LSSL : Abstract
- Linear State Space Layer : mapps a sequence by simulating a linear cont-time state space representation
- Theroetic : LSSL = RNN, NDE, Temp. convolution과 모두 관련이 있음
- generalize A matrix for cont. time memorization
Intro
- RNN = natural stateful model : constant computation and storage per t. but slow train + opt. difficulties (Vanishing gradient)
- CNN = local context, parallelizable train b. not sequential → expensive inference, context lenght limitation
- NDE = matehmatical, theroetically addressable, but inefficient
⇒ combinational benefits of parallelizable training, stateful inference, time scale adaptation!
- 이러한 장점들을 모두 가지기 위한 여러 모델들이 등장했으나 여전히 reduced expressivity problem 존재 → 보다 expressive한 모델을 만들자

- Linear State Space Layer : maps 1 dimensional function or sequence through an implicit state
- A : controls evolution of the system
- B, C, D : projection parameters
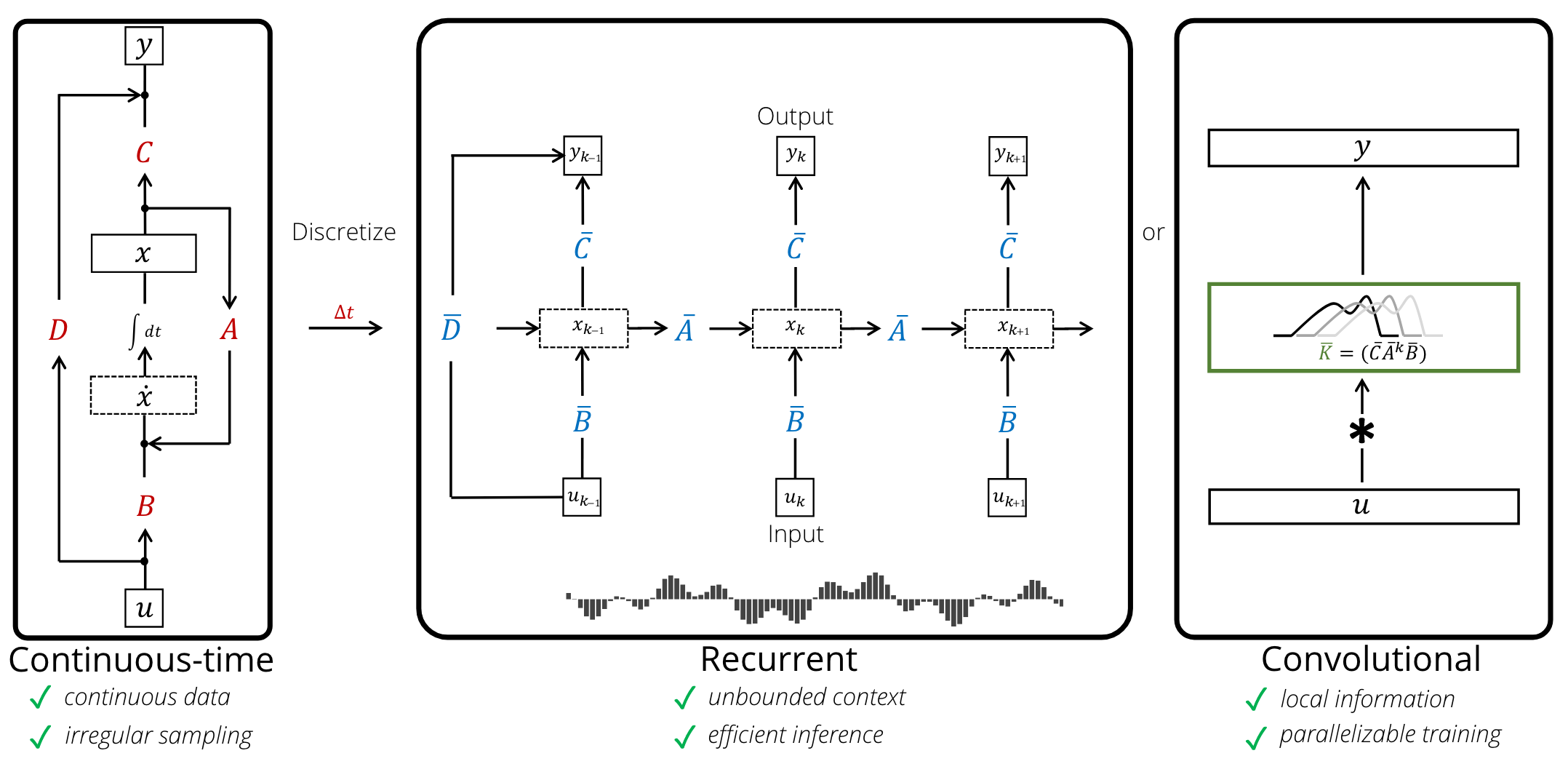
- LSSL = instantiation of each family
- recurrent : discrete step size specified → discretized into a linear recurrence
- convolutional : continuous convolution수식이라고 볼 수 있으며 discretize될 경우엔 병렬 계산도 가능함
- cont-time : differential equation → continuous 하게 작업이 가능함
- 또한 express-able : generalize CNN and RNN
- control theory - 1-D conv.kernels can be approximated by an LSSL
- RNN = ODE (gate mechanism) related and derived from ODE approx → LSSL = special case
- generality = tradeoff
- limitation of RNN and CNN is inherited
- state matix A and time scale is very critical and computationally infeasible
- 어떤 행렬을 골라야하는지를 골라둘 것임
Technical Background
- Approximation of diff. eq
- finds a sequence of functions x0(t), x1(t), . . . that approximate the solution x(t) of the integral equation.
- Discretization
- generalized bilinear transform for linear ODE

- alpha = 0 : Euler, 1 : backward-Euler, 1/2 : bilinear (stability preserving)
- generalized bilinear transform for linear ODE
- as Time scale
- 대부분의 경우 length of dependencies 에 반비례함 → timescale이라고 볼 수 있음 = ODE-RNN들의 기조
- Cont-time memory
- HIPPO 참조 : exponential -growing continuous time memory
LSSL : Linear State-Space Layers
- As a recurrence : t-1 시점의 x가 앞선 정보를 모두 가지고 있다고 생각하면 recurrent한 모델으로 정의가 가능함. y는 최종 결과물임. 고정된 computation과 storage로 계산이 가능함
- As a convolution : initial state - 0 이라고 하면 앞선 수식을 커널 연산으로 정의할 수 있음

- 최종적으로는 푸리에 연산으로 한번에 계산이 가능함
- 병목현상 = 행렬벡터 계산과 krylov function으로 해결할 수 있음 (캐싱해두고 가져와서 쓸 수 있음 )
- 물론 이걸 구하는거 자체가 문제가 될 수 있음..
Expressivity of LSSLs
- Convolutions are LSSLs
- output y = convolution of input u (h = impulse response)
- arbitrary convolutional filter h = approximated by a rational function and represented by an LSSL
- Hippo matrix를 가진 경우에는 고정된 dt에 대해서 윈도우 사이즈만큼에서의 특징을 뽑아내는 것임
- RNNs are LSSLs

-
gating mechanism of RNN = smooth optimization = analog of a step size!

-
each layer = Picard iteration → can be approximated by ODE
-
Deep LSSL
- seq2seq of parameters with size N
- hidden dim H에 대해서 각 parameter broadcast(independent)
Combining LSSLs with Continuous-time Memorization
Incorporating Long Dependencies into LSSLs
- Hippo = how to memorize a function in continuous time w.r.t a measure
- Optimal memorization operator hippo(w) has form x(t) = A(x(t) + Bu(t), A = low recurrence=width state matrix
Theoretically Efficient Algorithms for the LSSL

