Inter/intra domain routing
-
오늘날의 인터넷은 너무 커졌기 때문에 여러개의 routing protocol이 필요
-
그중 Unicast(1대1)는 Inter domain routing과 intra domain routing으로 나뉨
-
AS(autonomous system): 거대한 인터넷을 쪼갬 -
intra domain routing: AS 내부 routing -
inter domain routing: AS 간의 routing
routing protocols
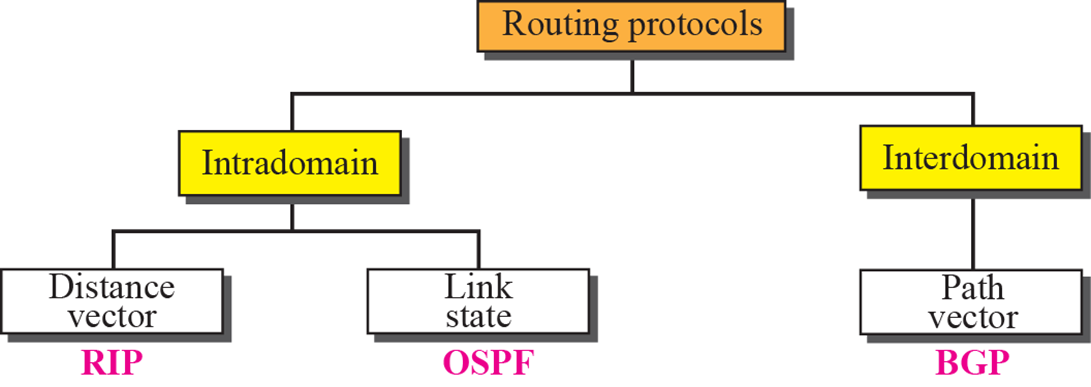
Intra doamin
Distance vector
- hop 수 기준으로 거리(hop count) 측정
Bellman-Ford algorithm
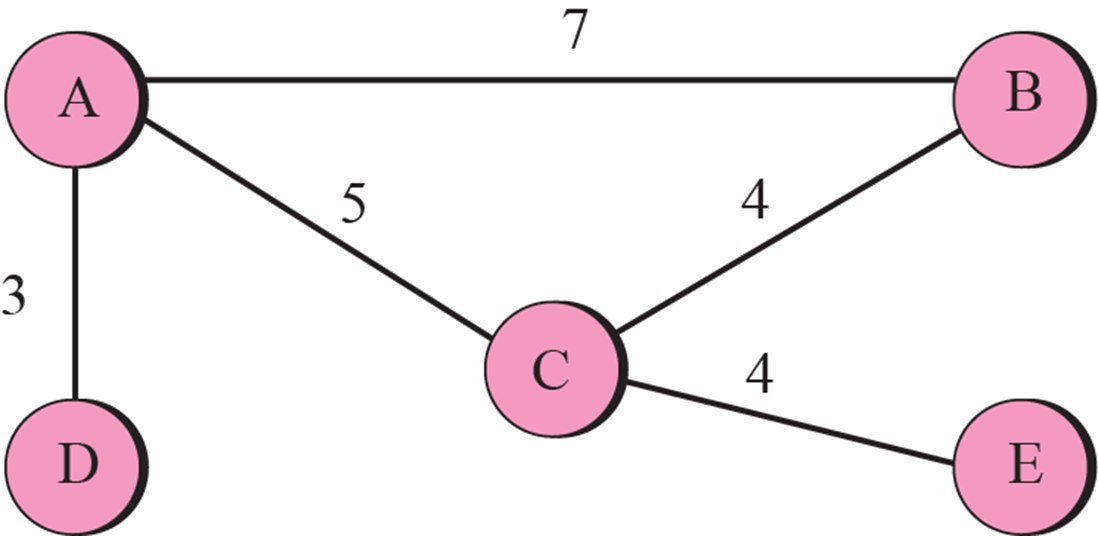
- 각각의 거리를 알면 A-E는 5 + 4 = 9이다.

- 알고 있는 거리들 중 최솟값(i-1의 최솟값 ) + 새로운 router로 가는 최솟값(1-j의 최솟값 )
- ()...() 중 최솟값이 i에서 j로 가는 최솟값이다.
bellman-ford algorithm package

- 출발지와 목적지가 같은 경우,
- 그렇지 않은 경우, 거리계산이 되지 않은 상태이기 때문에 무한대(RIP에서는 16)
Distance vector algorithm package


- 전원 키면 routing table 작성
- 작성한 routing table 이웃과 교환
- routing table update
- update한 routing table 이웃과 교환
update (distance vector)
- 이웃이 보낸 routing table의 hop수 +1(본인 포함)
- 위 table과 나의 table cost 비교
- update가 필요하면 table 수정 (cost와 next hop)
새로운 router 등장
-
무조건 등록
-
이후 sort(정렬)
- routing table은 network address가 긴 순으로 내림차순 정렬함
-
다른 neigbor router가 routing table을 전송하기 전에 기존 router에 새로운 router 추가로 hop수가 증가하게 된다면, 더 짧은 길이 있음에도 무조건 update 함.
-
이후 다른 neigbor router가 더 좋은 길을 제시하면 그 때 수정됨
-
각각의 router는 각기 다른 routing table을 가지고 있다.
-
routing table은 destination, cost, next hop + (port number)로 구성
단점
Two-node instability

- 연결된 router가 down된 경우, Ark 16(down routing table)을 전송하는 것보다 B가 2를 전송하는게 빠른 경우 발생
- 최댓값(16)이 되기 전까지 loop됨
- 16이 되기까지의 network에 무리가 감
해결법
Split Horizon: A가 전송한 정보를 B가 다시 전송하지 못하도록 차단
- 일정 시간마다 routing table을 전송하기 때문에 완벽한 해결이 아님
- router가 down되었는지 오해가 발생할 수 있음
Poison Reverse: cost를 16으로 설정하여 전송
- 방금 알려준 network이라는 의미
- 즉시 안정화 가능
Three-node instability

-
상호 연결된 3개의 node 중 무한대(16) 정보가 유실 등의 이유로 제대로 전송되지 못한 경우 발생
-
Three-node이기 때문에 split horizon과 poison reverse로 해결불가
-
시간이 지날 때까지 기다려야 함
RIP(Routing Information Protocol)
- Distance vector algorithm 사용
- 내가 가진 routing table의 모든 정보를 이웃 router에게 전송
RIP message format
 `command`: request(1)/response(2)
`version`: RIP version(현재는 2)
`Network address`: 알고 싶은 network 주소. All 0s인 경우 모든 table 정보 요청
`command`: request(1)/response(2)
`version`: RIP version(현재는 2)
`Network address`: 알고 싶은 network 주소. All 0s인 경우 모든 table 정보 요청
RIP Timer
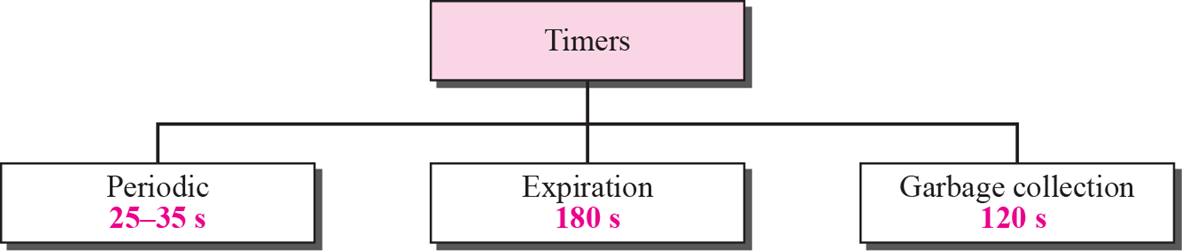
periodic timer: 주기적으로 routing table을 알려주는 기준 timer
- 동시에 보내면 network에 무리가 가기 때문에 25~35로 랜덤함Expiration timer: 180s 동안 새로운 정보가 오지 않을 경우 대상 router가 down되었다고 판단Garbage collection: Expiration timer 만료 후, 120s 동안 응답이 없으면 routing table에서 삭제
RIP version 2

- 당시 새로 생긴 Classless address를 지원하기 위해 생김
Authentication
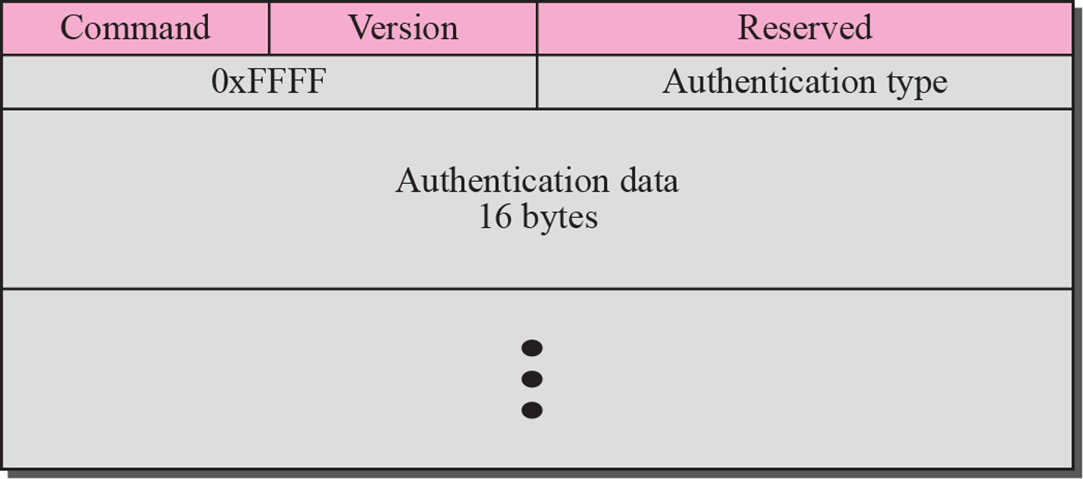
- 보안을 위한 기능
- 비밀번호 설정
- RIP는 UDP well-known port 520 사용
Link state
- hop 수, 속도, 신뢰성, 암호화 등 종합적인 요소를 고려하여 거리(cost) 측정
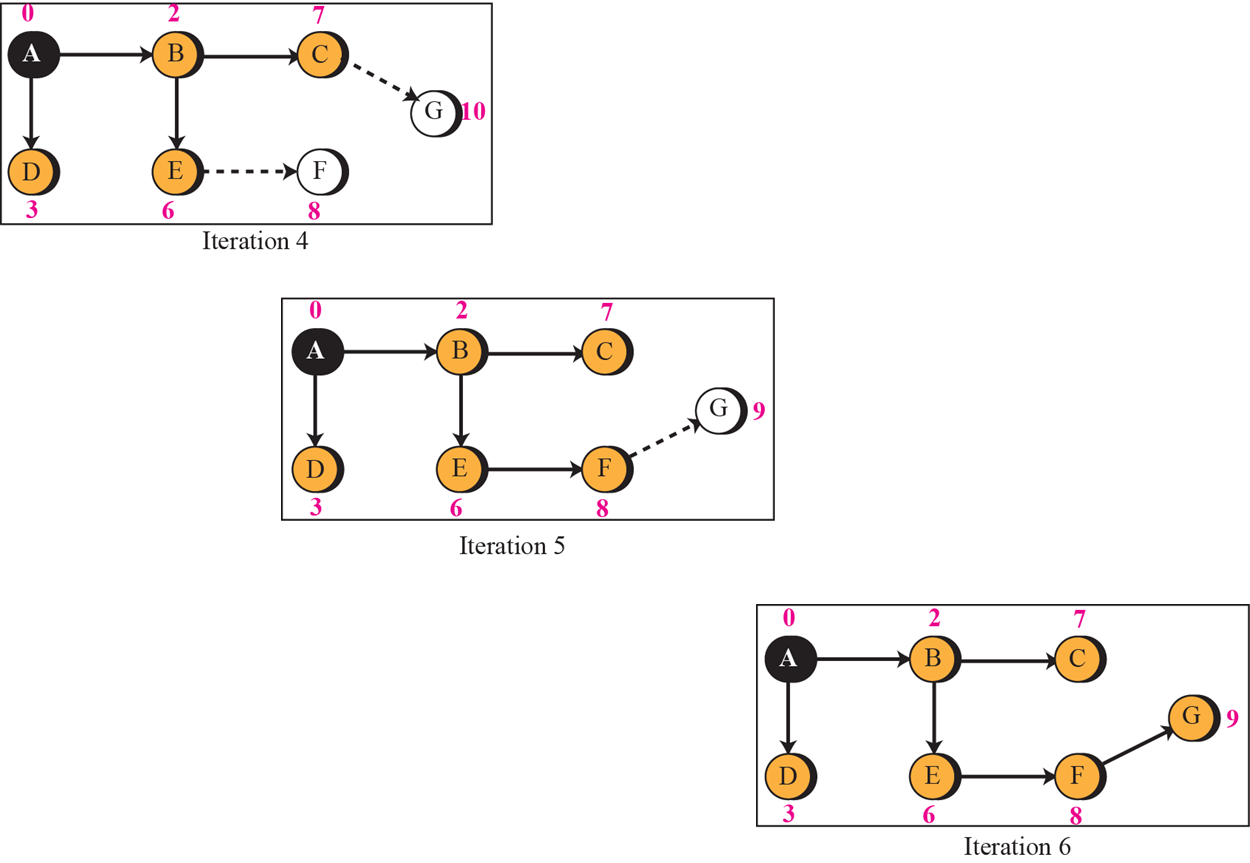
Dijkstra's Algorithm
- 이웃 router에 대한 정보를 모든 router에게 플러딩
- 위 과정의 반복으로 각각의 router가 전체적인 network의 형상을 파악하고 적절한 routing table을 생성할 수 있음

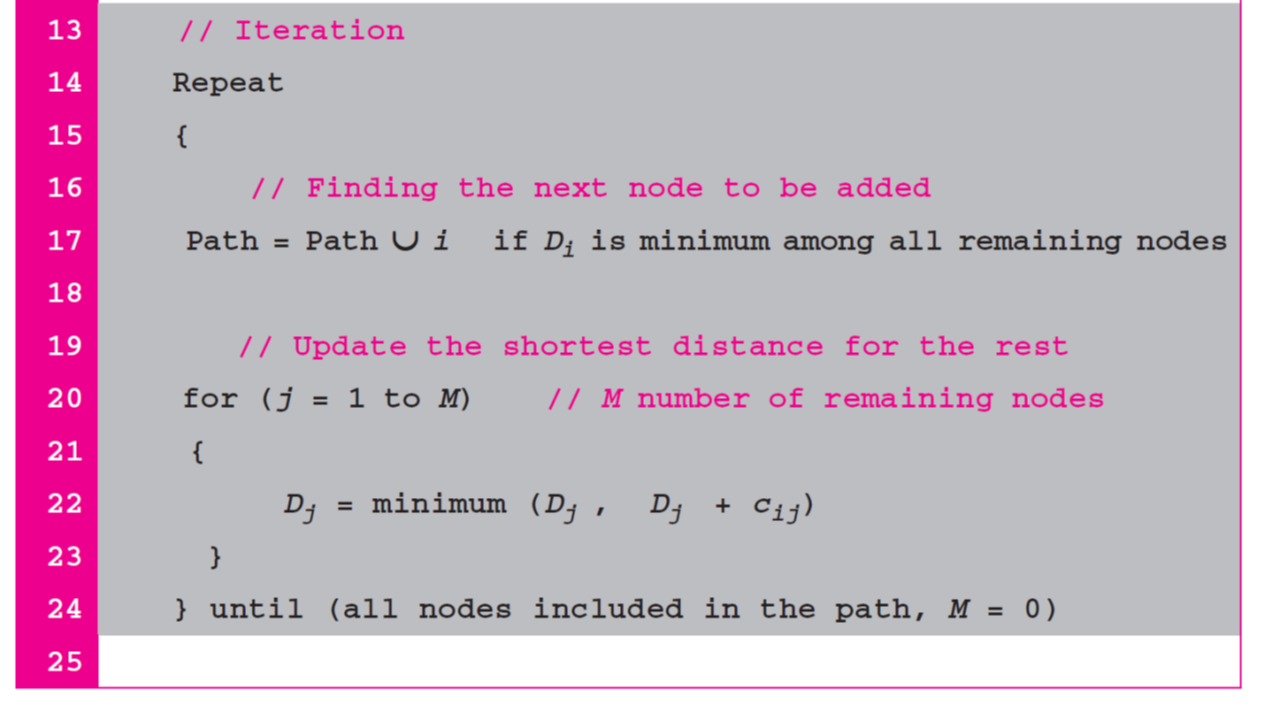
- 이웃 router cost 확인
- 확인한 모든 이웃 router cost중 최솟값을 path에 등록
- 1,2 반복
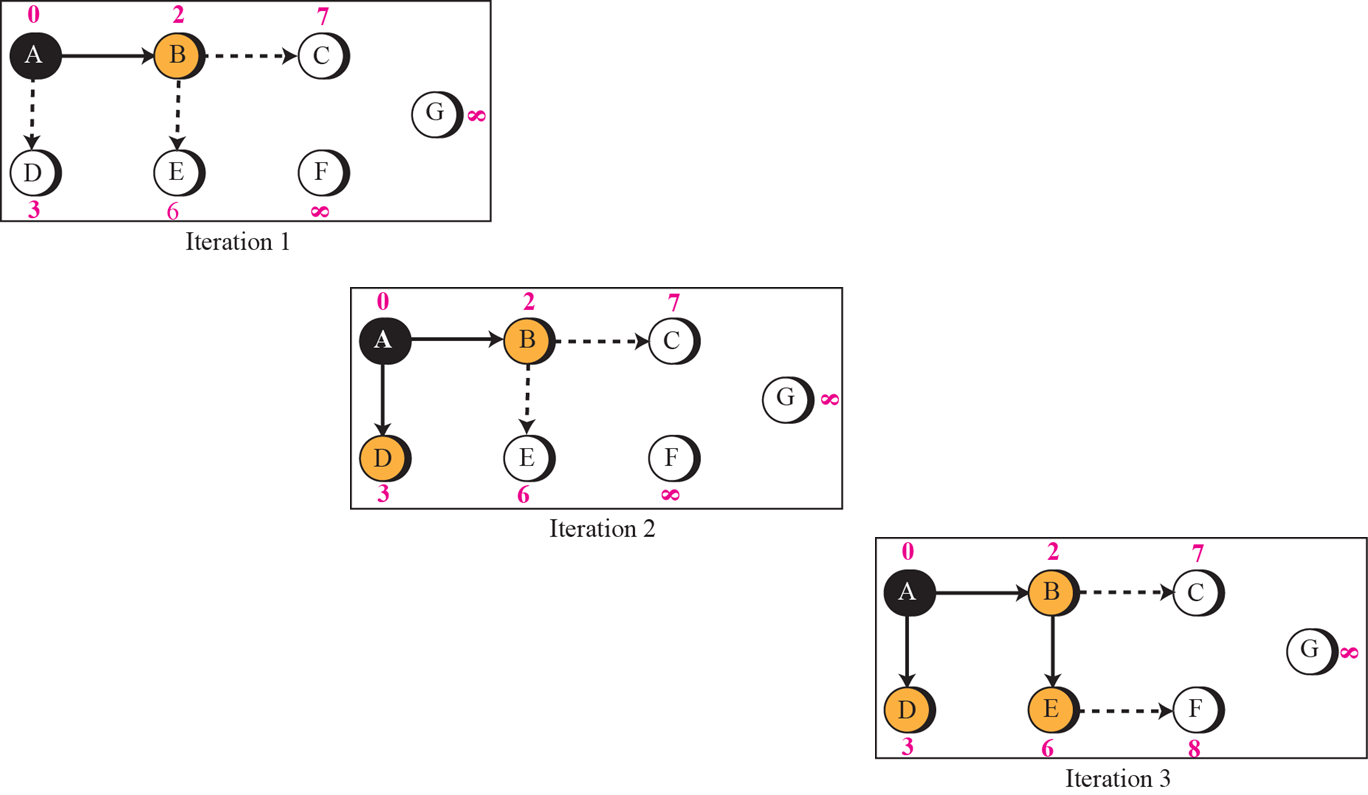
OSPF(Open Shortest Path First)
- Link state algorithm 사용
- 내가 가지고 있는 이웃에 대한 정보를 모든 router에게 전송
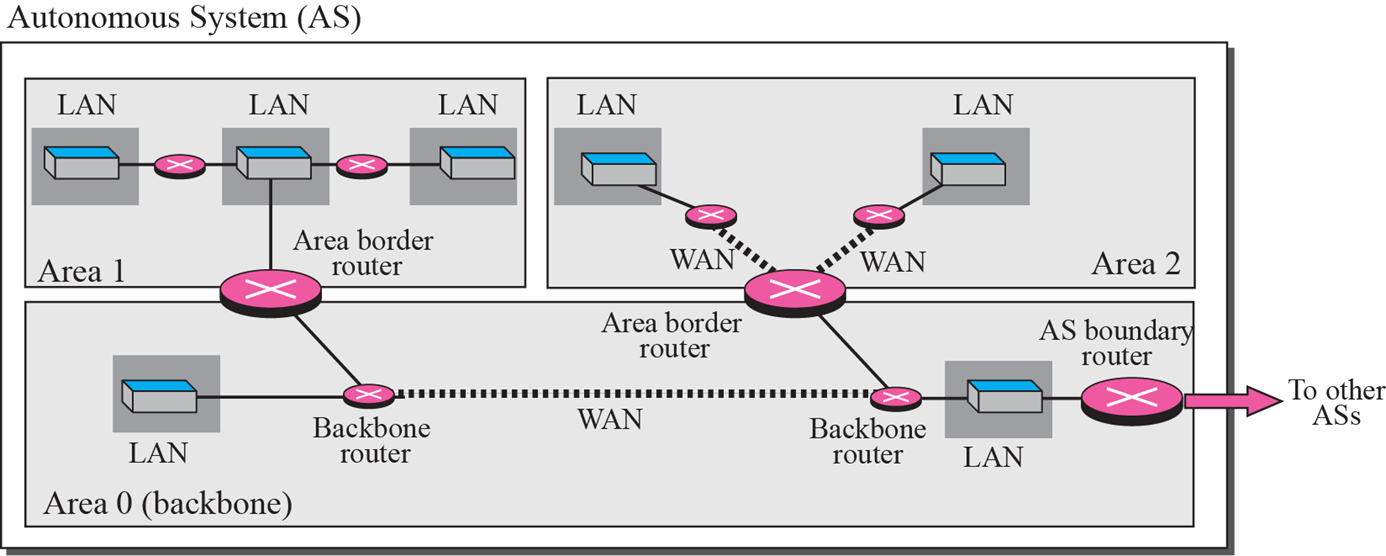
- AS가 너무 크기 때문에 area로 나눔
- Area 0는 backbone area로 area끼리 연결 및 다른 AS와의 연결을 담당
Types of links
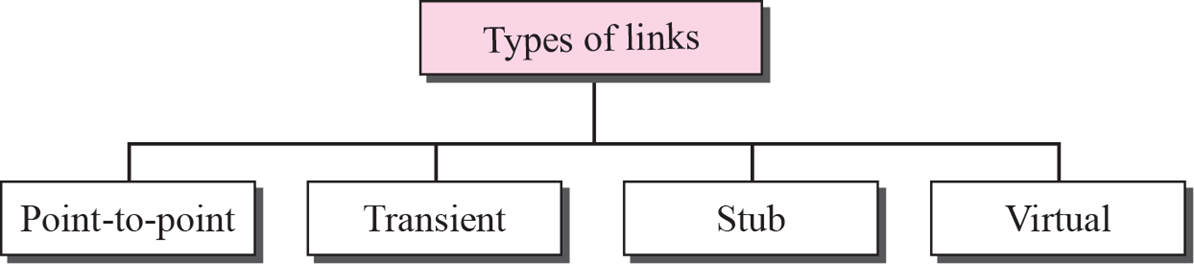
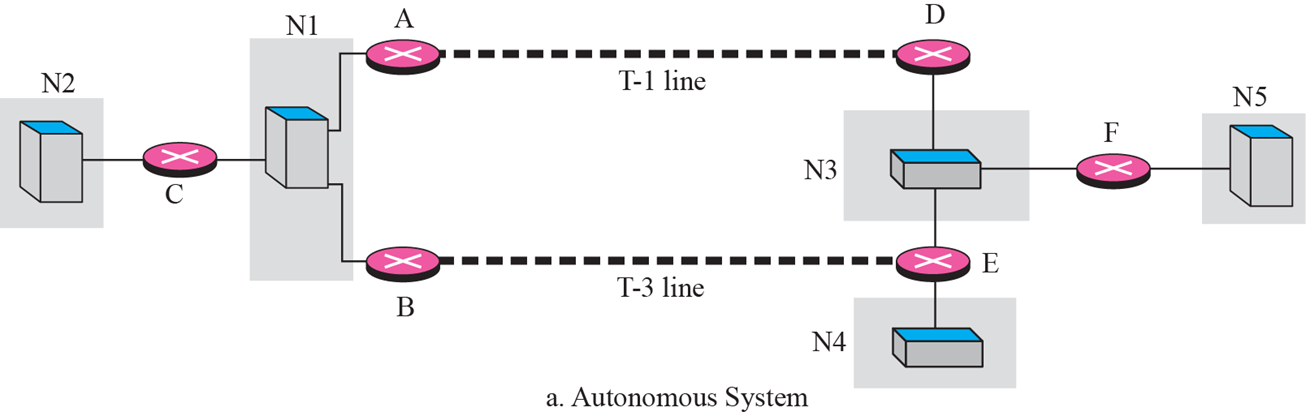

Point-to-point link


- 전용 외선, 두 개의 router만 direct로 연결된 것
- network이 없지만 network이 있는 것으로 간주하여 Routing table을 만듦
Transient link
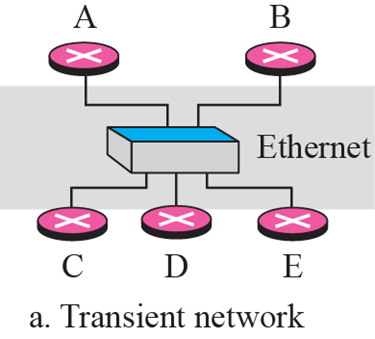
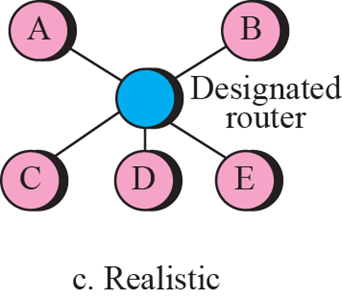
- 하나의 hub에 여러개의 router가 물려있는 형태
- Designated router가 다른 router들을 대표하여 통신
- Designated router는 priotic 값이 높은 router가 Designated router가 됨
Stub link
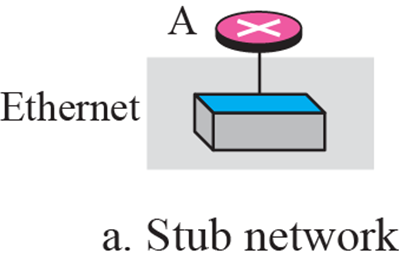
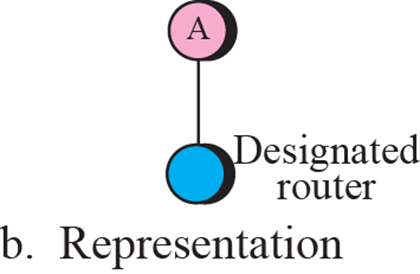
- network의 끝단에 연결된 형태
- Designated router가 될 수 있는 router는 하나뿐
Virtual
- 중간의 router 하나가 고장이 난 경우, 가상의 link를 설정하는 것
Types of OSPF packet

OSPF common header

Link state update packet
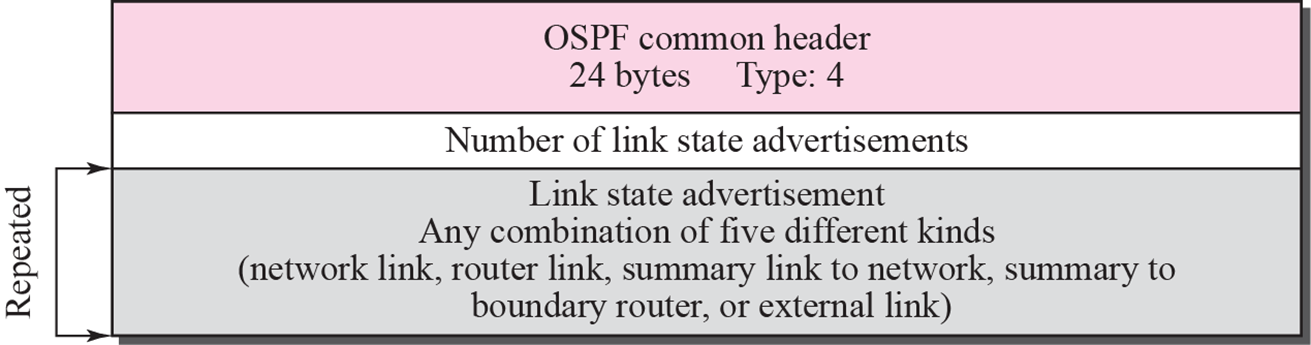
LSA(link state advertisement) general header

Link state age: LSA message가 만들어 진 후 경과 시간
E: Stub link 인지 여부
T: 제공 서비스 설정
Link state type

Router link
- Router에 붙어 있는 network를 알려줌
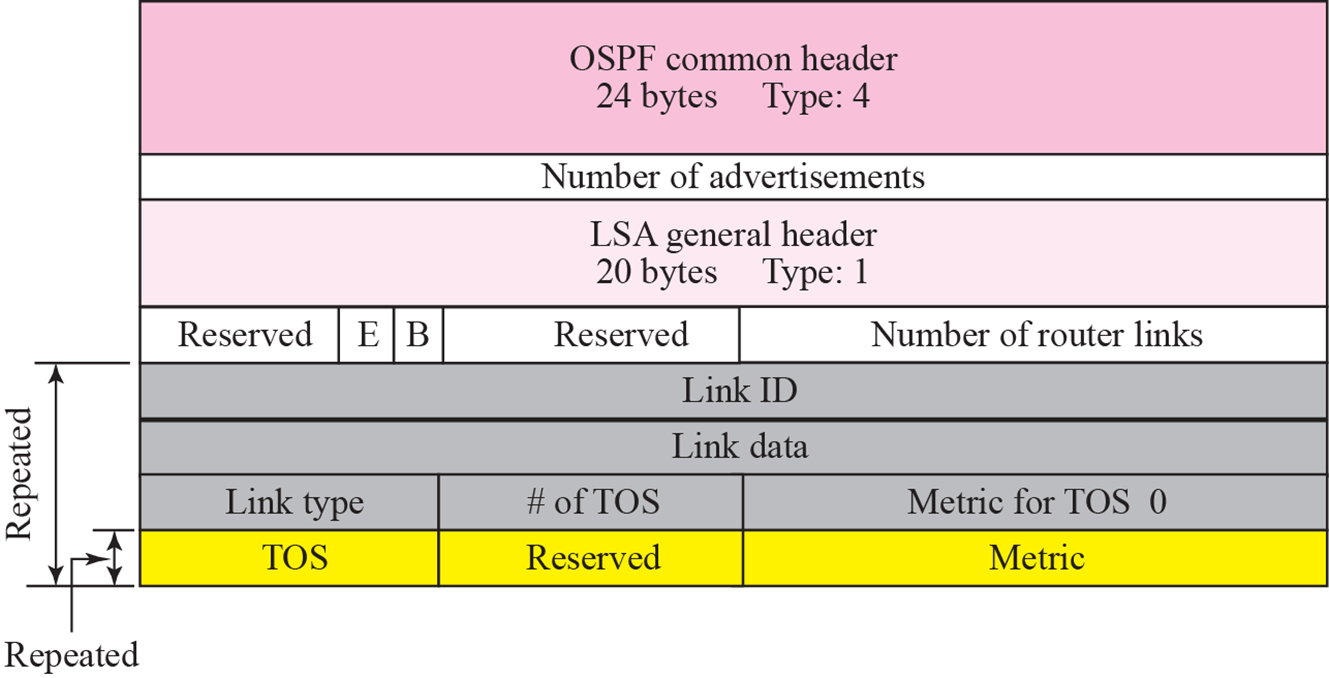 E: AS boundary router?1:0
B: area boundary router?1:0
TOS: time of service
Metric: cost
E: AS boundary router?1:0
B: area boundary router?1:0
TOS: time of service
Metric: cost

Network link
- Network에 붙어 있는 router를 알려줌
- Network 대신 Designated router가 전송
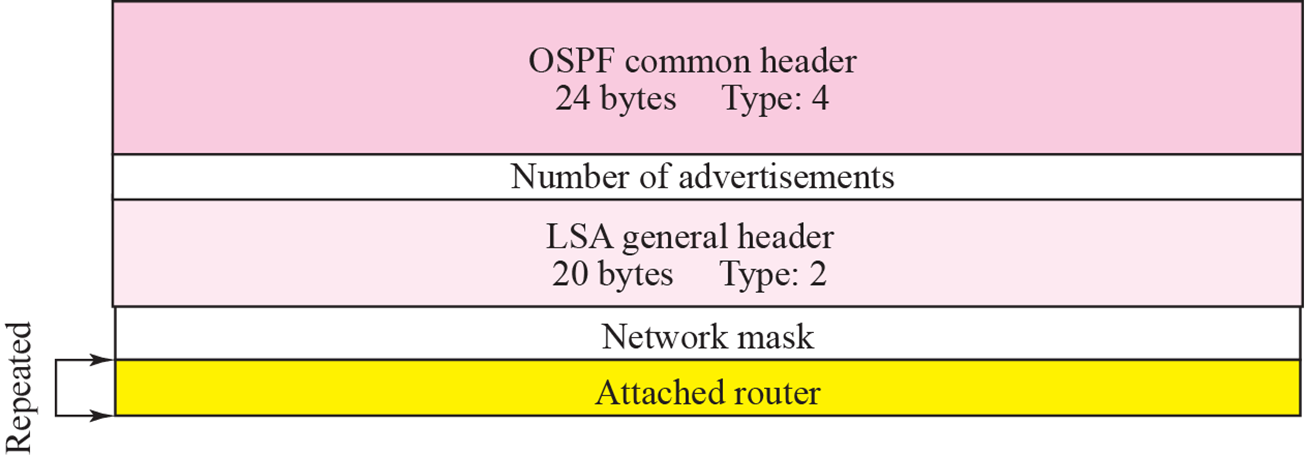
- Network mask만 들어가는 이유는 OSPF common header에 IP address가 포함되기 때문
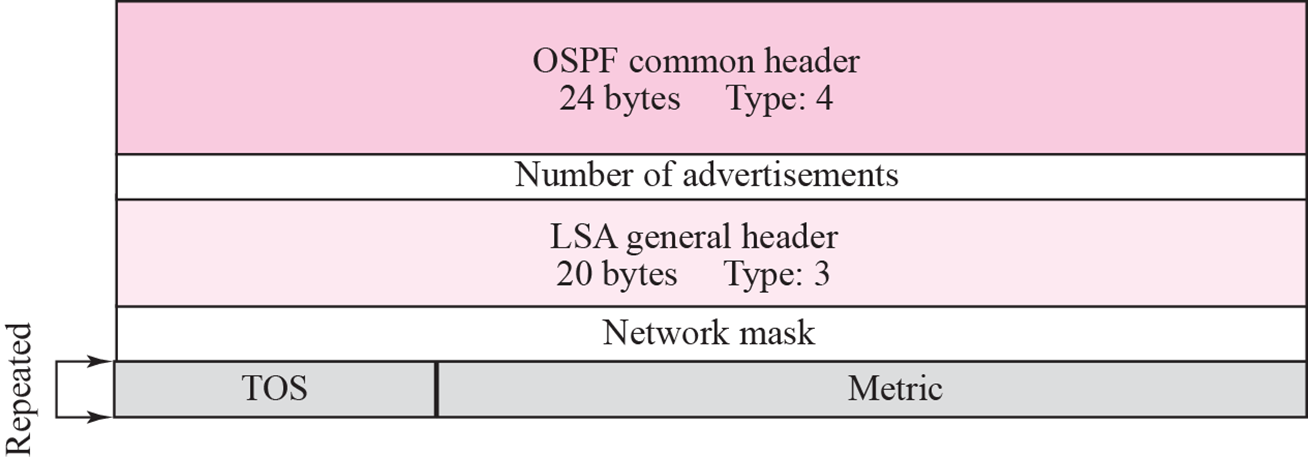
summery link to network
- area 0로 가는 network를 알려줌
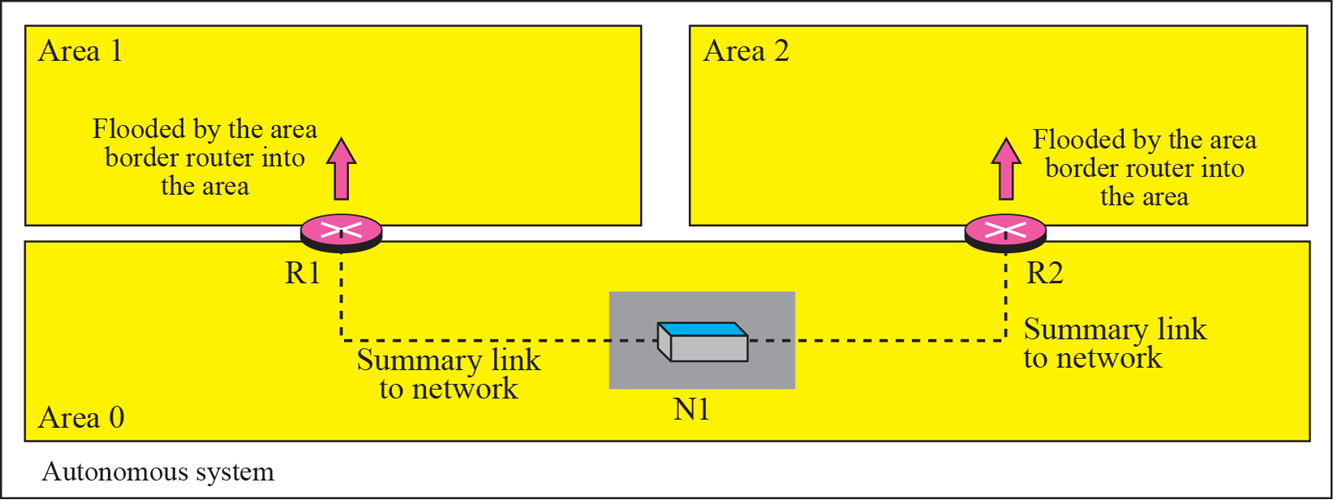
summery lnk to AS boundary router
- AS boundary router 주소를 알려줌

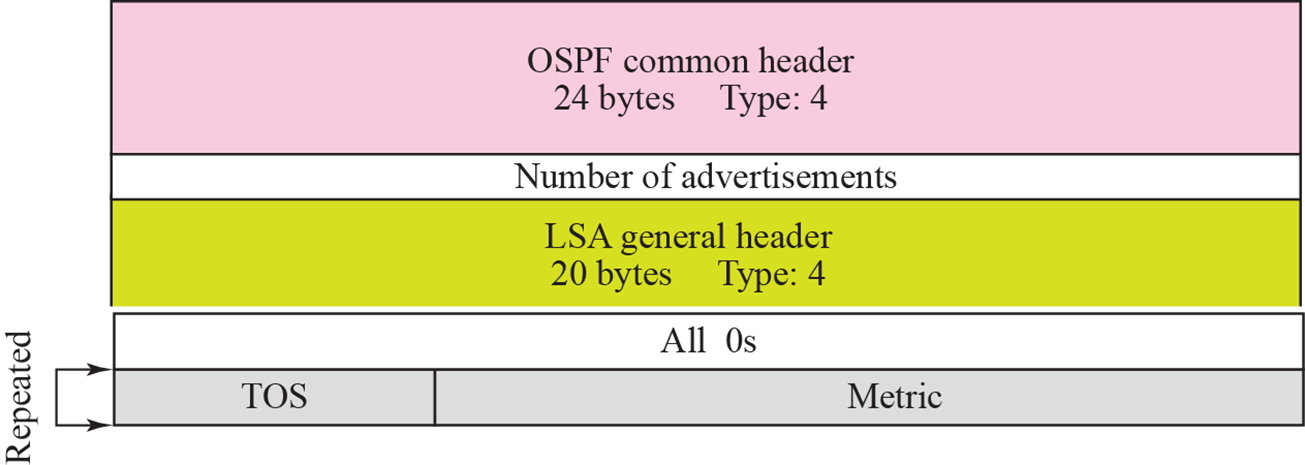
- address는 OSPF common header에 있음
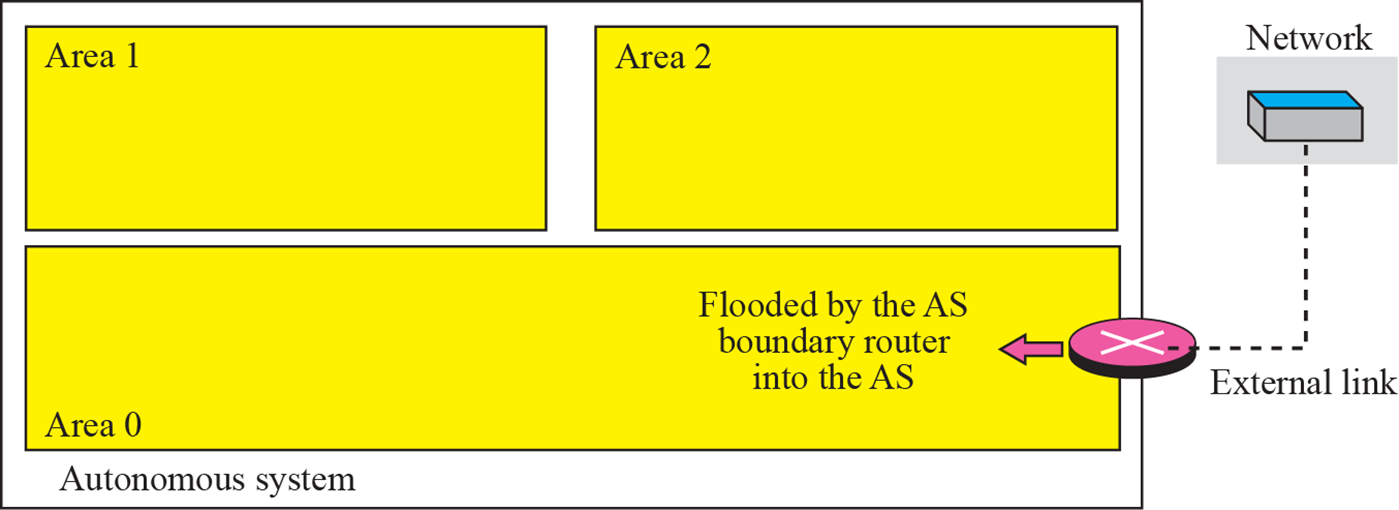
External link
- AS 외부의 특정 network에 접속하는 방법을 알려줌
Hello packet
- router 접속 시, 기본 정보 제공
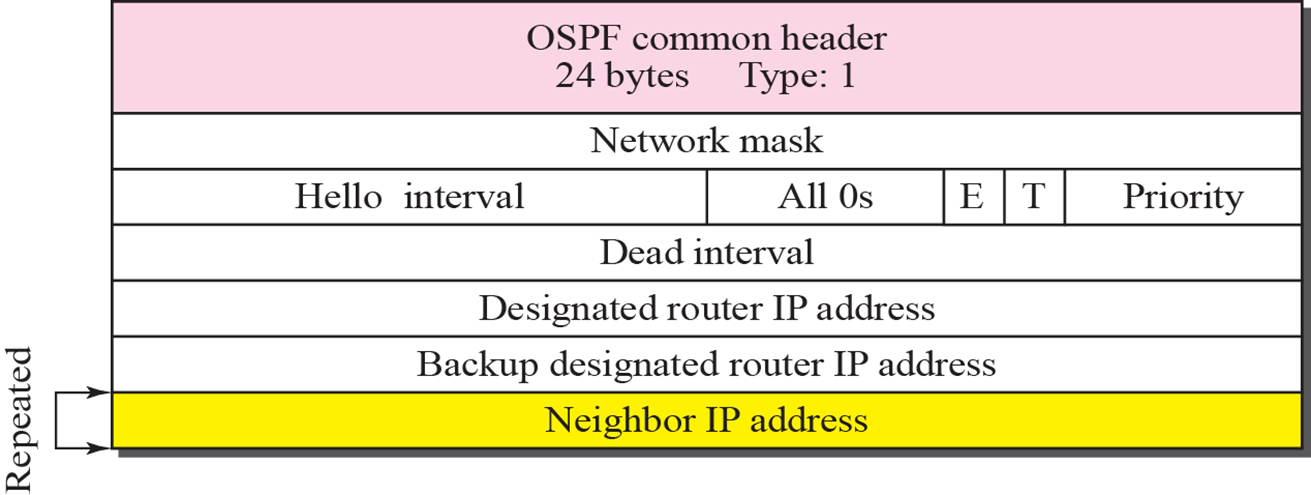
- Hello interval: down 여부 확인 위한 지속적인 packet 전송 시간
- Priority: 우선 순위 (designated router 선정 기준)
- Dead interval: Hello packet이 오지 않으면 이웃 router가 down 되었다고 판단
Database description packet
- Hello packet에 대한 응답으로, 자신이 가진 대략적인 network 정보롤 담아 전송
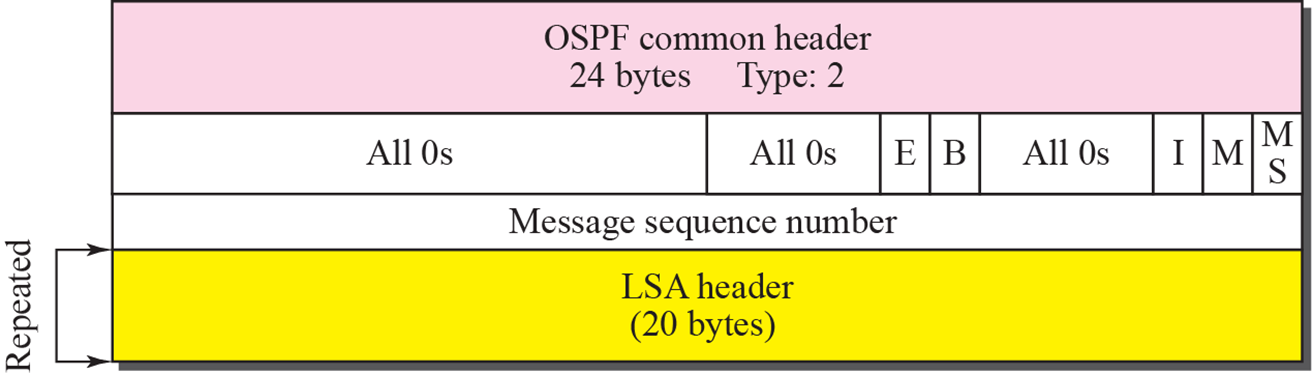
I: 상대 router와 첫 통신
M: more bit data, 뒤에 data가 더 있음 여부
MS: Master(전송 측)/slave(수신 측)
Link state request packet
- 자세히 알고 싶은 network address에 대한 정보 요청
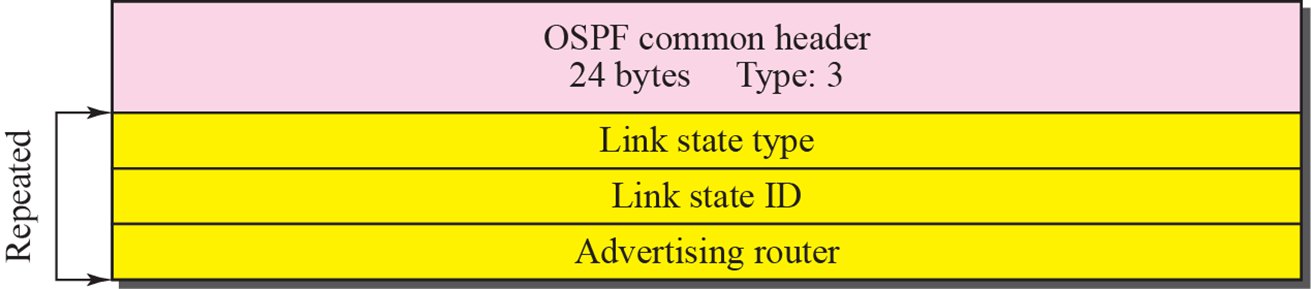
Link state acknowledgment packet
- link state advertisement에 대한 확인 응답

- OSPF는 IP datagram에 encapsulation 됨
Inter domain
Path vector
- AS 간의 routing
- AS 경계 router를 specker router라 함
- Path가 나열되어 있는 방식
Reachability
- Reachability table을 작성, 교환, 반복
address aggregation(축약)
- table이 길어지기 때문에 aggregation 필요


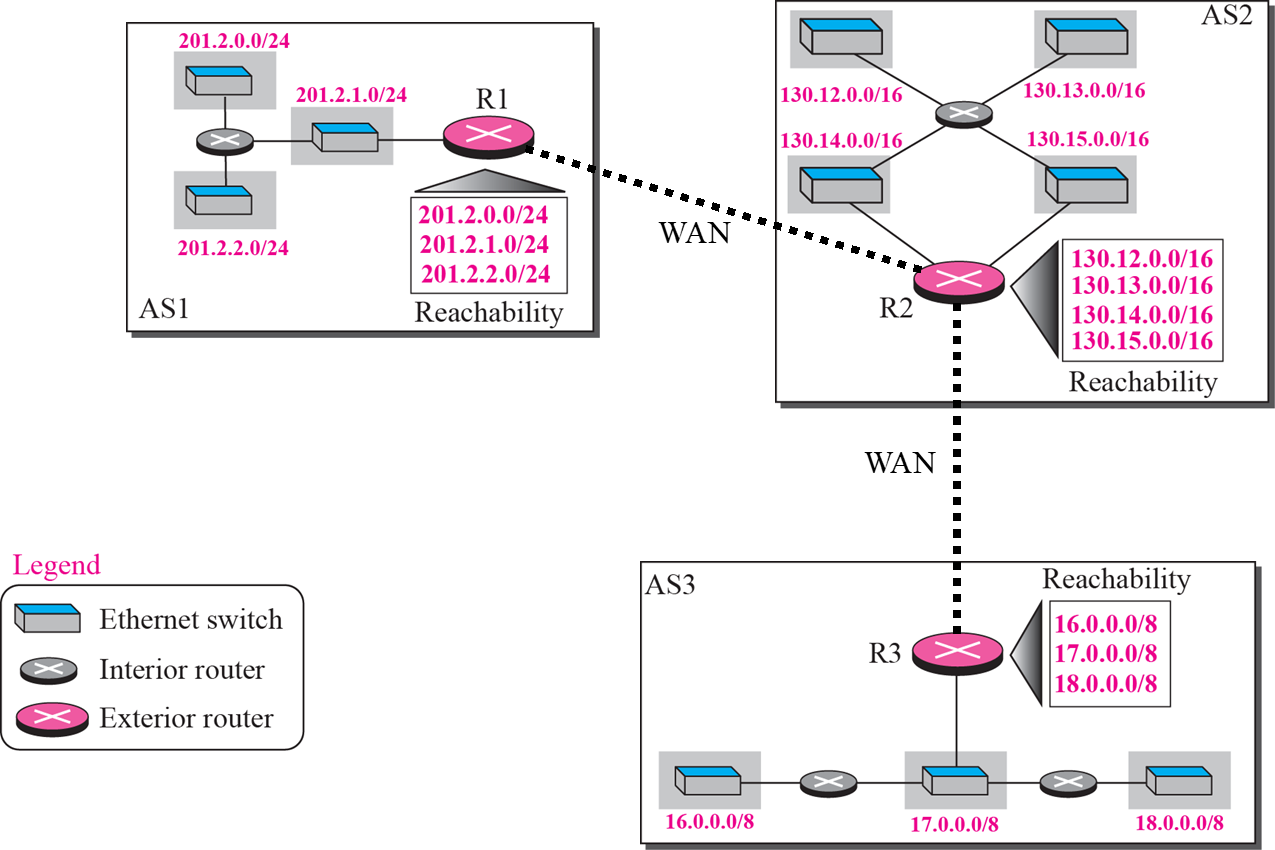
BGP(Border Gateway Protocol)
- Path vector 사용
- 현재 version 4
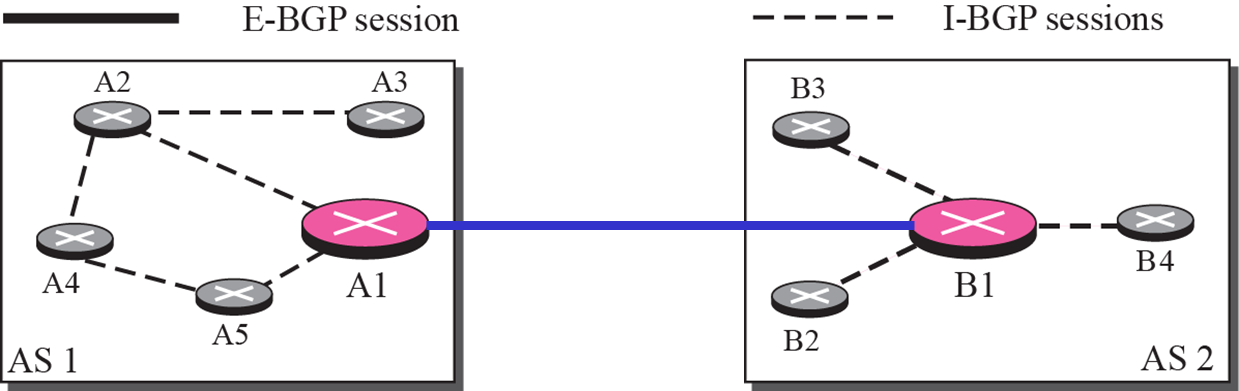
- 두 AS가 TCP로 session 연결
- E는 외부, I는 내부 라는 뜻
BGP message types
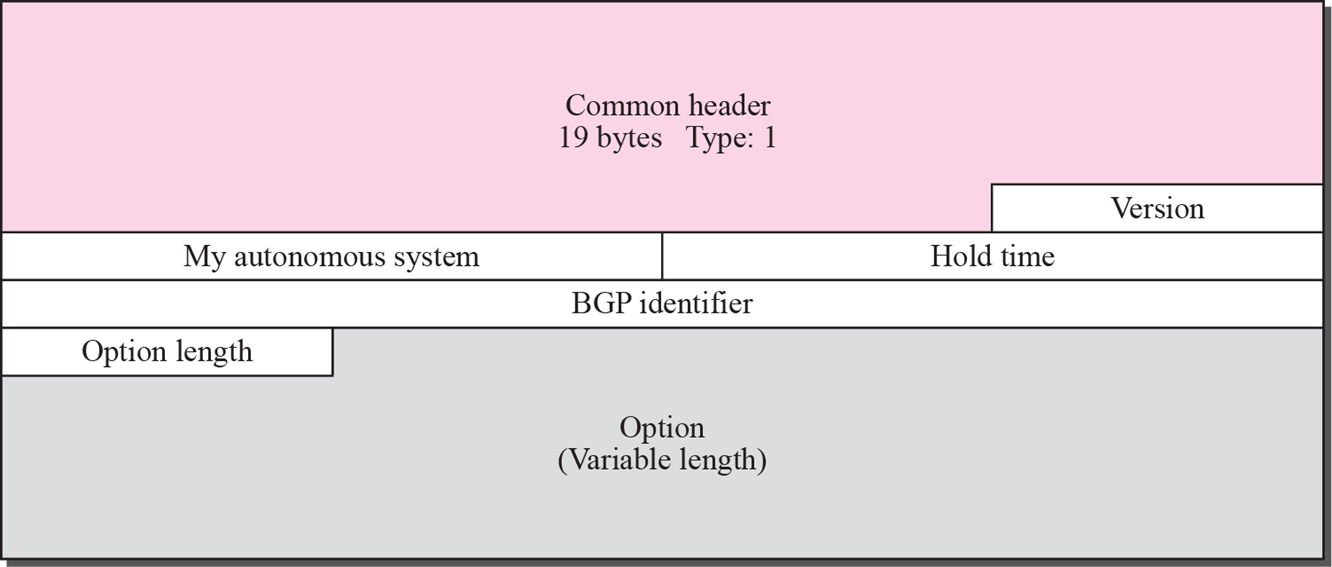
BGP packet header

Marker: 인증을 위한 데이터로 현재까지 명확히 규정되지 않음
Open message
- session 연결 요청
Update message
- table update

Unfeasible routes lenth: 사용 불가 path
Path attribute lent
- BGP는 CIDR(classless inter domain routin)
Keepalive message
- 살아있는지 확인

Notification
- error control

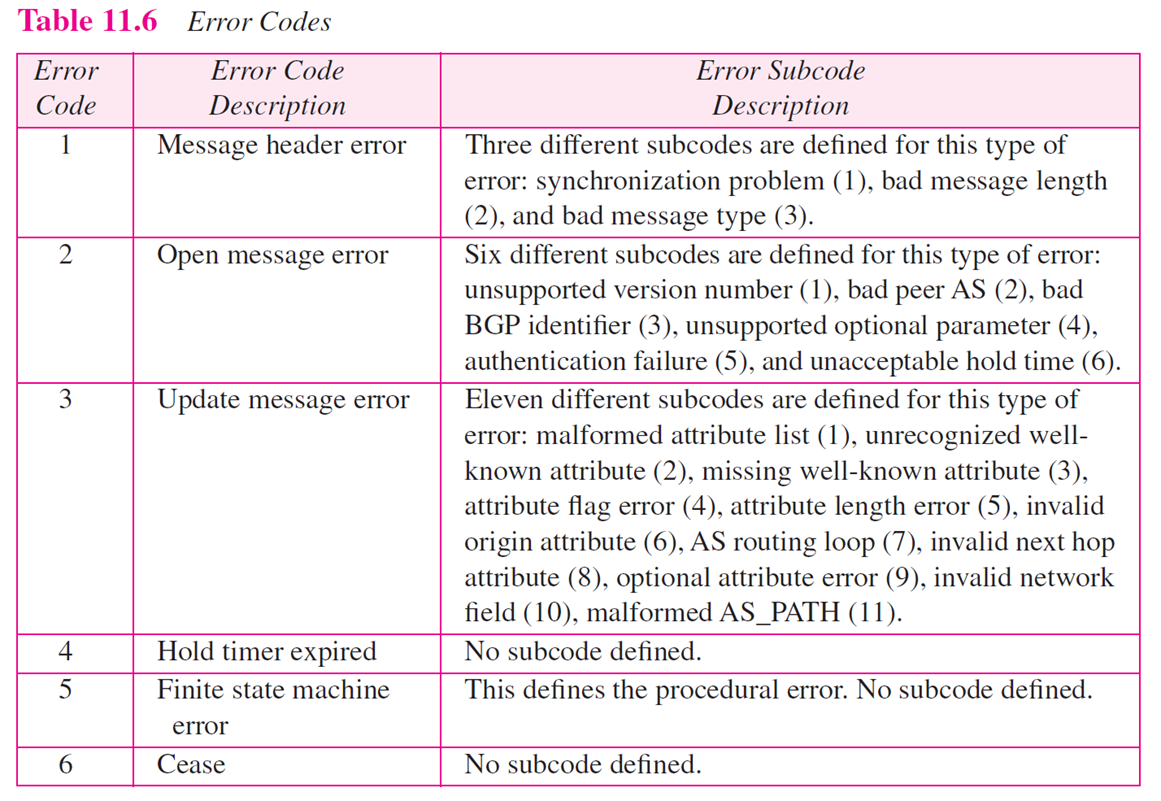
- BGP는 TCP port 179 사용
