Data-driven approach
- collecet a dataset of images and labels
- use machine learning to train an image classifier
- evaluate the classifier on a withheld sest of test images
-> test & evaluate
Nearest Neighbor Classifier
- 모든 training image와 label을 기억하고, input과 가장 비슷한 것의 class를 return하는 classifier
Linear Classification
ex) image captioning = CNN + RNN
CNN - object classification from image
RNN - caption generation (RNN은 sequence 처리에 강한 network임)
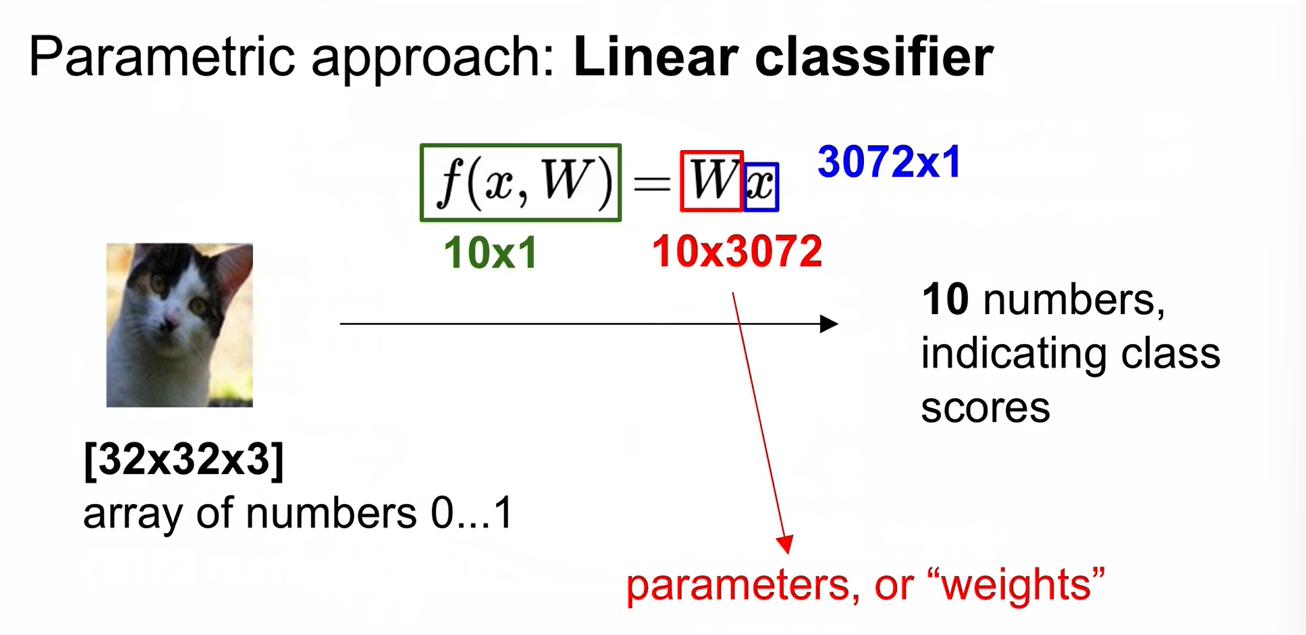
Parametric approach
Linear Classifier가 구분하기 어려운 dataset?
-
negative image, grey-scaled image, texture와 shape은 다르지만 색이 같은 경우
-
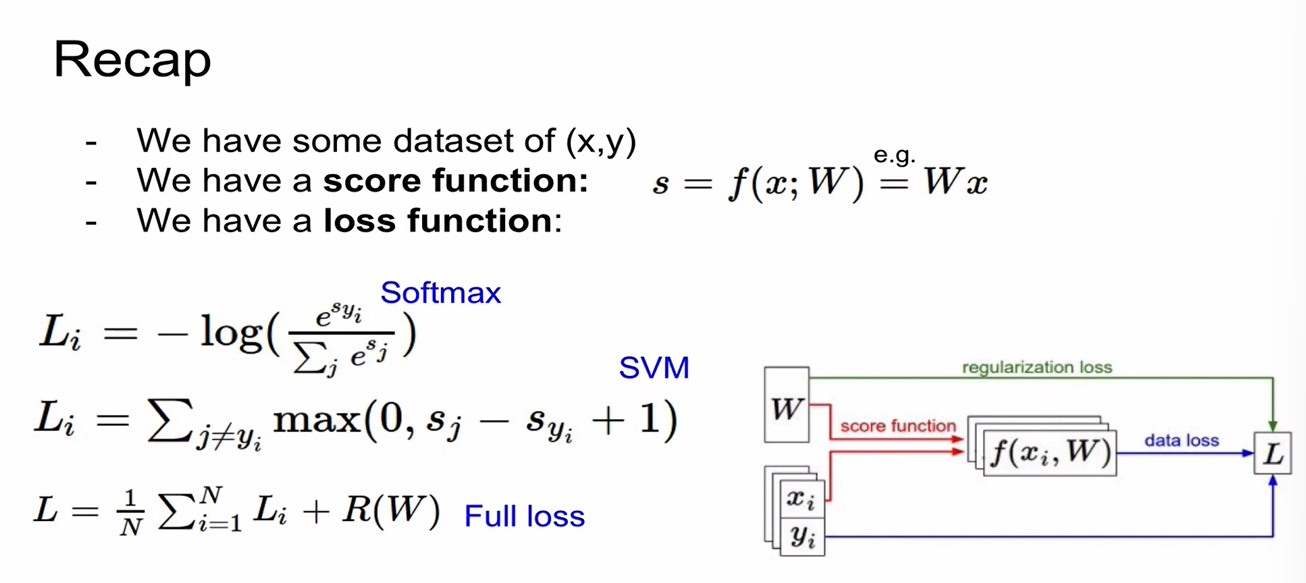
Linear score function을 정의한 것임. -> loss funcion이 score를 loss로 정량화함.
Loss Function
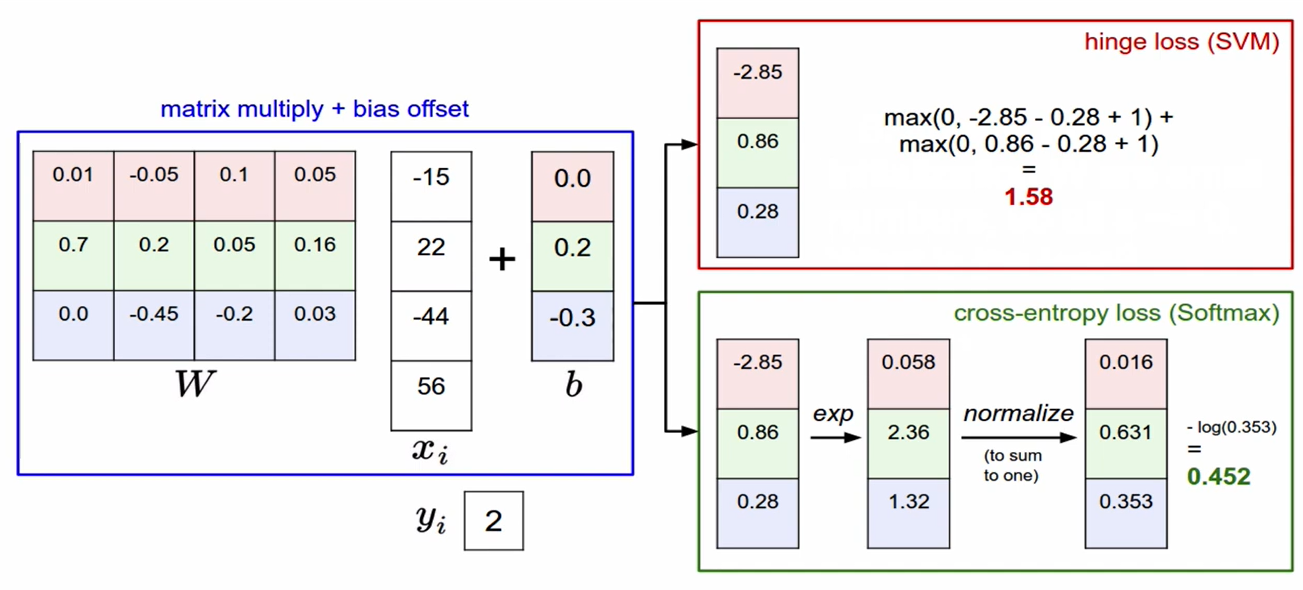
SVM - Hinge Loss
Softmax - Cross Entropy Loss
Multiclass SVM loss
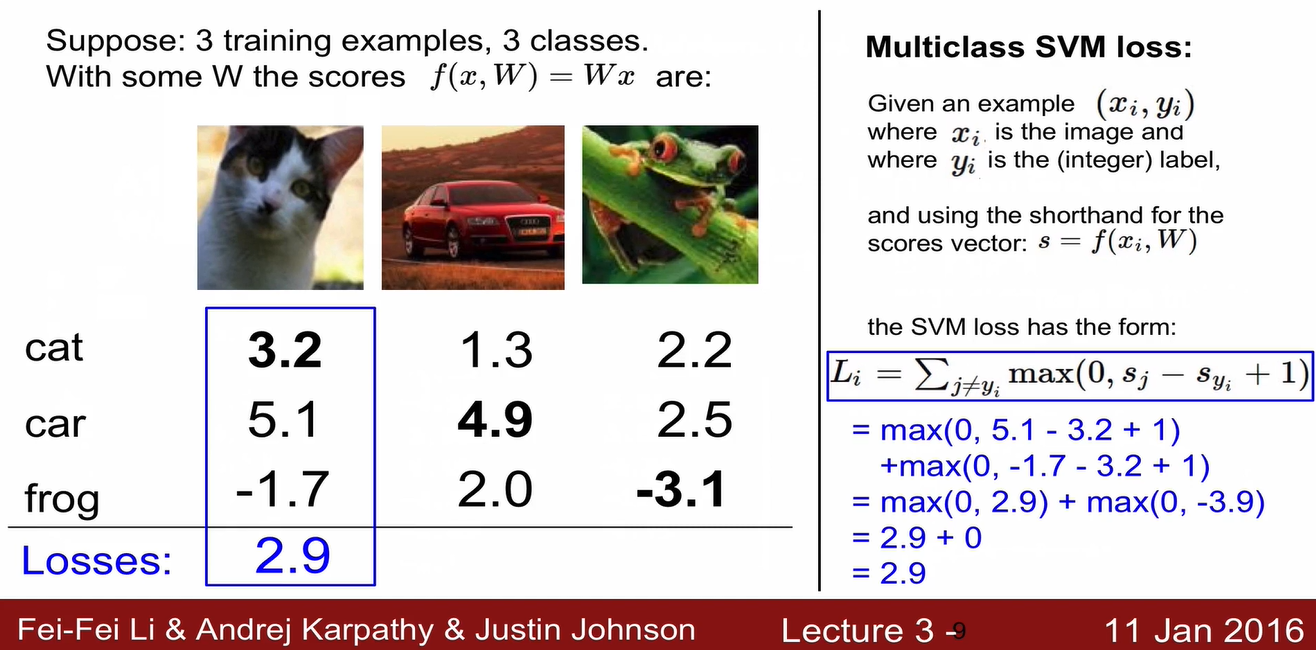
sj: 잘못된 label의 score
syi: 정답 label의 score
- correct label의 score가 incorrect label의 score보다 1 이상 크면 loss = 0

-
Sanity check: 초기 loss 값 == (클래스 수) -1
학습 진행 전 초기 값 확인. -
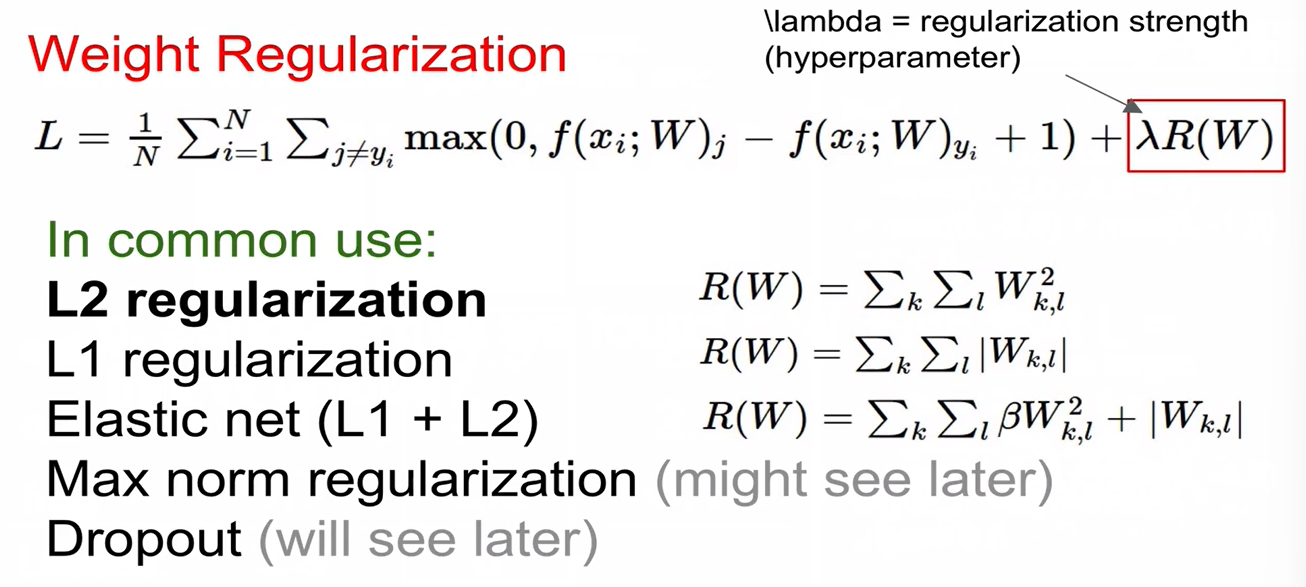
loss를 0으로 만드는 W의 값이 unique 하지 않다는 버그가 있음. 이를 해결하지 위해 Regularization을 함.

- Regularization 도입 시 training error는 커지겠지만(training data에 대한 performance는 안 좋아지겠지만) test set performance는 더 좋아짐.
- L2 regularization: weight를 spread out해서 모든 input feature를 고려하도록 함.
위 그림에서 w2가 더 좋은 weight임.
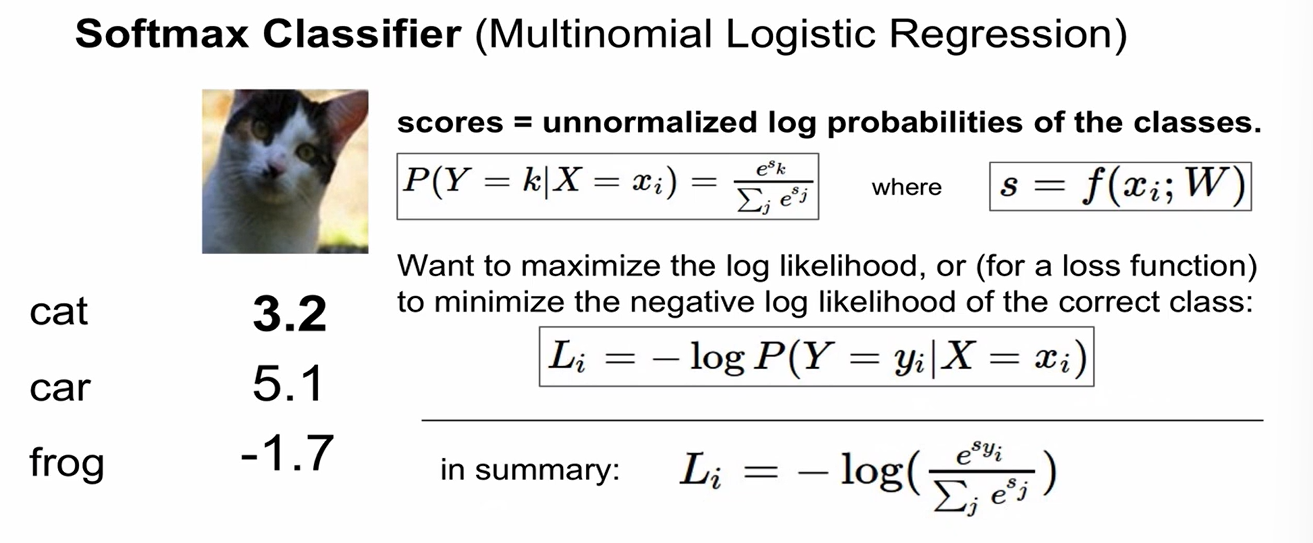
Softmax Classifier (Multinomial Logistic Regression)
- scores = unnormalized log probabilities of the classes
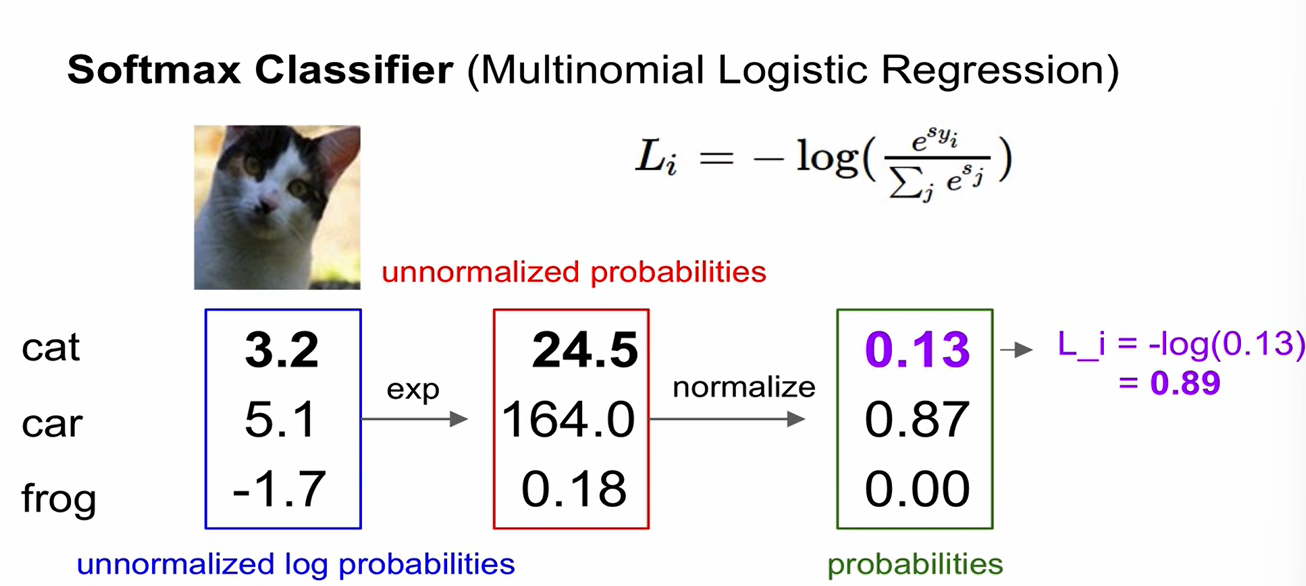
- 최솟값 = 0 (x=0) / 최댓값 =
- Sanity check:
initial loss (when W is small num so all s~=0)
=
-
datapoint의 값이 약간 변하게 되면?
- SVM: safety margin(1)을 더해줘서 robust. loss에 변화 없음. 둔감함
- Softmax: 모든 인자를 고려하기 때문에 매우 sensitive한 모델임.
-
Regularization loss의 경우, 데이터의 함수가 아니라 Weight만의 함수임. Weight에만 영향을 받음.
Optimization
-
Random Search (X)
-
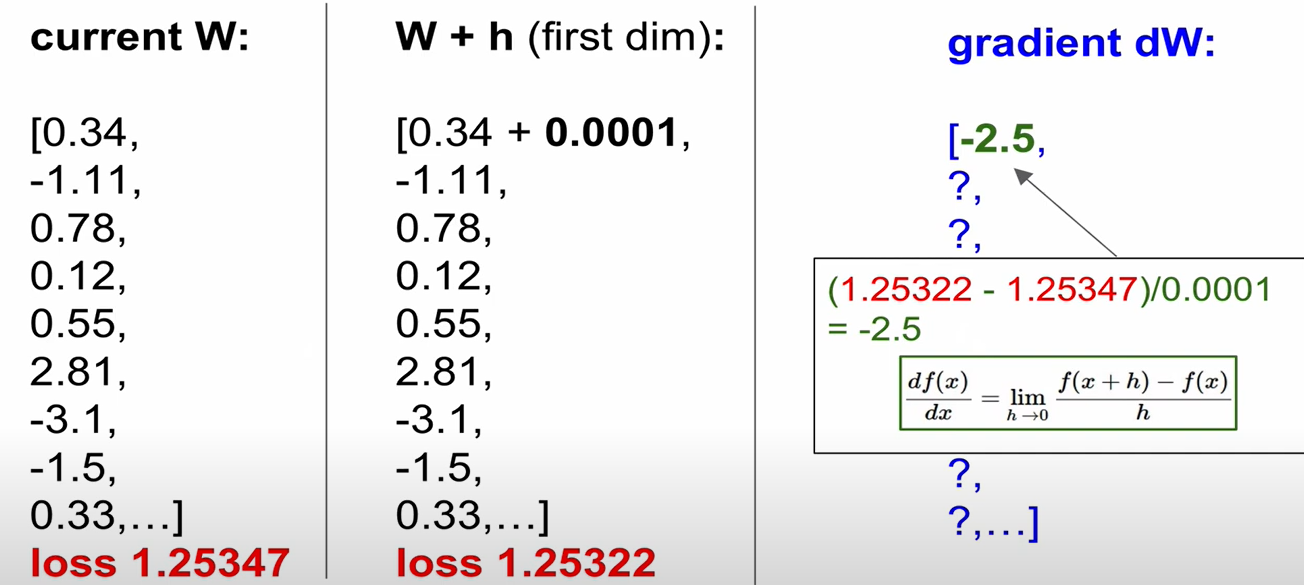
Follow the Scope - (1) numerical gradient: 하나하나 계산해서 미분을 구함

Gradient 음수 -> downward / 양수 -> upward
-
-
(2) analytic gradient: 미분해서 gradient를 구함
-
Gradient Check: 항상 analytic gradient를 사용하지만, numerical gradient를 사용해서 맞게 구현되었는지 확인해야 함.
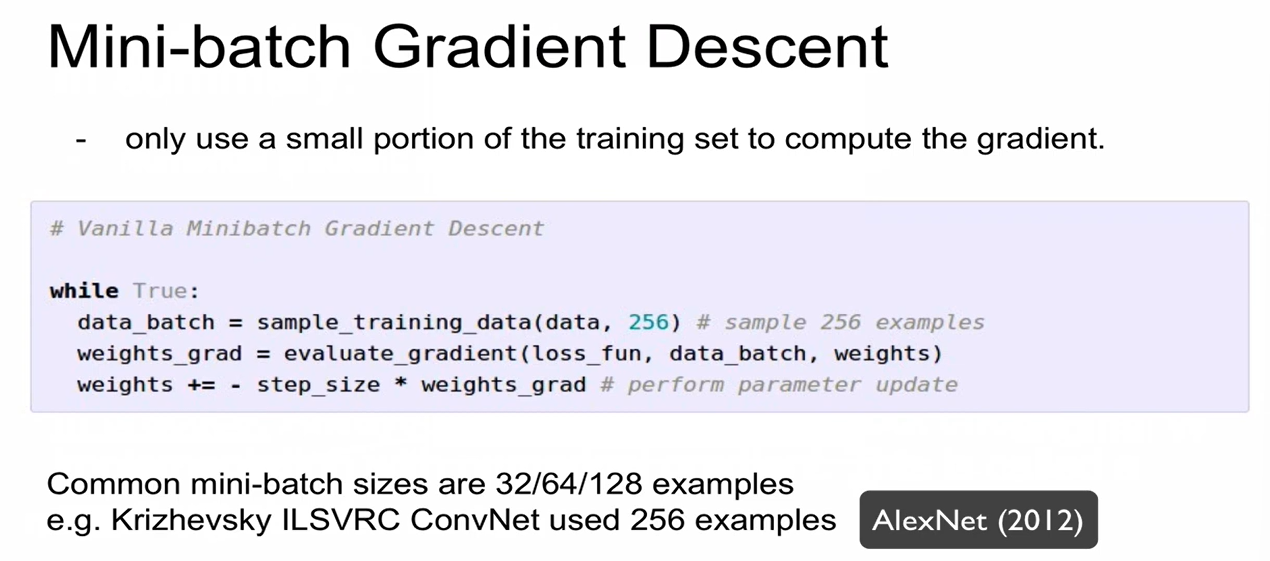
- Full batch graident descent: 모든 training set을 사용함
- Mini batch gradient descent: training set 중 일부만 활용하여 gradient를 계산함
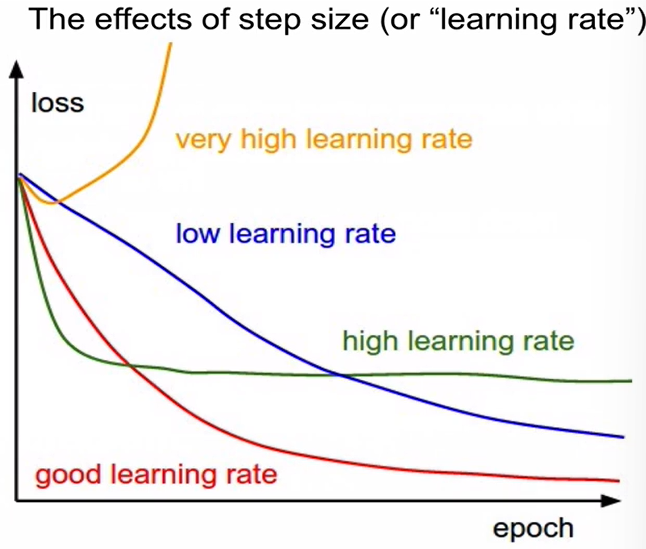
- Decay: learning rate를 높게 잡았다가 낮추는 것
ex) other fomulas: momentum, adagrad, rmsprop, adam ...
+) deep learning을 사용하지 않고 image feature를 추출하는 방식
(1) color (hue) histogram
(2) hog/sift features (edge의 orientation을 feature로 추출)
(3) bag of words: visual word vector -> learn k means centorids vocabulary of visual words -> feature 추출

Back Propagation
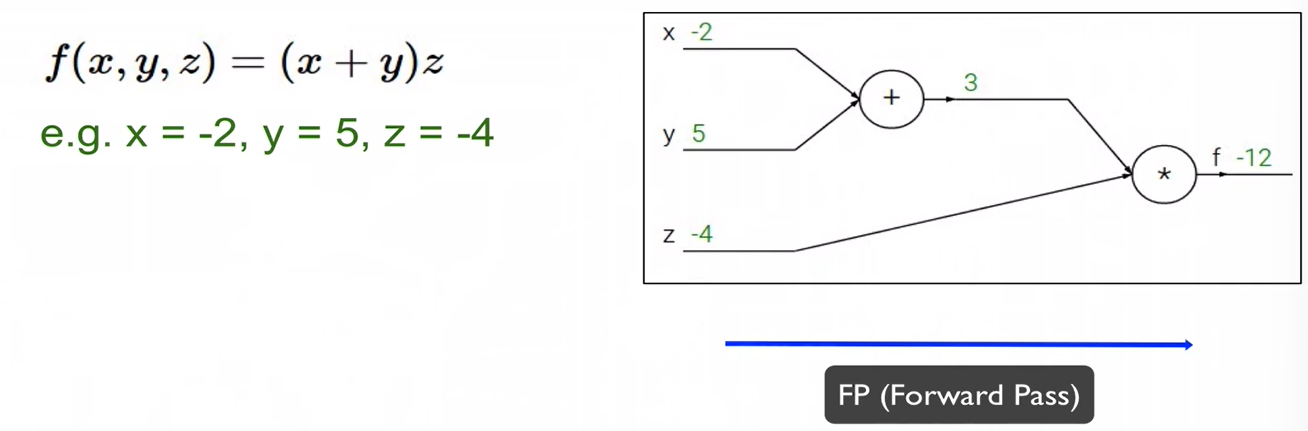
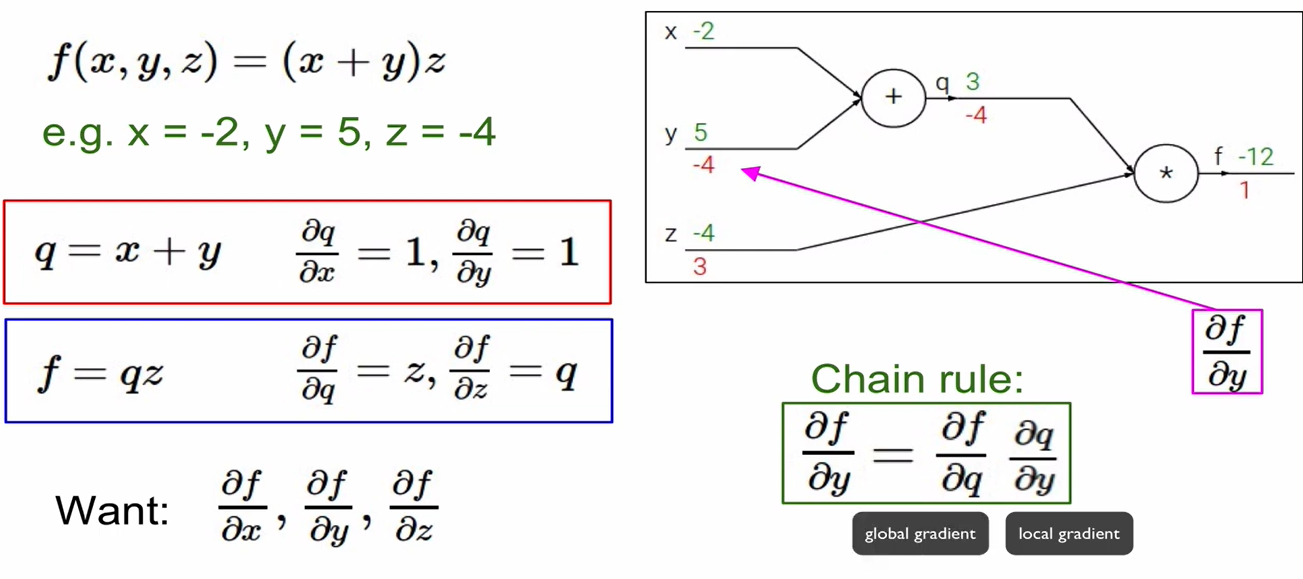
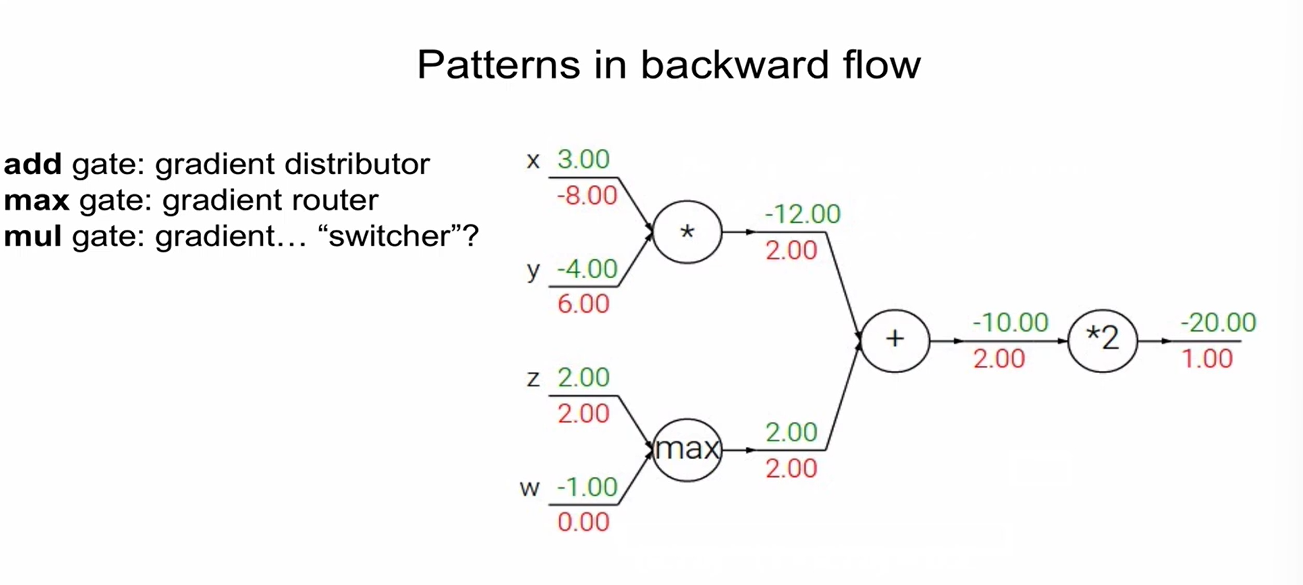
- x에 대한 gradient를 구할 때, x에 대한 미분식은 local gradient가 되고, 만약 x에 대한 미분항이 아닌 경우 이를 global gradient라 한다.
- 덧셈으로 연결된 경우 gradient 값은 항상 1이며, 곱셈으로 연결된 경우 gradient 값은 항상 반대(곱해진 것)의 값임.
-->
--> - 즉, local gradient는 forward pass 시에 구해서 memory에 저장해둠.
- global gradient는 backward pass 시만 구할 수 있음.
-> local graident와 global graident를 곱해서 gradient를 얻을 수 있음.
backward pass 시에 최종적으로 chaining이 일어남.
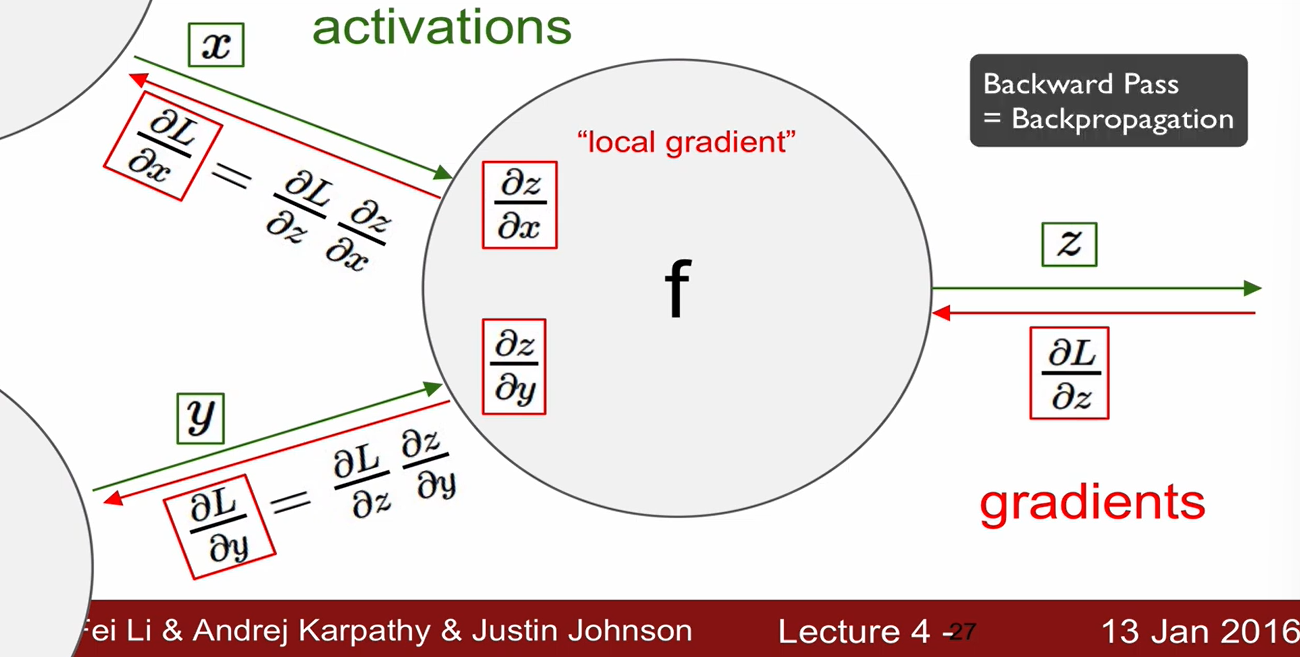
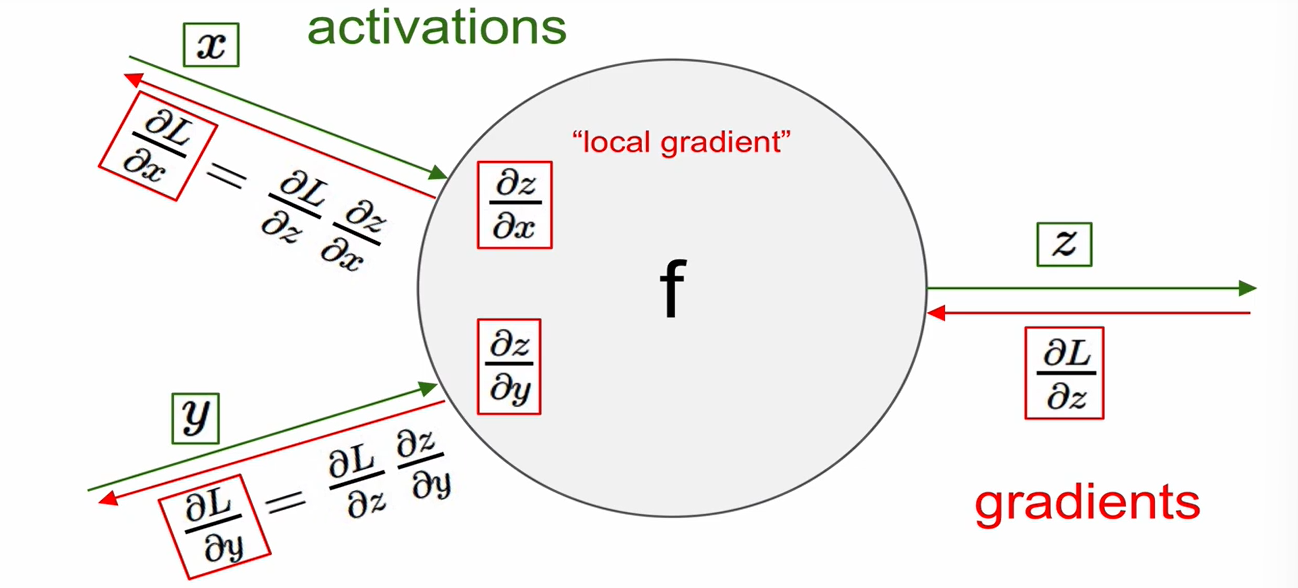
-
z가 여러 개의 노드로 이루어진 경우에는 다 더해주면 됨.
-
예시
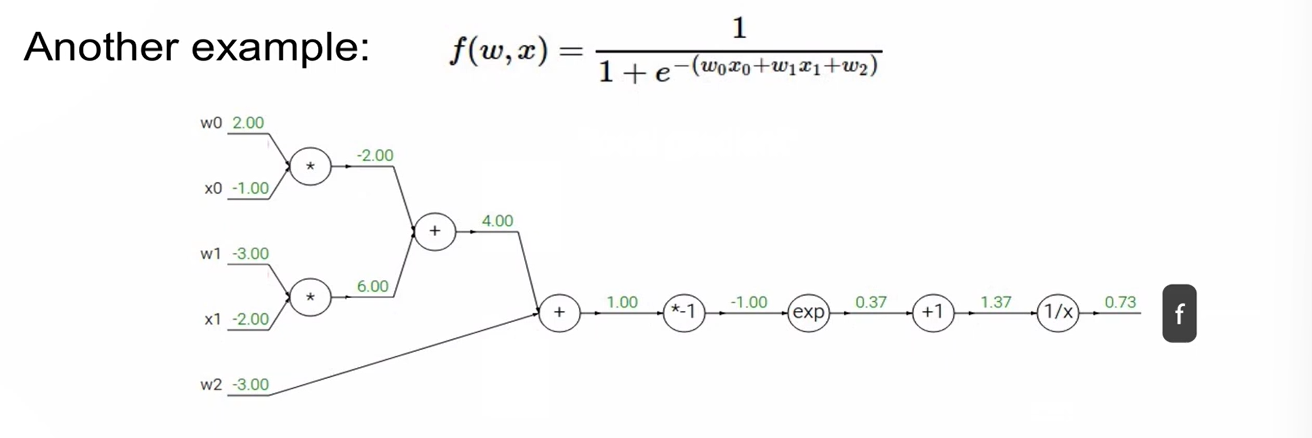
- 구하고자 하는 것: input(w0,x0,w1,x1,w2) 각각에 대한 loss에 대한 영향력
즉, 의 값 - 초록색: 실제 변수 값, local gradient (에 값을 넣어서 구해줌
- 빨간색: global gradient
- 더하기 연산 = gradient distributor (gradient를 동일한 값으로 전파해줌)
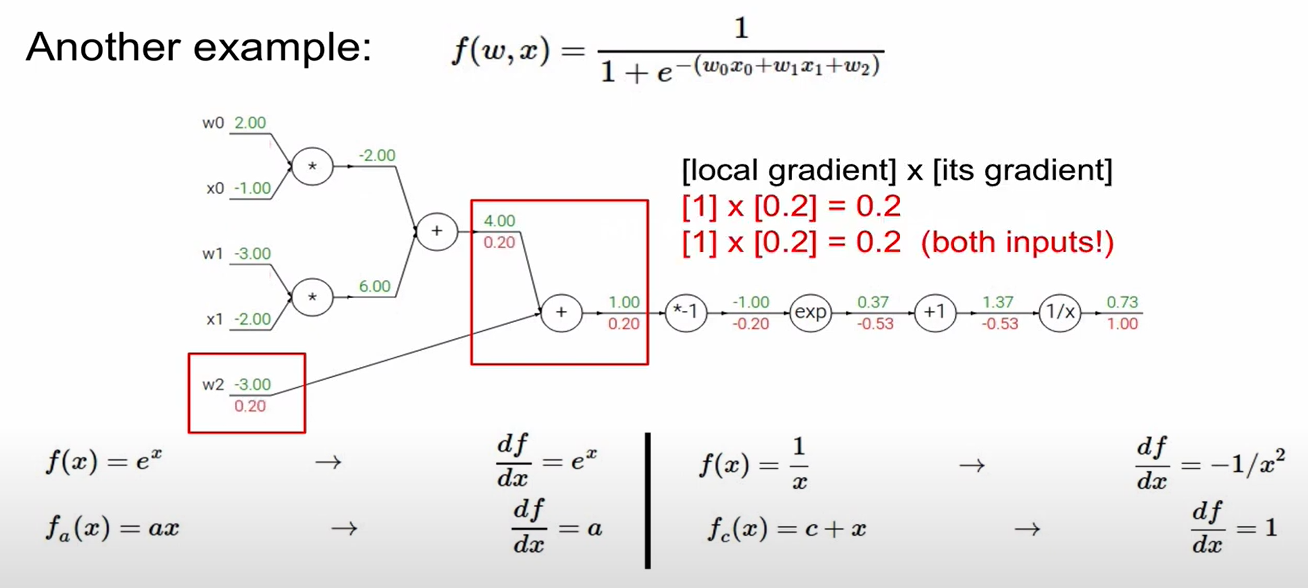
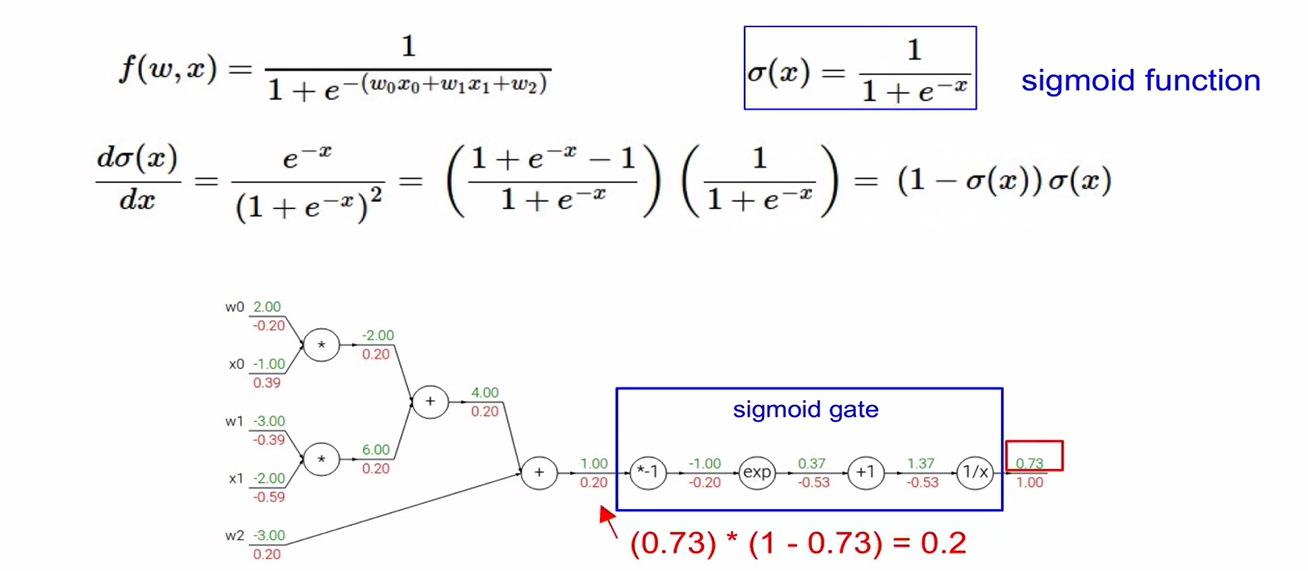


- sigmoid 함수
- forward pass:
- backward pass: (미분한 형태)

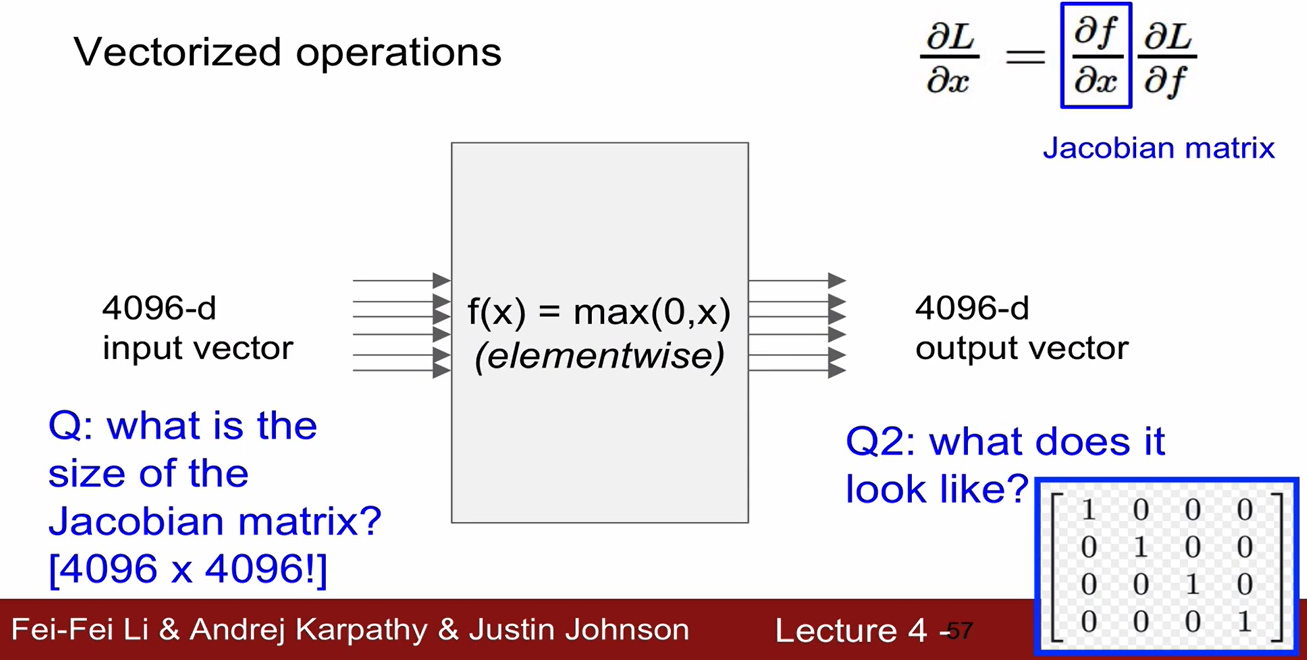
** assignment하기! forward pass & backward pass 구현하기
