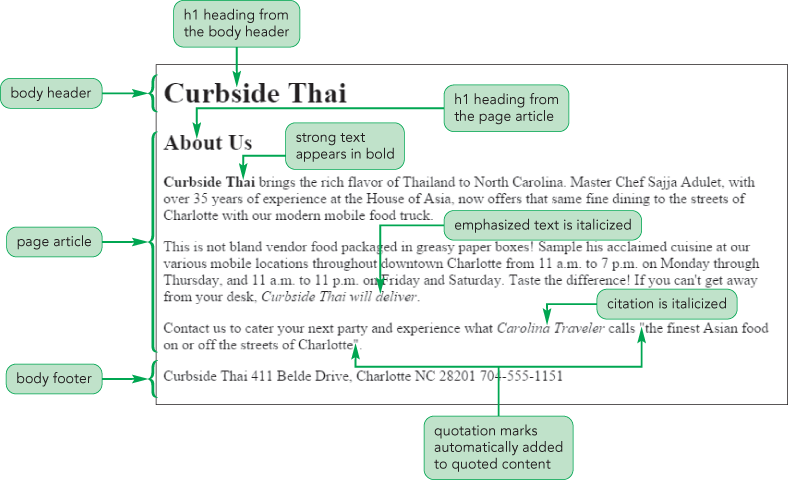
Elements and attributes from an HTML document
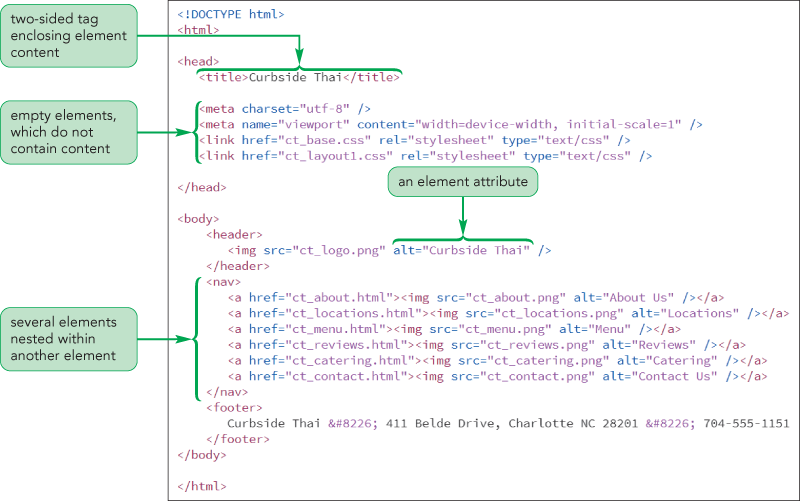
source:
The Document Type Declaration
the first line in an HTML file is the document type declaration.
The browser uses the document type declaration to know which standard to use to display the content.
<!DOCTYPE html>Basic Sctructure
We should write starting tag, content, ending tag.
For example,
<element>content</element><!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
head content
</head>
<body>
body content
</body>
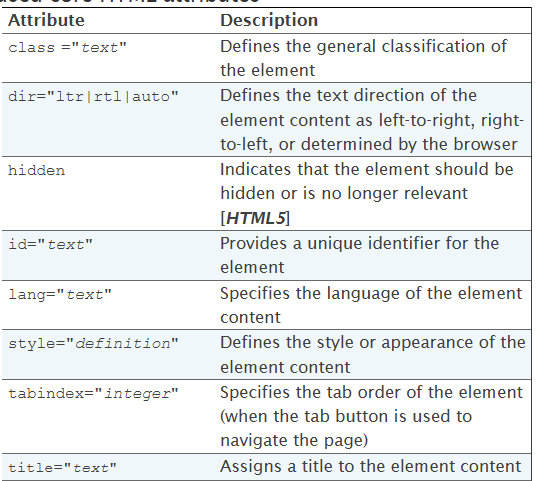
</html>Commonly used core HTML attributes
HTML meta data elements
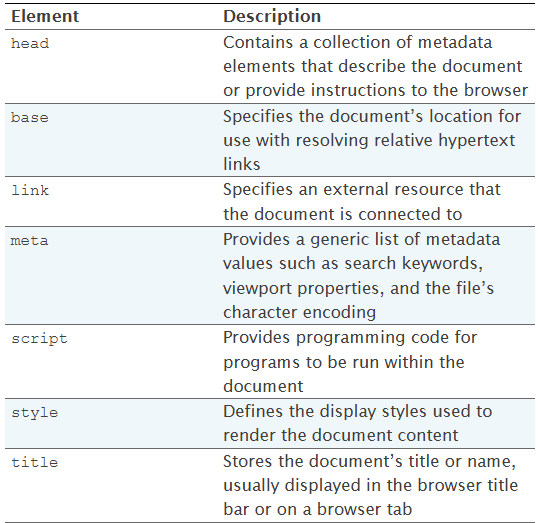
If I select the most commonly used meta data element among the above tags, it will be title. The <title> tag in <head> tag area refer to name of tab.

like this!
I don't have to mention now, but the icon in the tab is called favicon(favorite icon).
Attributes of the meta element
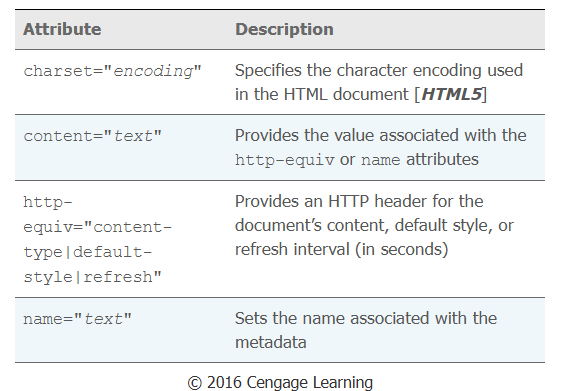
The most used common character encoding in use is "UTF-8", which supports almost all of the characters you will need.
You can write like this!
<meta charset="utf-8">UTF-8 is a variable-length encoding method that represents Unicode code points using 1 to 4 bytes.
Although modern search engines no longer rely heavily on the keywords meta tag, the name and content attributes in meta elements are still important, as they can provide descriptions and context that influence how a page appears in search results.
<meta name="description" content="...">For improving SEO, you should write title and description well.

Adding comments
There are many ways to add comments in programming language. For example, we can use // in C or Python.
In HTML, we can use <!-- ddd --> this format to add comments.
<!-- information about this document -->HTML Elements
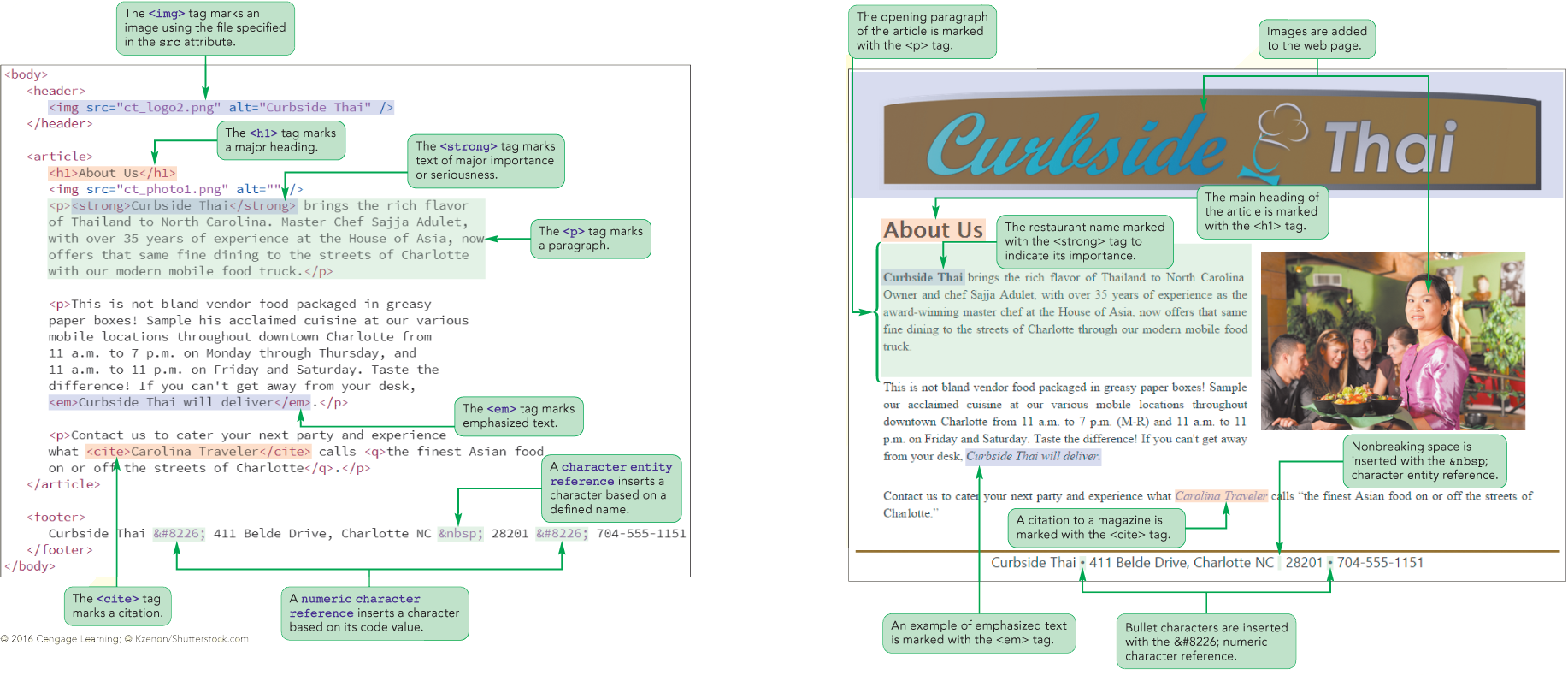
Using sectioning elements
Using sectioning elements (such as <header>, <nav>, <section>, <article>, and <footer>) helps define the structure and hierarchy of a web page. They make the content more meaningful and easier to understand, not only for developers and users but also for search engines and assistive technologies. By providing semantic structure, sectioning elements improve accessibility, SEO, and overall readability of the page.
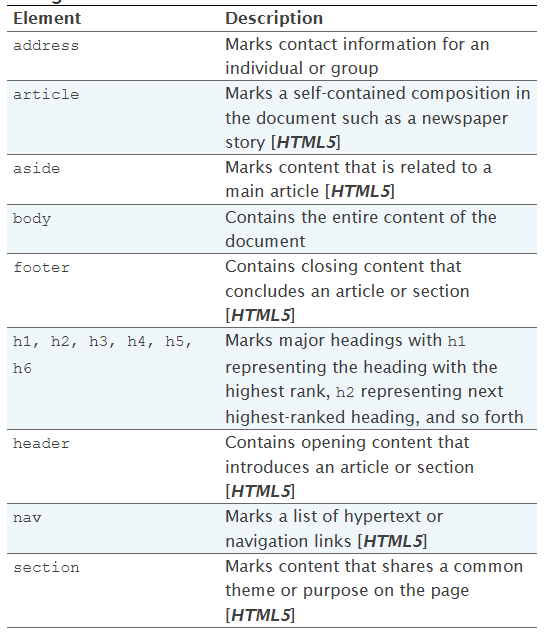
-
To mark the page header, use the
headerelement. -
To mark self-contained content, use the
articleelement. -
To mark a navigation list of hypertext links, use the
navelement. -
To mark a sidebar, use the
asideelement. -
To mark the page footer, use the
footerelement. -
To group general content, use the
sectionelement.
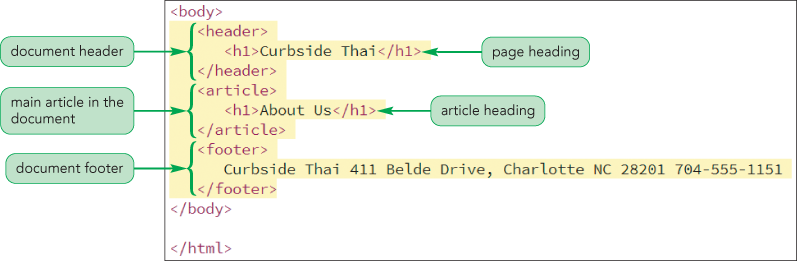
If you want to group article content, you can use <p> tag.
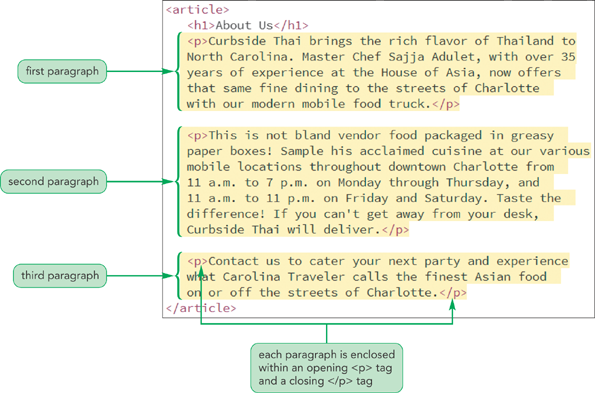
HTML text-level elements
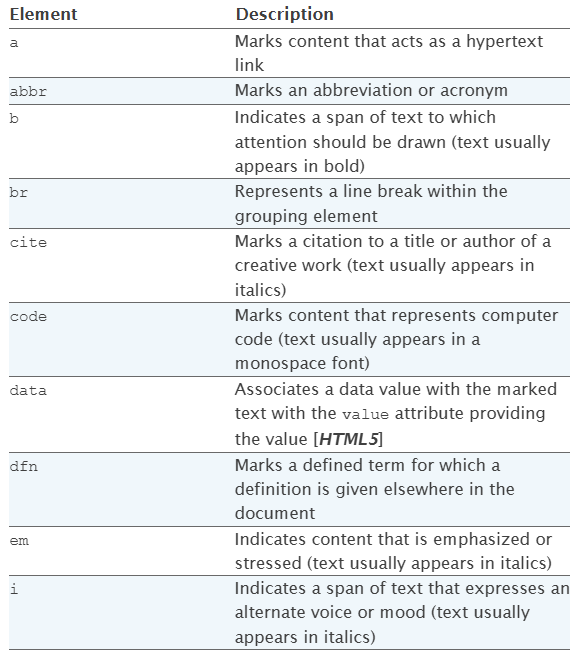
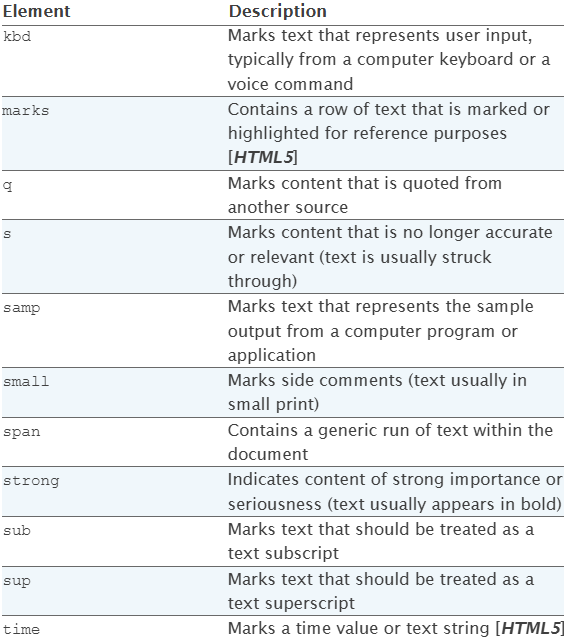
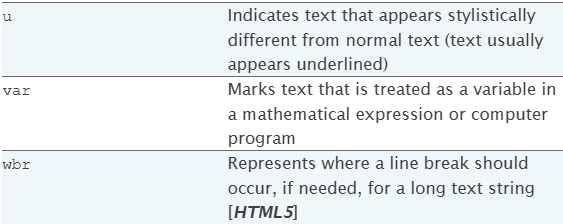
This is the example of HTML
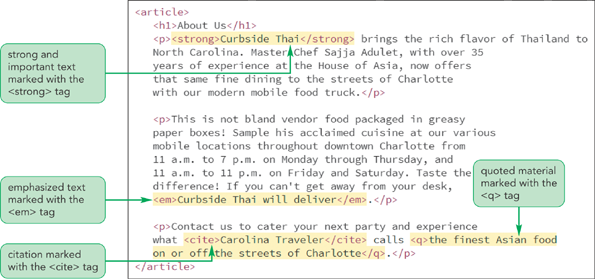
And this is the result of above code