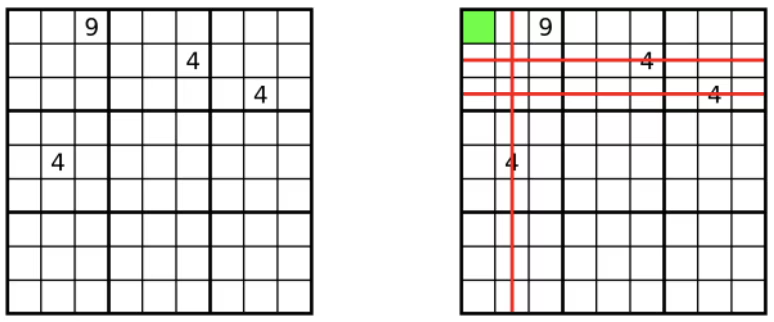
👨💻 문제
✍️ 풀이
✅ 사용된 숫자 확인
스도쿠 문제를 풀기 위해선 각 행, 열, 박스 마다 사용된 숫자들을 파악하는 것이 중요하다.
그것을 파악하기 위해 우선 각 행, 열, 박스 별로 boolean배열을 만들었다.
private static boolean[][] usedNum_row = new boolean[9][10]; // 각 행에 i를 사용했는가
private static boolean[][] usedNum_col = new boolean[9][10]; // 각 열에 i를 사용했는가
private static boolean[][] usedNum_box = new boolean[9][10]; // 각 박스에 i를 사용했는가객체 구조
풀다 보니 객체지향적으로 구현하게 되었다.
물론 철저히 객체지향 규칙을 지키지는 않았다
private static SudokuBox[] sudokuBoxes = new SudokuBox[9];
private static class SudokuBox {
int boxIdx;
List<SudokuElement> elements = new ArrayList<>();
...
}
private static class SudokuElement {
int r;
int c;
int boxIdx;
int value;
...
}구조를 박스 기준으로 만들었다.
처음에는 그냥 9*9 배열을 사용하였는데,
후술할 Cross-hatching 방식에는 적합하지 않았다.
✝️ Cross-hatching
해당 문제는 Cross-hatching 방식만으로 스도쿠를 완성한다.
그렇기에 우선 Cross-hatching 방식을 구현해야 한다.
이를 구현하기 위해서는 아래와 같이 박스 별로 각 칸의 요소들을 나누는 것이 적합하겠다고 판단하였다.
박스마다 1~9 까지의 숫자 중 유일하게 채울 수 있는 칸이 존재한다면 채워넣는다.
private static class SudokuBox {
...
// 각 숫자마다 유일하게 채워지는 칸인지 확인 후 채운다
public void cross_hatch() {
for (int value = 1; value <= 9; value++) {
if (usedNum_box[boxIdx][value]) {
continue;
}
for (SudokuElement e : elements) {
if (canFillOnly(e, value)) {
e.fill(value);
}
}
}
}
...🔱 모순
해당 스도쿠 문제에서 모순이란 2가지를 확인해야 한다.
1. 각 행, 열, 박스에 중복된 숫자가 할당되는 경우
1 . . 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
이 경우, 입력 시에만 검증한다.
나는 중복된 값을 넣지 않을 것이기 때문이다.
그래도 굳이 분리하지 않고 값을 입력하는 메소드는 통일시켰다.
private static class SudokuElement {
...
public void fill(int value) {
if (!canFill(value)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("모순 : 잘못된 값을 채움");
}
this.value = value;
usedNum_row[r][value] = usedNum_col[c][value] = usedNum_box[boxIdx][value] = true;
}
public boolean canFill(int value) {
return this.value == NULL && !usedNum_row[r][value] && !usedNum_col[c][value] && !usedNum_box[boxIdx][value];
}
2. 무슨 짓을 해도 스도쿠를 완성할 수 없게 되는 경우
. . . . . . . . 2 . . 1 . . . . . . . . . . . 1 . . . . . . . . . 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 위 예의 경우 2가 있는 자리에 1이 존재해야 한다. // 이거 안 했다가 한 번 틀렸다.
각 박스마다 1~9까지 하나의 숫자라도 이미 채워져 있지 않거나, 채울 수 없다면 모순인 상황이다.
private static class SudokuElement {
...
// 숫자를 채울 수 없는 모순 찾기
public void checkCanFillNumbers() {
for (int value = 1; value <= 9; value++) {
boolean canFill = false;
for (SudokuElement e : elements) {
if (e.value == value || e.canFill(value)) {
canFill = true;
break;
}
}
if (!canFill) {
throw new IllegalStateException("모순 : 해당 숫자를 절대 채울 수 없음");
}
}
}📄 전체 소스코드
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.Set;
public class Main {
private static final int NULL = 0;
private static SudokuBox[] sudokuBoxes = new SudokuBox[9];
private static boolean[][] usedNum_row = new boolean[9][10]; // 각 행에 i를 사용했는가
private static boolean[][] usedNum_col = new boolean[9][10]; // 각 열에 i를 사용했는가
private static boolean[][] usedNum_box = new boolean[9][10]; // 각 박스에 i를 사용했는가
private static class SudokuBox {
int boxIdx;
List<SudokuElement> elements = new ArrayList<>();
public SudokuBox(int i) {
boxIdx = i;
}
public void add(SudokuElement e) {
elements.add(e);
}
// 각 숫자마다 유일하게 채워지는 칸인지 확인 후 채운다
public void cross_hatch() {
for (int value = 1; value <= 9; value++) {
if (usedNum_box[boxIdx][value]) {
continue;
}
for (SudokuElement e : elements) {
if (canFillOnly(e, value)) {
e.fill(value);
}
}
}
}
// 숫자를 채울 수 없는 모순 찾기
public void checkCanFillNumbers() {
for (int value = 1; value <= 9; value++) {
boolean canFill = false;
for (SudokuElement e : elements) {
if (e.value == value || e.canFill(value)) {
canFill = true;
break;
}
}
if (!canFill) {
throw new IllegalStateException("모순 : 해당 숫자를 절대 채울 수 없음");
}
}
}
private boolean canFillOnly(SudokuElement target, int value) {
for (SudokuElement e : elements) {
if (e == target) {
if (!e.canFill(value)) {
return false;
}
}
else if (e.canFill(value)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
private static class SudokuElement {
int r;
int c;
int boxIdx;
int value;
public SudokuElement(int r, int c) {
init(r, c);
value = NULL;
}
public SudokuElement(int r, int c, int value) {
init(r, c);
fill(value);
}
private void init(int r, int c) {
this.r = r;
this.c = c;
this.boxIdx = calcBoxIndex(r, c);
}
public void fill(int value) {
if (!canFill(value)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("모순 : 잘못된 값을 채움");
}
this.value = value;
usedNum_row[r][value] = usedNum_col[c][value] = usedNum_box[boxIdx][value] = true;
}
public boolean canFill(int value) {
return this.value == NULL && !usedNum_row[r][value] && !usedNum_col[c][value] && !usedNum_box[boxIdx][value];
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try {
input();
for (int i=0; i<81; i++) {
for (SudokuBox box : sudokuBoxes) {
box.cross_hatch();
box.checkCanFillNumbers();
}
}
// logSudoku();
printSudoku();
}
catch (IllegalStateException e) {
System.out.println("ERROR");
}
}
private static void input() throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
for (int i=0; i<9; i++) {
sudokuBoxes[i] = new SudokuBox(i);
}
for (int r=0; r<9; r++) {
String str = br.readLine();
for (int c=0; c<9; c++) {
char value = str.charAt(c);
SudokuElement e = value == '.' ? new SudokuElement(r, c) : new SudokuElement(r, c, value - '0');
sudokuBoxes[calcBoxIndex(r, c)].add(e);
}
}
}
private static int calcBoxIndex(int r, int c) {
int box_r = r / 3;
int box_c = c / 3;
return box_r * 3 + box_c;
}
private static void printSudoku() {
PriorityQueue<SudokuElement> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((e1, e2) -> {
if (e1.r == e2.r) {
return e1.c - e2.c;
}
return e1.r - e2.r;
});
for (SudokuBox box : sudokuBoxes) {
for (SudokuElement e : box.elements) {
pq.add(e);
}
}
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int r=0; r<9; r++) {
for (int c=0; c<9; c++) {
int value = pq.poll().value;
sb.append(value == NULL ? "." : value);
}
sb.append('\n');
}
System.out.print(sb);
}
// 로깅용 함수
// private static void logSudoku() {
// PriorityQueue<SudokuElement> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((e1, e2) -> {
// if (e1.r == e2.r) {
// return e1.c - e2.c;
// }
// return e1.r - e2.r;
// });
//
// for (SudokuBox box : sudokuBoxes) {
// for (SudokuElement e : box.elements) {
// pq.add(e);
// }
// }
//
// System.out.println("-----row[i] 사용한 숫자-----");
// for (int i=0; i<9; i++) {
// System.out.printf("---%d---\n", i);
// for (int j=1; j<=9; j++) {
// if (usedNum_row[i][j]) {
// System.out.printf("%d ", j);
// }
// }
// System.out.println();
// }
//
// System.out.println("-----col[i] 사용한 숫자-----");
// for (int i=0; i<9; i++) {
// System.out.printf("---%d---\n", i);
// for (int j=1; j<=9; j++) {
// if (usedNum_col[i][j]) {
// System.out.printf("%d ", j);
// }
// }
// System.out.println();
// }
//
// System.out.println("-----box[i] 사용한 숫자-----");
// for (int i=0; i<9; i++) {
// System.out.printf("---%d---\n", i);
// for (int j=1; j<=9; j++) {
// if (usedNum_box[i][j]) {
// System.out.printf("%d ", j);
// }
// }
// System.out.println();
// }
//
// for (int r=0; r<9; r++) {
// for (int c=0; c<9; c++) {
// SudokuElement e = pq.poll();
// System.out.printf("[%d] (%d,%d) : %d | ", e.boxIdx, r, c, e.value);
// }
// System.out.println();
// }
// }
}
🔍️ 참고
🔁 반복 횟수
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try {
input();
for (int i=0; i<81; i++) {
for (SudokuBox box : sudokuBoxes) {
box.cross_hatch();
box.checkCanFillNumbers();
}
}
// logSudoku();
printSudoku();main문에서 채우는 작업과 모순을 확인하는 작업을 총 81회씩 수행한다.
이는 그냥 총 스도쿠 칸 수인 9*9 인 81을 의미하는데,
회마다 1개씩 채워 81개라면 스도쿠가 아예 비었다는 것을 의미하기에 엄밀히 말하자면 최악은 81회가 아니다.
반복문의 횟수를 지정하지 않고 반복문 돌 때마다
숫자를 하나도 채우지 않았다면 반복을 중단한다.
그러면 필요한 만큼만 반복할 수 있다.
근데 그랬더니 오히려 시간이 더 많이 소요되었다.
테스트케이스의 문제거나, 스도쿠의 크기가 9*9 밖에 되지 않아서일 것 같다.
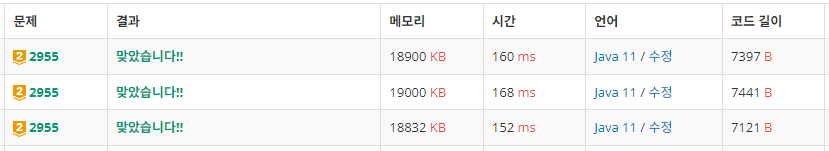
160ms : 채웠는가? boolean 사용
168ms : 채운 칸 수 int 사용
152ms : 무지성 81회