[JavaScript] 반복문, 조건문 이해하기
🐾 동등 비교 및 동일성 총정리
🔎 Comparison
📌 == Operator
equal to
📌 === Operator
equal value and equal type
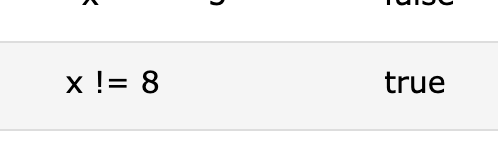
📌 != Operator
not equal
📌 !== Operator
not equal value or not equal type
📌 > Operator
greater than
📌 < Operator
less than
📌 >= Operator
greater than or equal to
📌 <= Operator
less than or equal to
🔎 Logical Operators
📌 && / AND
The && operator returns true if both expressions are true, otherwise it returns false.
- 둘다성립되어야 true
let x = 6;
let y = 3;
(x < 10 && y > 1) is true📌 || / OR
The || returns true if one or both expressions are true, otherwise it returns false.
- 둘중에 하나라도 성립되면 true
- 둘다 성립되지 않으면 false
let x = 6;
let y = 3;
(x == 5 || y == 5) is false
📌 ! / NOT
The NOT operator (!) returns true for false statements and false for true statements.
!(x == y) is true
//x와 y는 같이않다. =>true🐾 조건문 총정리
🔎 if, else, and else if, switch
🔎 if Statement
📌 Use if to specify a block of code to be executed, if a specified condition is true
syntax
if (condition) { // block of code to be executed if the condition is true }
🐾 Make a "Good day" greeting if the hour is less than 18:00:
if (hour < 18) { greeting = "Good day"; }
🔎 The else Statement
📌 Use else to specify a block of code to be executed, if the same condition is false
Use the else statement to specify a block of code to be executed if the condition is false.
syntaxif (condition) { // block of code to be executed if the condition is true } else { // block of code to be executed if the condition is false }
🐾 If the hour is less than 18, create a "Good day" greeting, otherwise "Good evening":
if (hour < 18) { greeting = "Good day"; } else { greeting = "Good evening"; }
🔎 The else if Statement
📌 Use else if to specify a new condition to test, if the first condition is false
Use the else if statement to specify a new condition if the first condition is false.
Syntax
if (condition1) { // block of code to be executed if condition1 is true } else if (condition2) { // block of code to be executed if the condition1 is false and condition2 is true } else { // block of code to be executed if the condition1 is false and condition2 is false }
🐾 If time is less than 10:00, create a "Good morning" greeting, if not, but time is less than 20:00, create a "Good day" greeting, otherwise a "Good evening":
if (time < 10) { greeting = "Good morning"; } else if (time < 20) { greeting = "Good day"; } else { greeting = "Good evening"; }
🔎조건(삼항)연산자
condition? exprIfTrue : exprIfFalse
🔎 switch
📌 Use switch to specify many alternative blocks of code to be executed
The switch statement is used to perform different actions based on different conditions.
Syntax
switch(expression) { case x: // code block break; case y: // code block break; default: // code block }
The getDay() method returns the weekday as a number between 0 and 6.
(Sunday=0, Monday=1, Tuesday=2 ..)
This example uses the weekday number to calculate the weekday name:switch (new Date().getDay()) { case 0: day = "Sunday"; break; case 1: day = "Monday"; break; case 2: day = "Tuesday"; break; case 3: day = "Wednesday"; break; case 4: day = "Thursday"; break; case 5: day = "Friday"; break; case 6: day = "Saturday"; }
let a = 2;
switch(a) {
case 1:
console.log('a는 1입니다.');
break;
case 2:
console.log('a는 2입니다.'); // a는 2입니다.
break;
default:
console.log('a는 1도 2도 아닙니다.');
}🐾 JS 반복문 총정리
🔎 For Loop
Instead of writing:
text += cars[0] + "<br>";
text += cars[1] + "<br>";
text += cars[2] + "<br>";
text += cars[3] + "<br>";
text += cars[4] + "<br>";
text += cars[5] + "<br>";You can write:
for (let i = 0; i < cars.length; i++) {
text += cars[i] + "<br>";
}
//BMW
//Volvo
//Saab
//Ford
//Fiat
//Audisyntax
초기값 조건식 증감식 for ([initialization]; [condition]; [final-expression]) statement
Expression 1 sets a variable before the loop starts (let i = 0).
- loop이 시작하기전에 첫번째로 체크
Expression 2 defines the condition for the loop to run (i must be less than 5).
- condition 체크, 충족한지
Expression 3 increases a value (i++) each time the code block in the loop has been executed.
- loop이 실행된다음에 값이 올라감 (either puls or minus depends )
- 다음번 condition 평가 이전에 발생
📌 for in Loop 객체, 배열 가능
🔎 For In Loop (obj사용)
for in을 객체로 돌렸을떄.
The JavaScript for in statement loops through the properties of an Object:
📌 for in문은 object 에 사용할 수 있는 반복문, 배열에도 사용할 수 있지만 배열 반복에는 추천되지 않는다.
Syntax
for (key in object) { // code block to be executed }
// 객체일때 **** => key 값 (프로퍼티명)
for (let key in obj) {
console.log(key) // name, age
console.log(obj[key]) // 이름, 나이
}
const person = {fname:"John", lname:"Doe", age:25};
let text = "";
for (let x in person) {
text += x; // fname lnam eage
text += person[x];// John Doe 25
}const obj = {
name : '이름',
age : '나이'
}
for(const key in obj){
console.log(`key 값 : ${key}`); // 1. key값 : name // 2. key값 :age
console.log(`value 값 : ${obj[key]}`); // 1. value 값 : 이름 // 2. value값 : 나이
}obj.name과 같이 사용하려면 object내에 name이라는
key값을 가진 value가 존재해야한다.
없는 key값을 사용하게 되면undefined가 출력
const person = {fname:"John", lname:"Doe", age:25};
let text = "";
for (let x in person) {
//x=fname,lname,age
text += person[x];
//John Doe 25
}🔎 For In Loop (Arrays사용)
for in을 배열로 돌렸을떄.
The JavaScript for in statement can also loop over the properties of an Array:
(키값하고 value값 모두 가능)
// 배열일때
for (let index in numbers) {
console.log(index) // 0, 1, 2, 3, 4
console.log(numbers[index]) // 45, 4, 9, 16, 25
}
// const numbers = {
// 0: 45,
// 1: 4,
// 2: 9,
// …
// }The for in statement can loops over array values:
(values값만 받을떄.)
const numbers = [45, 4, 9, 16, 25];
let txt = "";
for (let x in numbers) {
txt += numbers[x];
}
//45
//4
//9
//16
//25📌 Do not use for in over an Array if the index order is important.
📌 for of Loop 배열, 문자열 가능 ( 객체일때 => 불가능)
🔎 The For Of Loop
for of문은 반복 가능한 객체(Array,Map,Set,String,TypedArray,arguments 객체등 포함)에 대해 사용할 수 있다. 보통은 Array(배열)에 사용.
Syntax
for (variable of iterable) { // code block to be executed }
📌 Looping over an Array (배열)
// 배열일때 ****
for (let value of numbers) {
console.log(value) // 45, 4, 9, 16, 25
}📌 Looping over a String (문자열)
let language = "JavaScript";
let text = "";
for (let x of language) {
text += x;
}🔎 forEach()
배열에 사용되는 메서드. 인자에 콜백함수를 넣어 사용
Note that the function takes 3 arguments:
The itemvalue
The itemindex(생략가능)
The arrayitself(생략가능)
const numbers = [45, 4, 9, 16, 25];
numbers.forEach((value, index) => {
console.log(value, index) // [45, 0], [4, 1], [9, 2], [16, 3], [25, 4]
})
numbers.forEach((value) => {
console.log(value) // 45, 4, 9, 16, 25
})
🔎 While Loop
Syntax
while (condition) { // code block to be executed }
condition(조건)이 truthy 이면 반복문 본문의 코드가 실행됩니다.
아래 반복문은 조건 i < 3을 만족할 동안 i를 출력해줍니다.
let i = 3;
while (i < 3) {
console.log( i );// 출력값없음
i++;
}
🔎 Do While Loop
Syntax
do { // code block to be executed } while (condition);
let i = 3;
do {
console.log( i );//출력값: 3
i++;
} while (i < 3);3을출력하고, while문으로
do..while 문법은 조건이truthy인지 아닌지에 상관없이, 본문을 최소한 한 번이라도 실행하고 싶을 때만 사용해야 합니다. 대다수의 상황에선 do..while보다 while(…) {…}이 적합합니다.