array - 배열(Array)에 대해 알아보자
🐾 배열 array 총정리
🔎 array[]
// Create an Array
const cars = ["Saab", "Volvo", "BMW"];Create an empty array and add values:
// Create an Array
const cars = [];
// Add Values to the Set
cars.push("Saab");
cars.push("Volvo");
cars.push("BMW");
//Saab,Volvo,BMW🔎 at()
📌 배열에서 3번째요소를 가지려면 2가지방법이 있다.
- Get the third element of fruits:
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"]; let fruit = fruits.at(2);정답은 apple
- Get the third element of fruits:
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"]; let fruit = fruits[2];
📌 첫번째요소 찾기
An empty index like at() defaults to at(0).
Get the first element of fruits:
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
let fruit = fruits.at();📌 마지막요소 찾기
An index of -1 returns the last element from the array.
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
let fruit = fruits.at(-1);🔎 concat()
The concat() method concatenates (joins) two or more arrays:
Join two arrays:
const arr1 = ["Cecilie", "Lone"];
const arr2 = ["Emil", "Tobias", "Linus"];
const children = arr1.concat(arr2);
console.log(children)
//Cecilie,Lone,Emil,Tobias,Linusyou can even join three or more:
const arr1 = ["Cecilie", "Lone"];
const arr2 = ["Emil", "Tobias", "Linus"];
const arr3 = ["Robin"];
const children = arr1.concat(arr2, arr3);
console.log(children)
//Cecilie,Lone,Emil,Tobias,Linus📝The concat() method does not change the existing arrays.
📝The concat() method returns a new array, containing the joined arrays.
🔎 copyWithin()
📝copyWithin() copies array elements to another position in an array, overwriting existing values:
덮어씌우기
📝Copy to index 2, all elements from index 0:
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
fruits.copyWithin(2, 0);
console.log(fruits)
//Banana,Orange,Banana,Orange
//복사해서 넣을위치는 인덱스 번호 2.
//그래서 인덱스 번호 2인 apple 자리로 🔎📝 The copyWithin() method is not supported in Internet Explorer.
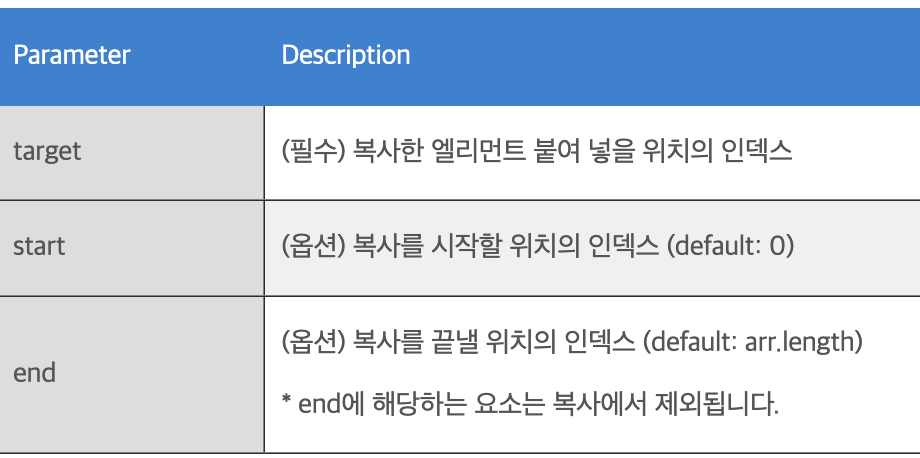
Syntax
array.copyWithin(target, start, end)
https://paperblock.tistory.com/75
🔎 entries()
The entries() method returns an iterator with the key/value pairs from an array:
// Create an Array
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
// Create an Iterator
const list = fruits.entries();
// List the Entries
let text = "";
for (let x of list) {
text += x;
}0,Banana
1,Orange
2,Apple
3,Mango📝 The entries() method is not supported in Internet Explorer.
🔎 every()
The every() method returns true if every element in an array pass a function test.
// Create an Array
const ages = [32, 33, 16, 40];
// Create a Test Function
function checkAge(age) {
return age > 18;
}
// Are all ages over 18?
ages.every(checkAge);
//Is every element over 18? -> false📝 The every() method returns true if the function returns true for all elements.
📝 The every() method returns false if the function returns false for one element.
🔎 fill()
Fill all the elements with a value:
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"]; fruits.fill("Kiwi");Fill all array elements with "Kiwi":
Kiwi,Kiwi,Kiwi,Kiwi
Fill the last two elements:
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"]; fruits.fill("Kiwi", 2, 4);Fill the last two array elements with "Kiwi":
Banana,Orange,Kiwi,Kiwi
Syntax
array.fill(value, start, end)
🔎 filter()
Return an array of all values in ages[] that are 18 or over.
요소중에서 true만 필터링해서 필터링된 배열로 반환:
const ages = [32, 33, 16, 40];
const result = ages.filter(checkAdult);
function checkAdult(age) {
return age >= 18;
}
//32,33,40📝The filter() method creates a new array filled with elements that pass a test provided by a function.
📝The filter() method does not execute the function for empty elements.
📝The filter() method does not change the original array.
Syntax
array.filter(function(currentValue, index, arr), thisValue)
🔎 find()
Find the value of the first element with a value over 18:
18보다큰 첫번째요소 찾기.
const ages = [3, 10, 18, 20];
function checkAge(age) {
return age > 18;
}
function myFunction() {
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = ages.find(checkAge);
}result: 20
📝The find() method returns undefined if no elements are found.
📝The find() method is not supported in Internet Explorer.
🔎 findIndex()
Find the first element with a value over 18:
18보다큰 첫번째요소의 index 번호 찾기.
const ages = [3, 10, 18, 20];
ages.findIndex(checkAge);
function checkAge(age) {
return age > 18;
}result: 18보다큰수는 20. 20의 index 번호는: 3.
📝The findIndex() method returns the index (position) of the first element that passes a test.
📝The findIndex() method returns -1 if no match is found.
📝findIndex() is not supported in Internet Explorer.
🔎 findLast()
Find the value of the last element with a value over 18:
18보다큰 마지막요소 찾기.
const ages = [3, 10, 18, 20];
function checkAge(age) {
return age > 18;
}
function myFunction() {
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = ages.findLast(checkAge);
}result: 20
📝The findLast() method returns undefined if no elements are found.
🔎 findLastIndex()
Find the last element with a value over 18:
const ages = [3, 10, 18, 20];
ages.findLastIndex(checkAge);
function checkAge(age) {
return age > 18;
}result: 3
📝The findLastIndex() method returns -1 if no match is found.
📝findLastIndex() is not supported in Internet Explorer.
🔎 flat()
Create a new array with the sub-array elements concatenated:
flat() 메서드는 복사 메서드입니다.
const myArr = [[1,2],[3,4],[5,6]];
const newArr = myArr.flat();result:1,2,3,4,5,6
const myArr = [1, 2, [3, [4, 5, 6], 7], 8];
const newArr = myArr.flat(2);result:1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8
🔎 flatMap()
const myArr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6];
const newArr = myArr.flatMap((x) => x * 2);result: 2,4,6,8,10,12
🔎 forEach()
Calls a function for each element in fruits:
const fruits = ["apple", "orange", "cherry"];
fruits.forEach(myFunction);result:
0: apple
1: orange
2: cherry
let sum = 0;
const numbers = [65, 44, 12, 4];
numbers.forEach(myFunction);
function myFunction(item) {
sum += item;
}result: 125
🔎 from()
Create an array from a string:
Array.from("ABCDEFG")result: A,B,C,D,E,F,G
console.log(Array.from('foo'));
// Expected output: Array ["f", "o", "o"]
console.log(Array.from([1, 2, 3], (x) => x + x));
// Expected output: Array [2, 4, 6]🔎 includes()
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
fruits.includes("Mango");result: true
📝The includes() method returns true if an array contains a specified value.
📝The includes() method returns false if the value is not found.
Start the search at position 3:
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
fruits.includes("Banana", 3);result: false
banana는 0 에있기떄문에,
🔎 indexOf()
📌 Find the first index of "Apple":
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
let index = fruits.indexOf("Apple");result: 2
📌 Start at index 3:
index3으로부터 시작해서 apple찾기.
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango", "Apple"];
let index = fruits.indexOf("Apple", 3);
//Search for "Apple", starting at position 3:result: 4
Syntax
indexOf(searchElement, fromIndex)
- fromIndex: Where to start the search.
Default value is 0.
📌 Find the first index of "Apple", starting from the last element:
- 찾을수없는 값은 -1나옴
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango", "Apple"];
let index = fruits.indexOf("Apple", -1);Search for "Apple", starting at the end:
-1은 맨 마지막 apple
result:4
🔎 isArray()
Check if an object is an array:
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"]; let result = Array.isArray(fruits);result:true
Array.isArray() returns true if a datatype is an arry, otherwise false:
let text = "W3Schools"; let result = Array.isArray(text);result:false
🔎 join()
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"]; let text = fruits.join();result:Banana,Orange,Apple,Mango
Another separator:
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"]; let text = fruits.join(" and ");result:Banana and Orange and Apple and Mango
🔎 keys()
Create an Array Iterator object, containing the keys of the array:
// Create an Array
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
// Create an Iterable
const list = fruits.keys();
// List the Keys
let text = "";
for (let x of list) {
text += x + "<br>";
}result:
0
1
2
3
🔎 lastIndexOf()
Find the last index of "Apple":
마지막에있는 apple찾기.const fruits = ["Apple", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"]; let index = fruits.lastIndexOf("Apple");result:2
More than one apple:
const fruits = ["Orange", "Apple", "Mango", "Apple", "Banana", "Apple"]; let index = fruits.lastIndexOf("Apple");result:5
Start the search at position 4:??????
const fruits = ["Orange", "Apple", "Mango", "Apple", "Banana", "Apple"]; let index = fruits.lastIndexOf("Apple", 4);result:3
Syntax
array.lastIndexOf(item, start)
- start: Optional.
Where to start the search.
Default is the last element (array.length-1).
🔎 length
The length property sets or returns the number of elements in an array.
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"]; let length = fruits.length;result:4
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"]; fruits.length = 2;result: Banana,Orange
🔎 map()
📌 Return a new array with the square root of all element values:
const numbers = [4, 9, 16, 25]; const newArr = numbers.map(Math.sqrt)result:2,3,4,5
📌 Multiply all the values in an array with 10:
const numbers = [65, 44, 12, 4]; const newArr = numbers.map(myFunction) function myFunction(num) { return num * 10; }result:650,440,120,40
📌Get the full name for each person:
const persons = [ {firstname : "Malcom", lastname: "Reynolds"}, {firstname : "Kaylee", lastname: "Frye"}, {firstname : "Jayne", lastname: "Cobb"} ]; persons.map(getFullName); function getFullName(item) { return [item.firstname,item.lastname].join(" "); }result:Malcom Reynolds,Kaylee Frye,Jayne Cobb
🔎 of()
Create a new array from a number of arguments:
let fruits = Array.of("Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"); document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = fruits;result:Banana,Orange,Apple,Mango
🔎 pop()
Remove (pop) the last element:
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"]; fruits.pop();result:Banana,Orange,Apple
pop() returns the element it removed:
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"]; fruits.pop();result:Mango
📝The pop() method removes (pops) the last element of an array.
🔎 prototype
Create a method that transforms array values into upper case:
Array.prototype.myUcase = function() { for (let i = 0; i < this.length; i++) { this[i] = this[i].toUpperCase(); } };Use the method on any array:
var fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"]; fruits.myUcase();result:BANANA,ORANGE,APPLE,MANGO
🔎 push()
Add a new item to an array:
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"]; fruits.push("Kiwi"); //Banana,Orange,Apple,Mango,Kiwi
Add two new items to the array:
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"]; fruits.push("Kiwi", "Lemon"); //Banana,Orange,Apple,Mango,Kiwi,Lemon
📝The push() method adds new items to the end of an array.
🔎 reduce()
Subtract all numbers in an array:
Subtract the numbers in the array, starting from the left:
const numbers = [175, 50, 25];
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = numbers.reduce(myFunc);
function myFunc(total, num) {
return total - num;
}
//100🔎 reduceRight()
Subtract the numbers in the array, starting from the end:
Subtract the numbers in the array, starting from the right:
const numbers = [175, 50, 25];
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = numbers.reduceRight(myFunc);
function myFunc(total, num) {
return total - num;
}
//-200🔎 reverse()
The reverse() method reverses the order of the elements in an array.
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
fruits.reverse();
//Mango,Apple,Orange,Banana🔎 shift()
Shift (remove) the first element of the array:
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
fruits.shift();
//Orange,Apple,MangoThe shift() method returns the shifted element:
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
fruits.shift();
//Banana📝The shift() method removes the first item of an array.
🔎 slice()
Select elements:
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Lemon", "Apple", "Mango"];
const citrus = fruits.slice(1, 3);
//Orange,LemonSelect elements using negative values
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Lemon", "Apple", "Mango"];
const myBest = fruits.slice(-3, -1);
//Lemon,Apple
//-3은 뒤에서 세번째. 그래서 lemon부터 start, Syntax
array.slice(start, end)
🔎 some()
Check if any values are over 18:
한개라도 충족되면 true 아니면 false
const ages = [3, 10, 18, 20];
ages.some(checkAdult);
function checkAdult(age) {
return age > 18;
}
//true🔎 sort()
The sort() method sorts the elements as strings in alphabetical and ascending order.
// Create an Array
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
// Sort the Array
fruits.sort();
//Apple,Banana,Mango,Orange// Create an Array
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
// Sort the Array
fruits.sort();
// Reverse the array
fruits.reverse();
//Orange,Mango,Banana,Apple🔎 splice()
기존 요소를 삭제 또는 교체하거나 새 요소를 추가
// Create an Array
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
// At position 2, add "Lemon" and "Kiwi":
fruits.splice(2, 0, "Lemon", "Kiwi");
//Banana,Orange,Lemon,Kiwi,Apple,Mango// Create an Array
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
// At position 2, remove 2 items
fruits.splice(2, 2);
//Banana,Orange// Create an Array
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
// At position 2, remove 1 item, add "Lemon" and "Kiwi"
fruits.splice(2, 1, "Lemon", "Kiwi");
//Banana,Orange,Lemon,Kiwi,Mango🔎 toReversed()
// Create an Array
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
// Reverse the Array
const fruits2 = fruits.toReversed();
//Mango,Apple,Orange,Banana🔎 toSorted()
The toSorted() method sorts the elements of an array in alphabetical order.
The toSorted() method is the copying version of the sort() method.
// Create an Array
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
// Sort the Array
fruits.sort();
//Apple,Banana,Mango,Orange🔎 toSpliced()
The toSpliced() method does not change the original array.
The toSpliced() method is the copying version of the splice() method.
// Create an Array
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
// At position 2, add "Lemon" and "Kiwi":
const fruits2 = fruits.toSpliced(2, 0, "Lemon", "Kiwi");
//Banana,Orange,Lemon,Kiwi,Apple,Mango🔎 toString()
Convert an array to a string:
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
let text = fruits.toString();
//Banana,Orange,Apple,Mango🔎 unshift()
Add new elements to an array:
The unshift() method adds new elements to the beginning of an array.
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
fruits.unshift("Lemon","Pineapple");
//Lemon,Pineapple,Banana,Orange,Apple,Mango🔎 values()
The values() method returns an Iterator object with the values of an array.
// Create an Array
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
// Create an Iterator
const list = fruits.values();
// List the Values
let text = "";
for (let x of list) {
text += x + "<br>";
}
//Banana
//Orange
//Apple
//Mango🔎 valueOf()
valueOf() returns the array itself:
The valueOf() method returns the array itself.
Get the value of fruits:
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
const myArray = fruits.valueOf();
//Banana,Orange,Apple,Mangofruits.valueOf() returns the same as fruits:
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
const myArray = fruits;
//Banana,Orange,Apple,Mango🔎 with()
Syntax
array.with(index, value)
const months = ["Januar", "Februar", "Mar", "April"];
const myMonths = months.with(2, "March");
//Januar,Februar,March,April