TCP/IP
1.TCP/IP(1)_1

CH5 IPv4 Addresses CH5-1 Internet address(IP address) : TCP/IP 프로토콜 제품군의 IP 계층에서 인터넷에 연결된 각 장치를 식별하는 데 사용되는 실별자 IPv4 호스트나 라우터의 인터넷 연결을 고유하고 보편적으로 정의
2.TCP/IP(1)_2
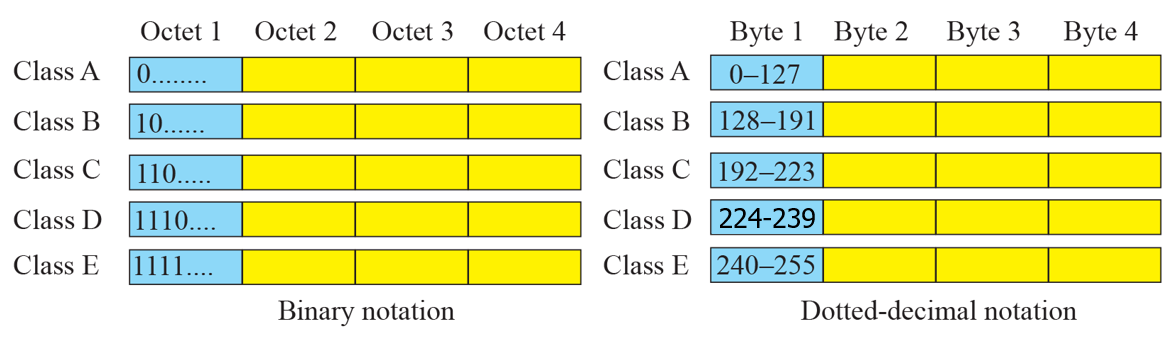
IP addresses를 처음 사용할 때 Class라는 개념을 사용한 것1990년대 중반 Classless addressing이 등장하여 Classful addressing을 대채Class는 A ~ E까지 존재각 Class는 총 32bit인 IPv4 address의 최
3.TCP/IP(1)_3

5-3 Classless Addressing Classful addressing의 subnetting, supernetting으로도 주소 고갈 문제를 완전히 해결하지는 못한다. 장거리는 IPv6, 단거리는 IPv4이지만 classless addressing 방법으로
4.TCP/IP(2)
1
5.TCP/IP(3)
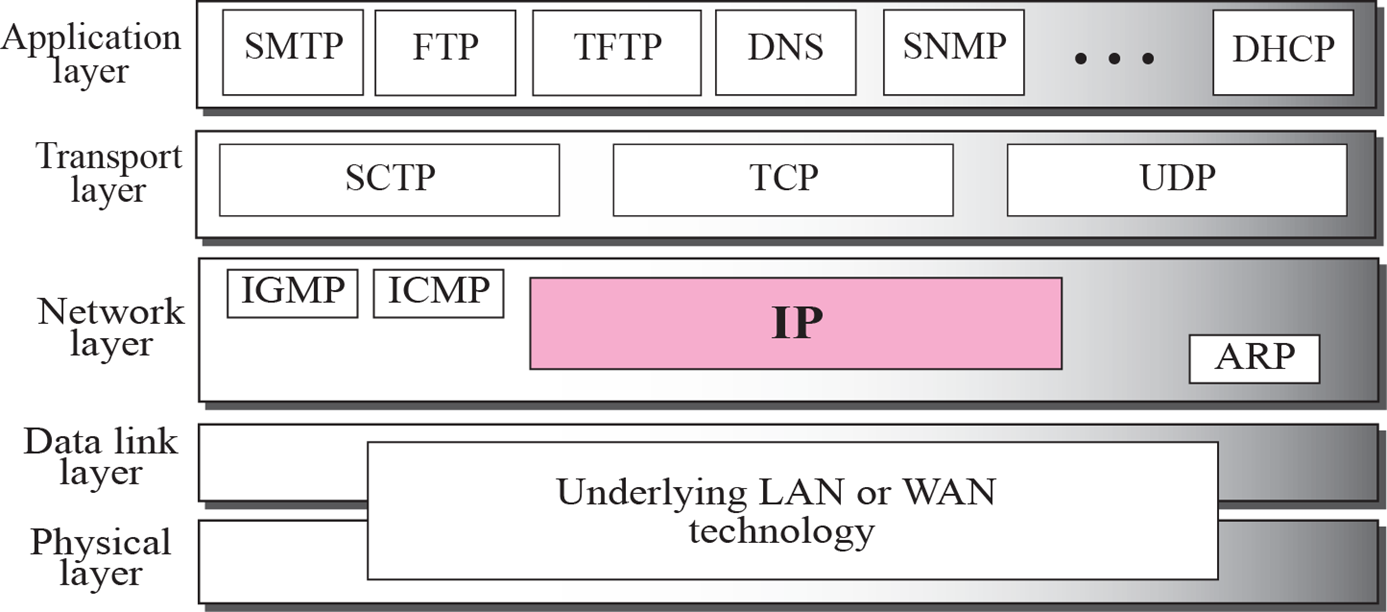
IP는 network layer(3계층)에서 사용되는 protocol이다.IP는 신뢰성이 없어 전달과정에서 오류가 생기면 packet을 버린다.ICMP는 패킷의 오류 등을 알려줌IGMP는 멀티캐스트 용도로 사용 (Internet Group Management Proto
6.TCP/IP(4)
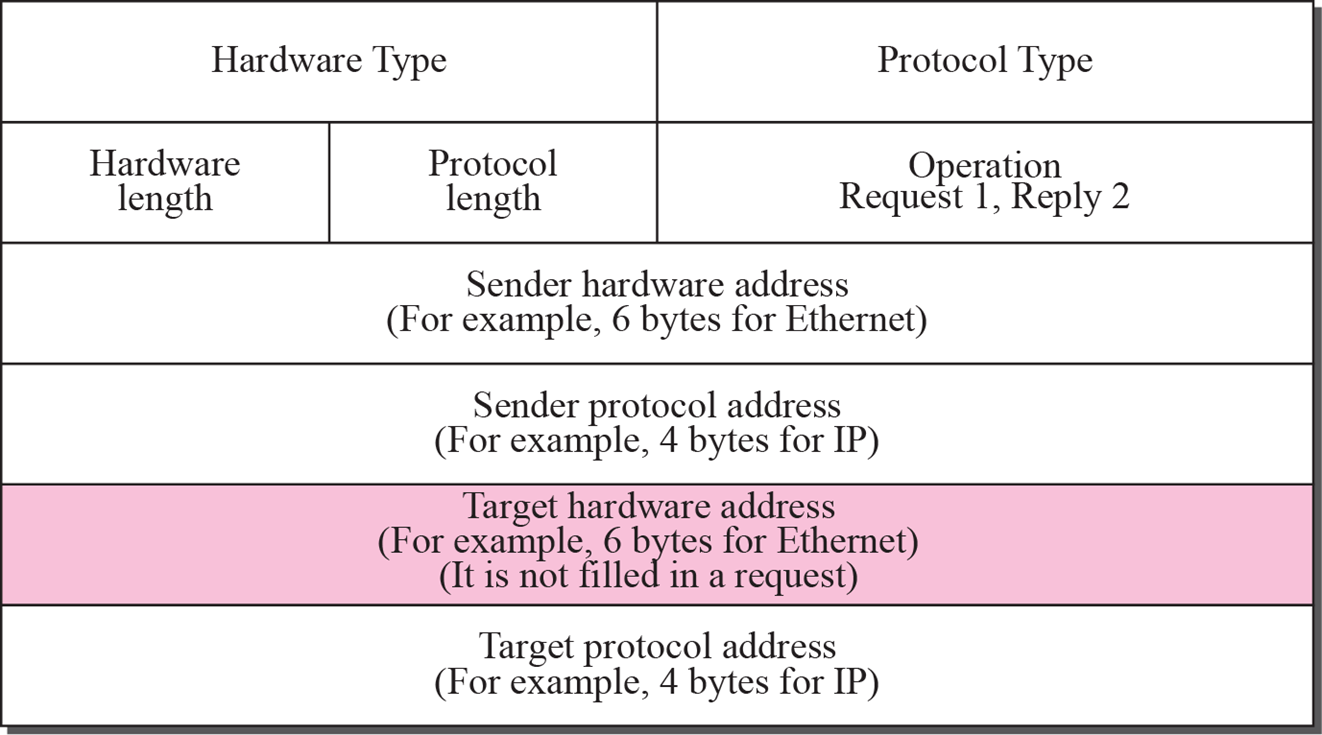
ARP: IP address(logical)을 MAC/ATM address(Physical)로 변경해주는 protocol초기에는 Static Mapping으로 직접 Mapping table을 작성했다.address가 늘어나며 Dynamic Mapping이 필요해졌고 A
7.TCP/IP_ICMP

ICMP(Internet Control Message Protocol) IP protocol은 eror-reporting 이나 error correcting 기능이 없다 (신뢰성 없음) ICMP가 이를 보완한다. ICMP Network layer protocol
8.TCP/IP_Mobile IP
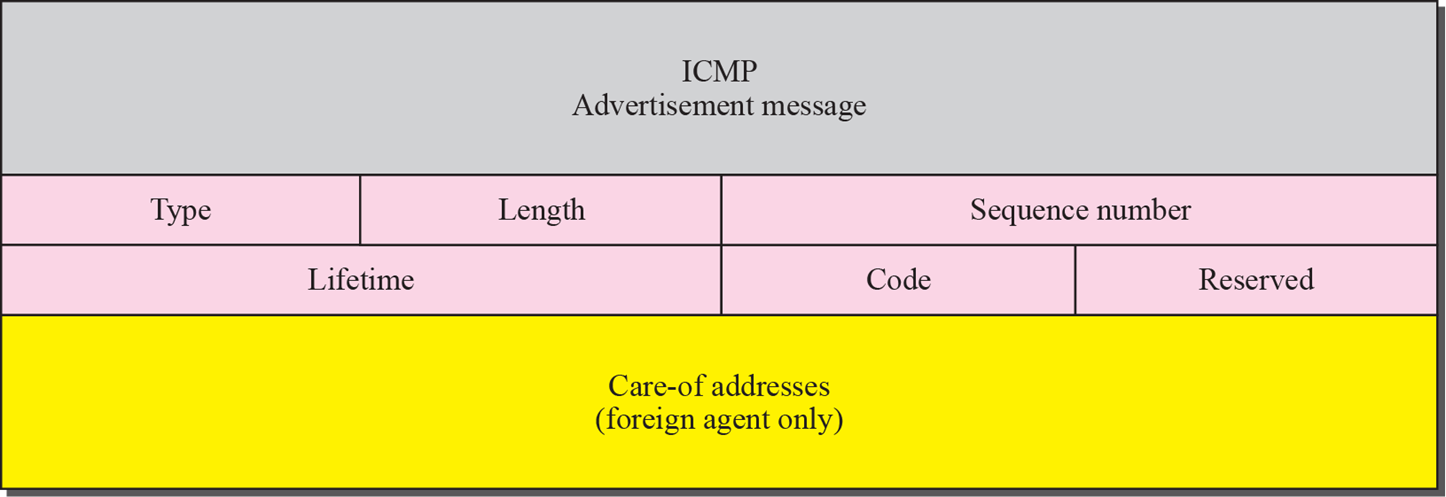
Mobile IP IP address의 일부는 연결되어 있는 Network address가 포함됨 IP address는 위치가 고정된 host에게 적합하게 설계됨(문제점) ex) 노트북, 스마트폰 이를 해결 하기 위해, Mobile IP는 home address와
9.TCP/IP_Unicast Routing Protocols
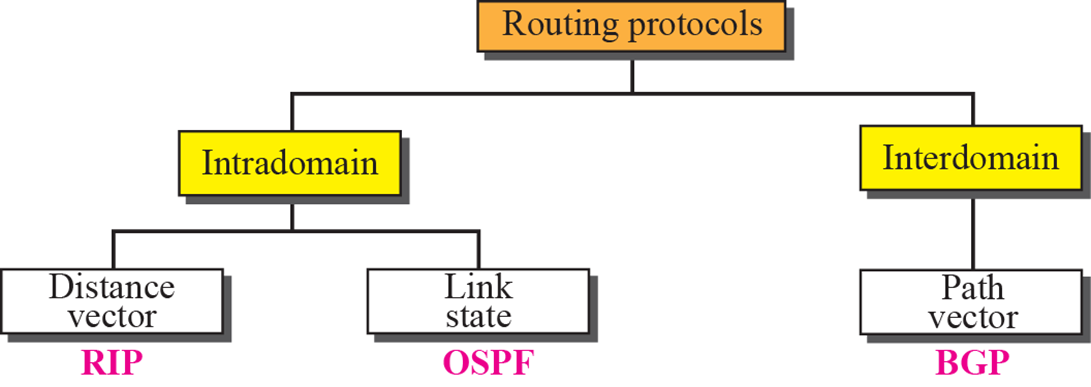
오늘날의 인터넷은 너무 커졌기 때문에 여러개의 routing protocol이 필요그중 Unicast(1대1)는 Inter domain routing과 intra domain routing으로 나뉨AS(autonomous system): 거대한 인터넷을 쪼갬intra
10.TCP/IP_Transport layer services
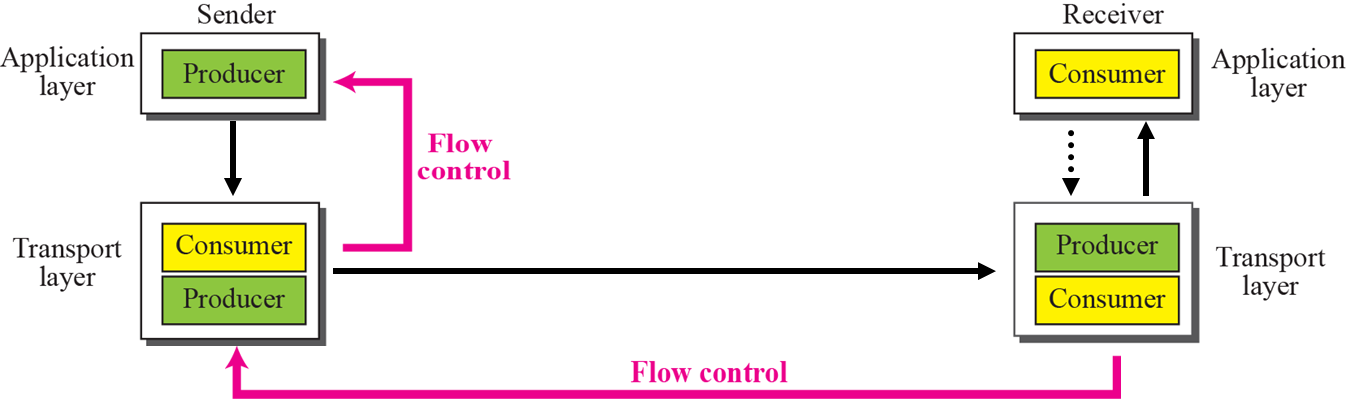
Transport-Layer Services Network-layer는 PC를 지칭하는 IP address 사용 Transport-layer는 processes와 port를 통해 연결 port number Socket address Encapsulation an
11.TCP/IP_User Datagram Protocol(UDP)

UDP packetsUDP는 error control, flow control 기능 없음Error checking은 option(checksum 설정)connectionless Simple protocolUDP는 신뢰성이 없음Source port number: 출발지
12.TCP/IP_Transmission Control Protocol(TCP)
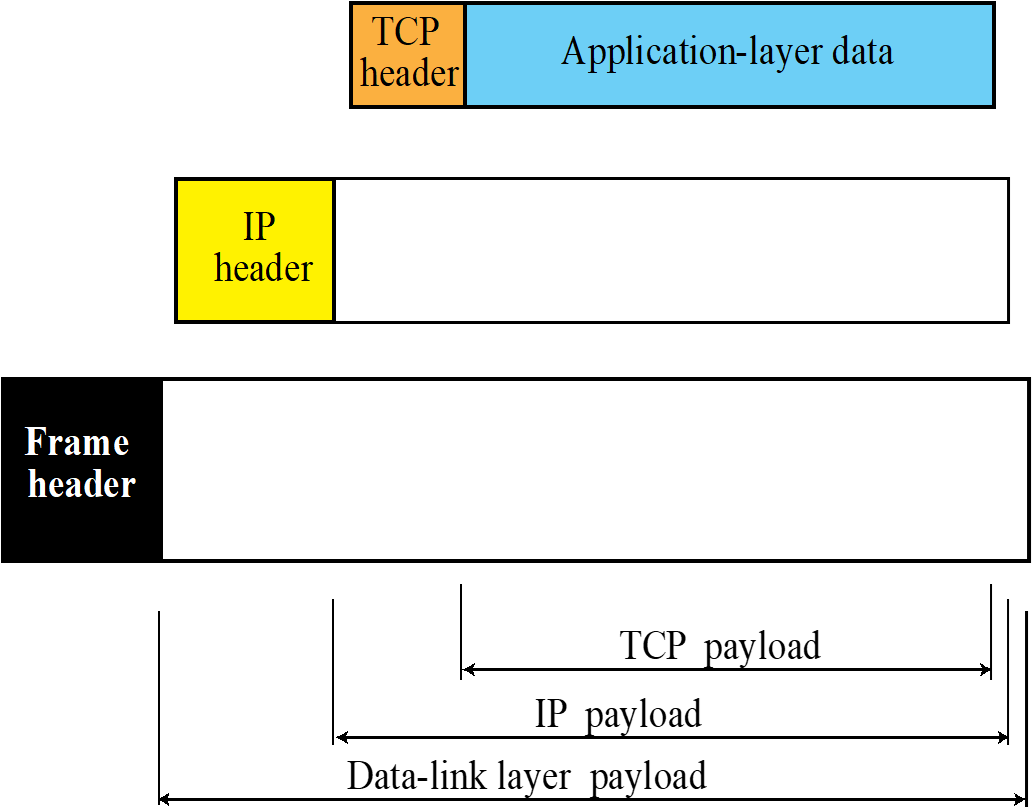
TCP Service error control, flow control, congestion control 다 가능 connection oriented방식 통신 시작 전 setup(연결) 과정이 있음 TCP의 well-known port Stream deliv