALUE) System.out.print("INF ");
else System.out.print(dist[i]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}우선순위 큐 - O(ElogV)
static class Node {
int to;
int weight;
public Node(int to, int weight) {
this.to = to;
this.weight = weight;
}
}
static void dijkstra(int v, int[][] data, int start) {
ArrayList<ArrayList<Node>> graph = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i <= v; i++) {
graph.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
for (int i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
graph.get(data[i][0]).add(new Node(data[i][1], data[i][2]));
}
int[] dist = new int[v + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= v; i++) {
dist[i] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
dist[start] = 0;
PriorityQueue<Node> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((x, y) -> x.weight - y.weight);
pq.offer(new Node(start, 0));
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
Node cur = pq.poll();
if (dist[cur.to] < cur.weight) {
continue;
}
for (int i = 0; i < graph.get(cur.to).size(); i++) {
Node adj = graph.get(cur.to).get(i);
if (dist[adj.to] > cur.weight + adj.weight) {
dist[adj.to] = cur.weight + adj.weight;
pq.offer(new Node(adj.to, dist[adj.to]));
}
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= v; i++) {
if (dist[i] == Integer.MAX_VALUE) System.out.print("INF ");
else System.out.print(dist[i]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}