sleep
- 일정 시간 동안 현재 스레드를 멈춘다.
TIME_WAITING상태로 진입한다.Thread.sleep()을 사용하면InterruptedException체크 예외가 발생한다.
join
WAITING상태로 진입한다.- 스레드가 다른 스에드의 특정 작업이 완료되기를 무기한 기다리는 상태이다.
public class JoinMainV0 {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(JoinMainV0.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
log.info("Start");
Thread thread1 = new Thread(new Job(), "thread-1");
Thread thread2 = new Thread(new Job(), "thread-2");
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
log.info("End");
}
static class Job implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
log.info("작업 시작");
try {
sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
log.info("작업 완료");
}
}
}실행 결과
15:13:40.734 [ main] Start
15:13:40.736 [ main] End
15:13:40.736 [ thread-2] 작업 시작
15:13:40.736 [ thread-1] 작업 시작
15:13:42.741 [ thread-1] 작업 완료
15:13:42.741 [ thread-2] 작업 완료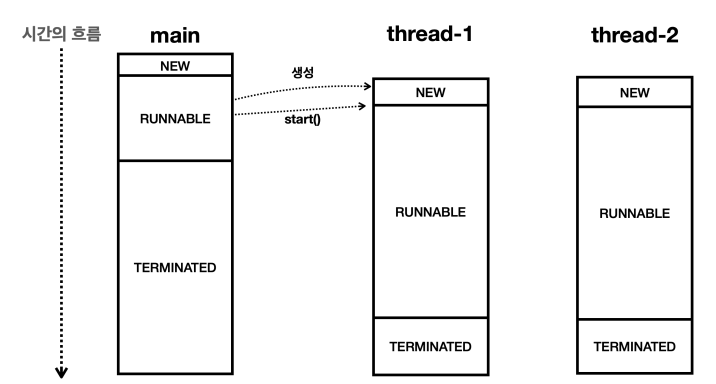
thread-1 , thread-2 는 각각 특정 작업을 수행한다. 작업 수행에 약 2초 정도가 걸린다고 가정하기 위해 sleep() 을 사용해서 2초간 대기한다. (그림에서는 RUNNABLE 로 표현되어있지만 실제로는 TIMED_WAITING 상태이다.) 예를 들어서 main 스레드가 thread-1 , thread-2 에 각각 어떤 작업을 지시하고 그 결과를 받아서 처리하고 싶다
면 어떻게 해야할까?
join이 필요한 상황
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {
sum += i;
}위와 같은 예제는 스레드를 하나만 사용하기 떄문에 CPU 코어도 하나만 사용할 수 있다. CPU 코어를 더 효율적으로 사용하려면 여러 스레드로 나누어 계산하면 된다.
1 ~ 100까지 더한 결과는 5050이다. 이 연산은 다음과 같이 둘로 나눌 수 있다.
- 1 ~ 50 더하기 = 1275
- 51 ~ 100 더하기 = 3775
두 결과를 합치면 5050이 나온다.
main 스레드가 1 ~ 100 으로 더하는 작업을 thread-1 , thread-2 에 각각 작업을 나누어 지시하면 CPU 코어를 더 효율적으로 활용할 수 있다. CPU 코어가 2개라면 이론적으로 연산 속도가 2배 빨라진다.
thread-1: 1 ~ 50 까지 더하기thread-2: 51 ~ 100 까지 더하기main: 두 스레드의 계산 결과를 받아서 합치기
public class JoinMainV1 {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(JoinMainV1.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
log.info("Start");
SumTask task1 = new SumTask(1, 50);
SumTask task2 = new SumTask(51, 100);
Thread thread1 = new Thread(task1, "thread-1");
Thread thread2 = new Thread(task2, "thread-2");
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
log.info("task1.result = {}", task1.result);
log.info("task2.result = {}", task2.result);
int sumAll = task1.result + task2.result;
log.info("task1 + task2 = {}", sumAll);
log.info("End");
}
static class SumTask implements Runnable {
int startValue;
int endValue;
int result = 0;
public SumTask(int startValue, int endValue) {
this.startValue = startValue;
this.endValue = endValue;
}
@Override
public void run() {
log.info("작업 시작");
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.warn("Interrupted!", e);
Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); // 인터럽트 상태 복원
return;
}
int sum = 0;
for (int i = startValue; i <= endValue; i++) {
sum += i;
}
result = sum;
log.info("작업 완료 result={}", result);
}
}
}실행 결과
15:36:28.347 [ main] Start
15:36:28.349 [ thread-1] 작업 시작
15:36:28.349 [ thread-2] 작업 시작
15:36:28.352 [ main] task1.result = 0
15:36:28.352 [ main] task2.result = 0
15:36:28.352 [ main] task1 + task2 = 0
15:36:28.352 [ main] End
15:36:30.355 [ thread-1] 작업 완료 result=1275
15:36:30.355 [ thread-2] 작업 완료 result=3775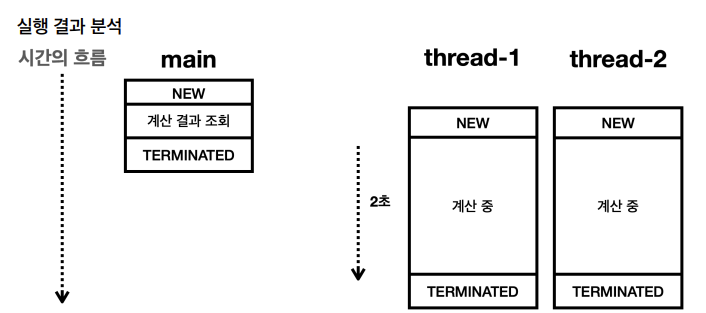
main 스레드는 thread-1 , thread-2 에 작업을 지시하고 thread-1 , thread-2 가 계산을 완료하기도 전에 먼저 계산 결과를 조회했다. 참고로 thread-1 , thread-2 가 계산을 완료하는데는 2초 정도의 시간이 걸린다. 따라서 결과가 task1 + task2 = 0 으로 출력된다.
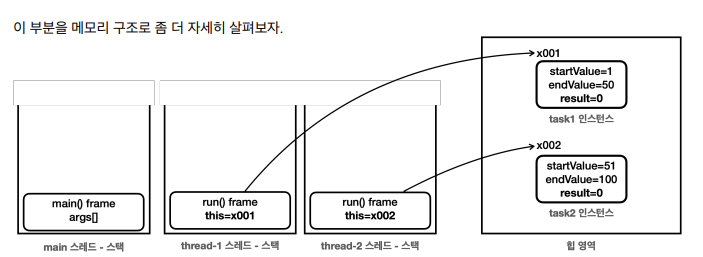
- 프로그램이 처음 시작되면
main스레드는thread-1,thread-2를 생성하고start()로 실행한다. thread-1,thread-2는 각각 자신에게 전달된 SumTask 인스턴스의run()메서드를 스택에 올리고 실행한다.thread-1은 x001 인스턴스의run()메서드를 실행한다.thread-2는 x002 인스턴스의run()메서드를 실행한다.
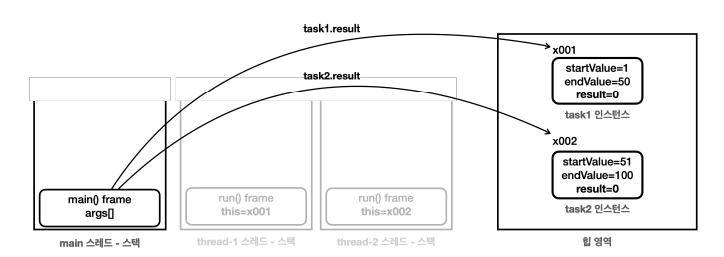
main 스레드는 두 스레드를 시작한 다음에 바로 task1.result , task2.result 를 통해 인스턴스에 있는 결과 값을 조회한다. 참고로 main 스레드가 실행한 start() 메서드는 스레드의 실행이 끝날 때 까지 기다리지 않는다. 다른 스레드를 실행만 해두고 자신의 다음 코드를 실행할 뿐이다.
thread-1 , thread-2 가 계산을 완료해서 result 에 연산 결과를 담을 때 까지는 약 2초 정도의 시간이 걸린다. main 스레드는 계산이 끝나기 전에 result 의 결과를 조회한 것이다. 따라서 0 값이 출력된다.
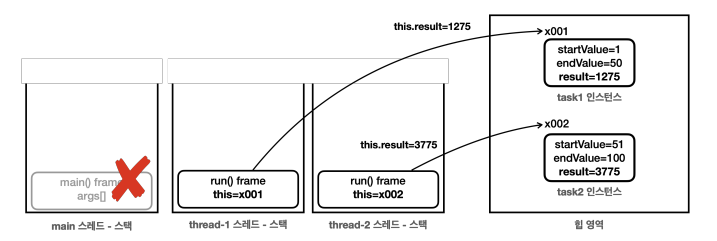
2초가 지난 이후에 thread-1 , thread-2 는 계산을 완료한다. 이때 main 스레드는 이미 자신의 코드를 모두 실행하고 종료된 상태이다. task1 인스턴스의 result 에는 1275 가 담겨있고 task2 인스턴스의 result 에는 3775 가 담겨있다.
여기서 문제의 핵심은 main 스레드가 thread-1 , thread-2 의 계산이 끝날 때 까지 기다려야 한다는 점이다.
join - sleep 사용
특정 스레드를 기다리게 하는 가장 간단한 방법은 sleep() 을 사용하는 것이다.
public class JoinMainV2 {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(JoinMainV2.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
log.info("Start");
SumTask task1 = new SumTask(1, 50);
SumTask task2 = new SumTask(51, 100);
Thread thread1 = new Thread(task1, "thread-1");
Thread thread2 = new Thread(task2, "thread-2");
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
log.info("main 스레드 sleep()");
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.warn("Main thread interrupted during sleep", e);
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
log.info("main 스레드 깨어남");
log.info("task1.result = {}", task1.result);
log.info("task2.result = {}", task2.result);
int sumAll = task1.result + task2.result;
log.info("task1 + task2 = {}", sumAll);
log.info("End");
}
static class SumTask implements Runnable {
int startValue;
int endValue;
int result = 0;
public SumTask(int startValue, int endValue) {
this.startValue = startValue;
this.endValue = endValue;
}
@Override
public void run() {
log.info("작업 시작");
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.warn("{} interrupted during sleep", Thread.currentThread().getName(), e);
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
return;
}
int sum = 0;
for (int i = startValue; i <= endValue; i++) {
sum += i;
}
result = sum;
log.info("작업 완료 result = {}", result);
}
}
}
main 스레드가 sleep(3000) 을 사용해서 3초간 대기한다.
실행 결과
16:28:05.002 [ main] Start
16:28:05.004 [ main] main 스레드 sleep()
16:28:05.004 [ thread-1] 작업 시작
16:28:05.004 [ thread-2] 작업 시작
16:28:07.015 [ thread-1] 작업 완료 result = 1275
16:28:07.015 [ thread-2] 작업 완료 result = 3775
16:28:08.005 [ main] main 스레드 깨어남
16:28:08.007 [ main] task1.result = 1275
16:28:08.008 [ main] task2.result = 3775
16:28:08.008 [ main] task1 + task2 = 5050
16:28:08.008 [ main] End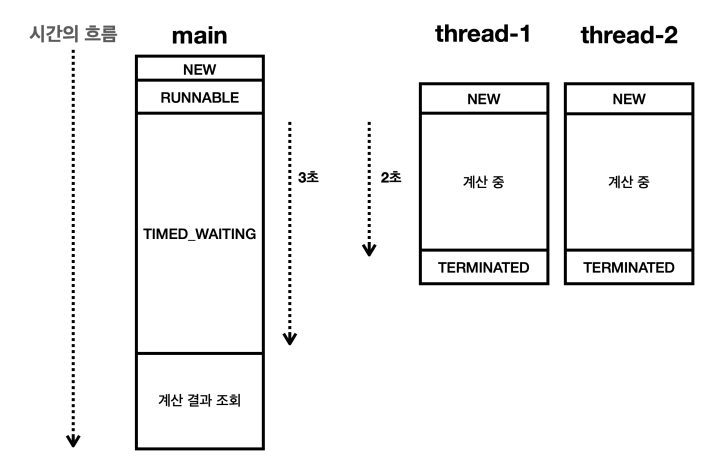
thread-1 , thread-2 는 계산에 2초 정도의 시간이 걸린다. 우리는 이 부분을 알고 있어서 main 스레드가 약 3초 후에 계산 결과를 조회하도록 했다. 따라서 계산된 결과를 받아서 출력할 수 있다. 하지만 이렇게 sleep() 을 사용해서 무작정 기다리는 방법은 대기 시간에 손해도 보고 thread-1 , thread-2 의 수행시간이 달라지는 경우에는 정확한 타이밍을 맞추기 어렵다.
더 나은 방법은 thread-1 , thread-2 가 계산을 끝내고 종료될 때 까지 main 스레드가 기다리는 방법이다.
예를 들어서 main 스레드가 반복문을 사용해서 thread-1 , thread-2 의 상태가 TERMINATED 가 될 때 까지 계속 확인하는 방법이 있다.
join - join 사용
public class JoinMainV3 {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(JoinMainV3.class);
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
log.info("Start");
SumTask task1 = new SumTask(1, 50);
SumTask task2 = new SumTask(51, 100);
Thread thread1 = new Thread(task1, "thread-1");
Thread thread2 = new Thread(task2, "thread-2");
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
log.info("join() - main 스레드가 thread1, thread2 종료까지 대기");
thread1.join();
thread2.join();
log.info("main 스레드 대기 완료");
log.info("task1.result = {}", task1.result);
log.info("task2.result = {}", task2.result);
int sumAll = task1.result + task2.result;
log.info("task1 + task2 = {}", sumAll);
log.info("End");
}
static class SumTask implements Runnable {
int startValue;
int endValue;
int result = 0;
public SumTask(int startValue, int endValue) {
this.startValue = startValue;
this.endValue = endValue;
}
@Override
public void run() {
log.info("작업 시작");
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.warn("{} interrupted during sleep", Thread.currentThread().getName(), e);
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
return;
}
int sum = 0;
for (int i = startValue; i <= endValue; i++) {
sum += i;
}
result = sum;
log.info("작업 완료 result = {}", result);
}
}
}
💡 join() 은 InterruptedException 을 던진다.
실행 결과
16:46:54.788 [ main] Start
16:46:54.790 [ thread-1] 작업 시작
16:46:54.790 [ thread-2] 작업 시작
16:46:54.790 [ main] join() - main 스레드가 thread1, thread2 종료까지 대기
16:46:56.801 [ thread-2] 작업 완료 result = 3775
16:46:56.801 [ thread-1] 작업 완료 result = 1275
16:46:56.802 [ main] main 스레드 대기 완료
16:46:56.803 [ main] task1.result = 1275
16:46:56.803 [ main] task2.result = 3775
16:46:56.804 [ main] task1 + task2 = 5050
16:46:56.804 [ main] End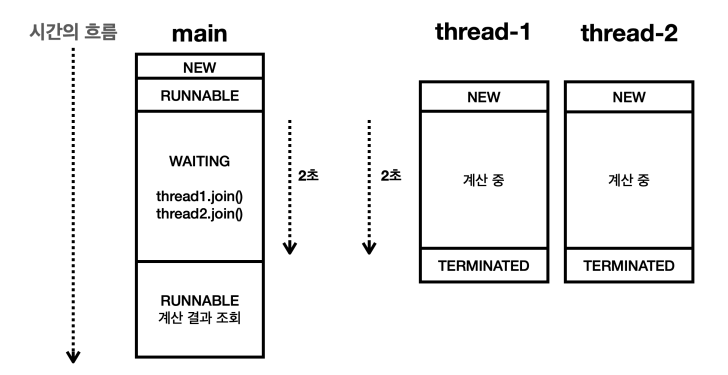
main 스레드에서 다음 코드를 실행하게 되면 main 스레드는 thread-1 , thread-2 가 종료될 때 까지 기다린다. 이때 main 스레드는 WAITING 상태가 된다.
thread1.join();
thread2.join();예를 들어서 thread-1 이 아직 종료되지 않았다면 main 스레드는 thread1.join() 코드 안에서 더는 진행하지 않고 멈추어 기다린다. 이후에 thread-1 이 종료되면 main 스레드는 RUNNABLE 상태가 되고 다음 코드로 이동한다.
이때 thread-2 이 아직 종료되지 않았다면 main 스레드는 thread2.join() 코드 안에서 진행하지 않고 멈추어 기다린다. 이후에 thread-2 이 종료되면 main 스레드는 RUNNABLE 상태가 되고 다음 코드로 이동한다. 이 경우 thread-1 이 종료되는 시점에 thread-2 도 거의 같이 종료되기 때문에 thread2.join() 은 대기하지 않고 바로 빠져나온다.
Waiting (대기 상태)
- 스레드가 다른 스레드의 특정 작업이 완료되기를 무기한 기다리는 상태이다.
join()을 호출하는 스레드는 대상 스레드가TERMINATED상태가 될 때 까지 대기한다. 대상 스레드가TERMINATED상태가 되면 호출 스레드는 다시RUNNABLE상태가 되면서 다음 코드를 수행한다
이렇듯 특정 스레드가 완료될 때 까지 기다려야 하는 상황이라면 join() 을 사용하면 된다.
하지만 join() 의 단점은 다른 스레드가 완료될 때 까지 무기한 기다리는 단점이 있다. 만약 다른 스레드의 작업을 일정 시간 동안만 기다리고 싶다면 어떻게 해야할까?
join - 특정 시간 만큼만 대기
join() 은 두 가지 메서드가 있다.
join(): 호출 스레드는 대상 스레드가 완료될 때 까지 무한정 대기한다.join(ms): 호출 스레드는 특정 시간 만큼만 대기한다. 호출 스레드는 지정한 시간이 지나면 다시RUNNABLE상태가 되면서 다음 코드를 수행한다.
public class JoinMainV4 {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(JoinMainV4.class);
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
log.info("Start");
SumTask task1 = new SumTask(1, 50);
Thread thread1 = new Thread(task1, "thread-1");
thread1.start();
log.info("join(1000) - main 스레드가 thread1 종료까지 1초 대기");
thread1.join(1000); // 최대 1초 대기
log.info("main 스레드 대기 완료");
log.info("task1.result = {}", task1.result);
}
static class SumTask implements Runnable {
int startValue;
int endValue;
int result = 0;
public SumTask(int startValue, int endValue) {
this.startValue = startValue;
this.endValue = endValue;
}
@Override
public void run() {
log.info("작업 시작");
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.warn("{} interrupted during sleep", Thread.currentThread().getName(), e);
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
return;
}
int sum = 0;
for (int i = startValue; i <= endValue; i++) {
sum += i;
}
result = sum;
log.info("작업 완료 result = {}", result);
}
}
}
실행 결과
17:34:54.572 [ main] Start
17:34:54.575 [ main] join(1000) - main 스레드가 thread1 종료까지 1초 대기
17:34:54.575 [ thread-1] 작업 시작
17:34:55.580 [ main] main 스레드 대기 완료
17:34:55.585 [ main] task1.result = 0
17:34:56.580 [ thread-1] 작업 완료 result = 1275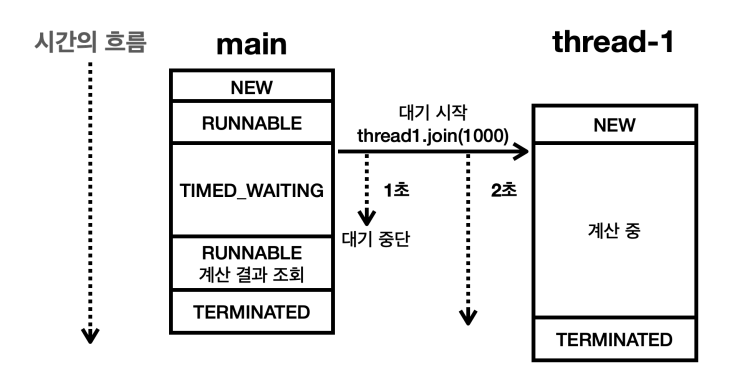
main스레드는join(1000)을 사용해서thread-1을 1초간 기다린다.- 이때 main 스레드의 상태는
WAITING이 아니라TIMED_WAITING이 된다. - 보통 무기한 대기하면
WAITING상태가 되고 특정 시간 만큼만 대기하는 경우TIMED_WAITING상태가 된다.
- 이때 main 스레드의 상태는
thread-1의 작업에는 2초가 걸린다.- 1초가 지나도
thread-1의 작업이 완료되지 않으므로main스레드는 대기를 중단한다. 그리고main스레드는 다시RUNNABLE상태로 바뀌면서 다음 코드를 수행한다.- 이때
thread-1의 작업이 아직 완료되지 않았기 때문에task1.result = 0이 출력된다.
- 이때
main스레드가 종료된 이후에thread-1이 계산을 끝낸다. 따라서 작업 완료result = 1275이 출력된다.
다른 스레드가 끝날 때 까지 무한정 기다려야 한다면 join() 을 사용하고 다른 스레드의 작업을 무한정 기다릴 수 없다면 join(ms) 를 사용하면 된다. 물론 기다리다 중간에 나오는 상황인데 결과가 없다면 추가적인 오류 처리가 필요할 수 있다.
📝 배운점
이번 학습을 통해 자바의 sleep()과 join()이 어떤 상태를 유발하고 실제 스레드 실행 흐름에서 어떤 차이를 만들어내는지 깊이 이해할 수 있었다. 특히 join()을 사용하지 않으면 메인 스레드가 작업 스레드의 결과를 기다리지 않고 먼저 종료될 수 있다는 점은 멀티스레드 프로그래밍에서 동기화가 얼마나 중요한지 보여주는 좋은 예였다.
또한 join(ms)를 통해 일정 시간만 대기하고 이후 로직을 유연하게 처리할 수 있다는 점도 실무에서 유용하게 활용할 수 있는 개념이라는 걸 느꼈다. 단순히 기능 구현을 넘어서 스레드의 생명주기와 상태를 기반으로 설계하는 습관이 멀티스레드 환경에서 안정성을 높이는 중요한 기반이 될 것 같다.
참고
