[논문리뷰] MAMBA360: Survey of State Space Models as Transformer Alternative for Long Sequence Modelling: Methods, Applications, and Challenges
SSM
목록 보기
4/8
Abstract
- 다양한 task에서 중요한 영역인 sequence modelling을 해결하고자 RNN, LSTM부터 현재의 Transformer까지 많은 발전이 있었다.
- 그러나, transformer는 의 계산 복잡도를 가지며, inductive bias를 반영하지 못한다는 단점을 가진다.
- 이를 해결하고자 여러 새로운 구조가 제안되었으나, 여전히 long sequence에서는 제대로 역할을 수행하지 못하였다.
- SSM은 이런 상황에서 새롭게 등장하였으며 S4와 그 변형들이 주된 모델들이다.
- 해당 논문에서는 이러한 SSM의 다양한 적용과 performance를 보여줄 것이다.
Introduction
- SSM은 고정된 길이를 가진 RNN이라고 볼 수 있다.
- 따라서 inference speed와 computation/memory complexity 부분에서 트랜스포머에 비해 압도적인 이점을 가진다.
- 그러나, 아직 트랜스포머에 비해 특정 영역에서는 부족한 퍼포먼스를 보인다. (특히 비전)
- 이러한 단점들은 특정 sequence processing task에서의 결점에 기인한다.
- copying long input sequence, in-context learning, induction heads(reproducing input pattern)
- 이 서베이 논문에서는 특정 SSM들의 장단점을 SOTA 트랜스포머 모델들과 비교한다. 어떤 task에서 SSM이 더 나은 성능을 보이고, 어떤 부분에서 트랜스포머가 나은지를 차차 살펴본다.
- Contents
- understanding of State Space Models
- Categorization and Recent Advances of SSMs
- Application of SSMs across Domains
- Performance Comparison of SSMs with Transformers
Basics of State Space Models(skip. 다른 글 참고)
- SSM은 보다 고차원의 미분값을 모델링할 수 있어 dynamic system 모델링에 적합하다.
- 예를들어, damped-mass-spring system 의 예시를 보자.
- 이러한 high-order derivative 들로 구성된 식을 다시 저차원 미분값과 벡터로 표현하면, state vector x를 만들 . 수있다.
- 그리고 이러한 x로의 전환 결과를 적용하면, position y(t)를 상태에 대한 선형함수로 정의할 수 있다.
- 즉, 어떠한 상태에 대한 변화를 알 수 있는 행렬을 구하면 그 다음의 위치정보를 알 수 있다는 것이다.
Spring-Mass-Damper system
- math formulation
- m : mass connected to a wall via a spring
- k: spring constant
- c: damping coefficient
- goal : describe the system’s behavior using stae variables
- x: displacement of the mass
- : velocity
- F: external force applied to the mass
- State Variables
- x1 : displacement of the mass from its equilibrium position
- \dot{x1} : velocity of x1
- System Dynamics : Newton’s second law of motion
- State Space Formulation
- SSM은 1차 미분방정식을 통해서 다양한 dynamic system을 모델링할 . 수있음. 특히 LTI한 특성을 가지는 시스템 모델링에 효과적임
- Interpretation
- State vector x : mass’s position과 속도에 대한 정보를 가짐
- input vector u : mass에 가해지는 외부의 힘을 표현
- y : displacement of x1
- Stability and Control
- Stability :행렬 A의 고유값을 점검
- Control: adjusting the control input u to achieve desired behavior
State Space Models
- Definition
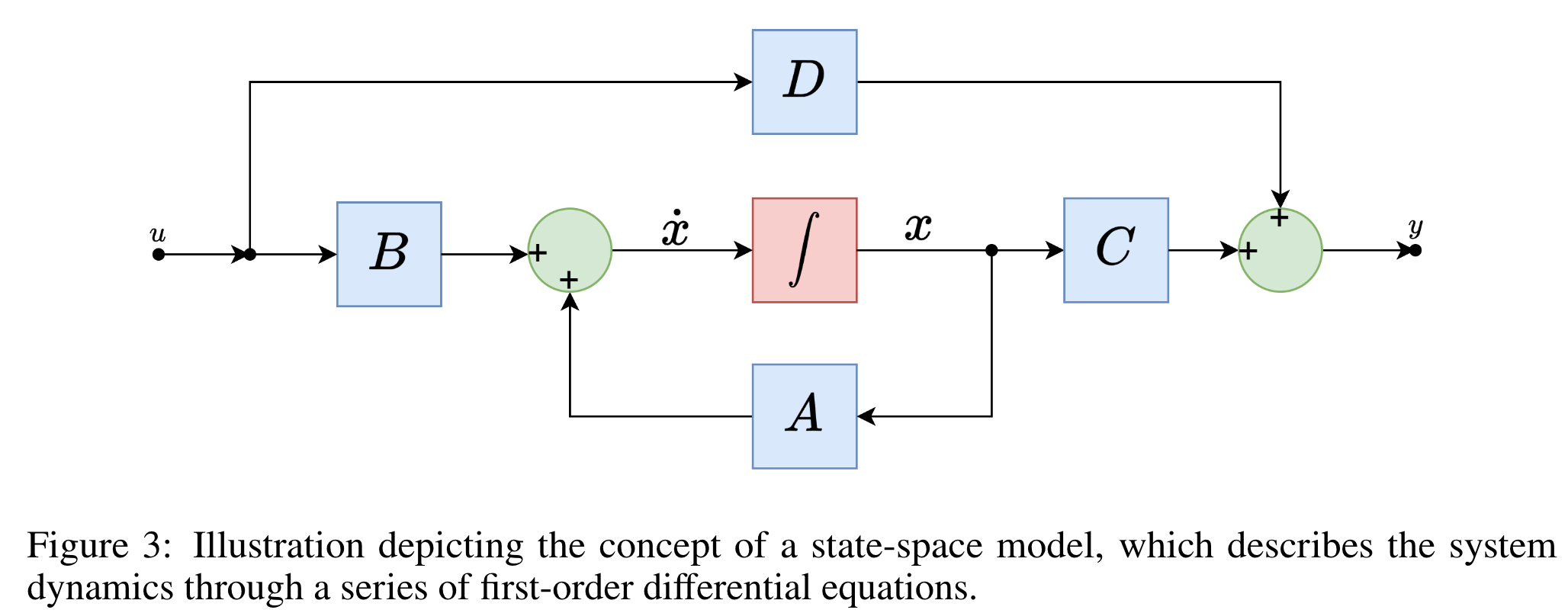
- 시간에 따라 변화하는 시스템의 상태 + 관측치와의 관계
- 상태방정식 :
- 관측방정식 :
- 가우시안 분포를 따른다고 가정하고 kalman filtering/ + smoothing 을 사용해 상태를 추정, 예측
- 1차 미분방정식 형태의 꼴로 state, input, output 세트를 나타낸다
- 시간에 따라 상태가 변하는 다중 입출력 시스템을 모델링한다
- 시간에 따라 상태가 변하는 다중 입출력 시스템을 모델링한다
- 앞선 논문들은 대부분 continuous time invariant 모델로 모델링함으로서 시퀀스 길이가 변하더라도 값이 변하지 않고 일정하게 계산할 수 있는 특징을 가지고 모델링한다.
- 이를 이산화하여 discrete 값으로 변환, 예측에 활용할 수 있다
용어 정리
- 상태 (State) : 어떤 시점(에서의 변수를 알고 일정 시간이 지난 어느 시점(에서의 입력을 알면, 입력이 주어진 시점에서 시스템의 거동을 완전히 결정할 수 있을 때, 이러한 상태 변수들의 최소집합
- 즉 어떤 시점에서의 변화 양상을 결정할 수 있을 때 그때의 상태변수들
- 상태변수 (State variable) : 동적시스템의 상태를 결정할 수 있는 최소 개수의 변수들
- 상태벡터 (State Vector) : 주어진 시스템의 상태를 표현하기 위해 n개의 변수 필요 → 벡터 x의 nth 성분
- 상태공간 (State Space) : x1~ xn으로 구성된 n 차원의 공간
결론적으로 역학 시스템을 미분 방정식으로 표현하는 과정이라고 볼 수 있다. 최종적으로는 이를 NN에 적용하여 모델 아키텍쳐로 이용한다.
- 어떠한 basis로 표현할지를 잘 결정하는 것이 중요! ex. 속도와 가속도, 혹은 높이와 위치, 운동에너지
Recent Advances in State Space Models
- Transformer’s limitation
- Computational Complexity
- Large Memory Requirement
- Fixed Sequence Length
- Attention Mechanism Scalability
- Lack of Causality in Standard attention
- Categories of SSM
- Structured SSMs : principled way to handle long-range dependencies
- S4 and variants (S4, HiPPo, H3, HyenaHierarchy, Liquid-S4, S4nd, DSS)
- Global convolution and variants ( LongConv, FFTFlashConv, SG-Conv)
- foundational model (LD-Stack, S5)
- Recurrent SSMs : based on RNNs
- RWKV, LRU, HGRN
- Gated SSMs: gating techniques to enhance perforamnce on long sequences
- GSS, Mega, TNN
- Miscellaneous SSMs: combining different categories for efficient sequence modeling
- MambaFormer, Mamba-Byte, Mamba-MoE
- Structured SSMs : principled way to handle long-range dependencies
Structured State Space Models
- polynomial projection operators, multi-input multi-output systems, convolutional kernels
- S4 (Structured State Space Sequence)
- Higher-Order Polynomial Project Operator (HiPPO) : signal history를 효과적으로 저장하여 long-term dependency를 잘 포착할 수 있도록 함
- Diagonal Plus Low-Rnak parameterization : SSM matrix(A) with low-rank correction → 안정화하여서 안정성과 대각화가능성을 보장하고자함
- Efficient Kernel computation : 효과적인 커널 컴퓨팅을 가능케함 : FFT와 iFFT를 이용하여 complexity를 O(NlogN)으로 줄임
- 결과 : LRA의 path-X를 처음으로 푼 SSM, CIFAR-10에서도 좋은 결과
- HiPPo (High-Order Polynomial Projection Operators)
- S4에 사용된 long range history를 기억하기 위한 행렬
- Legendre polynomial로 행렬을 왜 그렇게 만들었는지를 설명하고 S4보다 좋은 성능을 보이는 것들도 있음
- Hungry Hungry HiPPo
- 2가지 기존 SSM들이 고전하던 task를 해결하고자함
- recalling earlier tokens
- comparing the tokens across different sequence
- Solutions
- Stacked SSMs with Multiplicative Interactions : memory retention & cross sequence comparisions
- FlashConv for Training Efficiency: 8K까지 빠르게 계산가능함
- State-Passing algorithm for scaling : 8K 보다 더 긴 시퀀스에 대해서도 계산가능하도록함. SRAM에 들어갈 수 있는 최대길이로 시퀀스를 자름
- 트랜스포머보다 perplexity 측면에서는 부족한 결과를 보였으나 0-shot, few-shot (SuperGLUE)에서는 좋은 결과를 보였으며 LRA에서는 2배가량 빠른 계산속도를 보여줬다.
- 2가지 기존 SSM들이 고전하던 task를 해결하고자함
- Global Convolution
- LongConv authors : SSM은 hidden state matrix를 계속 곱해서 input sequence만큼 긴 커널을 만든다. 따라서 instability 와 hand-crafted initializations and hyperparmeter tuning을 필요로한다.
- 해결책 : parameterizing long kernel
- 기존 long conv 해결책은 그냥 FFT를 적용했는데 이는 시스템에 따라 quadratic time complexity를 가질 . 수있다.
- → regularization and IO aware algorithm : Flashbutterfly
- 결과
- WikiText 103에서 30% 적은 파라미터로 perplexity를 0.2 줄임
- LRA에서 7.2배 빠른 속도를 보임
- FlashFFTConv : matrix decomposition → FFT w. matrix multiplication
- kernel fusion by reducing IO
- Hyena Hierarchy (HH)
- perplexity gap을 줄이자!
-
perplexity : 언어 모델이 성능 평가를 위한 테스트 데이터셋에서 이전 단어들을 기반으로 다음 단어를 예측할 때마다 평균적으로 개의 단어 후보 중 정답을 찾는다는 의미. 즉, 모델이 언어를 헷갈리는 정도. 낮을수록 좋다.
-
- 기존 방법들은 subquadratic layer를 low rank 방법론을 통해 해결하고자 했으나 그만큼 dense later들을 필요로 했다.
- 이를 해결하고자 sub-quadratic attention alternativefmf wpdks
- attention to implicitly parametrized long ocnvolutions and data gating
- Flash Attention보다 100배 빠름, 6K-100K sequence length에 대해서
- 효과적으로 Long sequence handling이 가능한 것을 보임
- perplexity gap을 줄이자!
- RWKV
- RNN + KWV(linear attention aproximation mechanism)
- LTI recurrence를 이용 → ratio of two SSMs
- RNN과 Transformer의 장점을 모두 가져왔다고 말하지만 사실상 linear attention을 가진 transformer에 불과함
- LDStack
- RNN to MIMO(multi input multi output) LDS(Linear dynamic system)
- RNN도 LDS로 표현될 수 있다!
- parallel scan : MIMO LDS → aggregate → SIMO LDS
- discrete LDS == SSM → LDS is time-variant SSM
- S5
- LDStack의 extention - independent SSM sequentially
- LRA 특히 path-X에서 좋은 성능을 보임
- S4가 SISO SSM 을 독립적으로 핸들링했다면 S5는 single multi input → multi output SSM을 이용한 것. → 병렬화
- S4nd
- SSM 을 연속 데이터 도메인으로! (이미지와 비디오 데이터에 적용함)
- ODE로 표현되는 SSM을 PDE로 확장 → 여러 차원 간의 spatial dependencies를 잡을 . 수있게됨
- ConvNext를 백본으로 하여 테스트한 결과 ViT 보다 나은 성능을 보였음
- Diagonal State Spaces (DSS)
- parameterization of SSM through diagonal matrices plus low rank correction
- low rank correction 없이도 S4와 비슷한 결과 달성
- state space matrix의 초기화 방법에 대한 연구 결과도 제시함
- Liquid Structural State Spaces (Liquid S4)
- LTC + S4
-
LTC : liquid time-constant networks : causal continuous time NN, input specific state transitions
-
kernel structure, considers similarities among input sequence samples during both training and inference
-
다양한 벤치마크에서 SOTA 달성
-
- LTC + S4
- SPADE (State Space Augmented Transformer)
- global과 local 정보를 모두 가져가자
- 트랜스포머는 로컬 정보는 잘 가져가지만 글로벌 정보는 잘 못가져오고 SSM은 글로벌 정보는 잘 가져오지만 로컬 정보를 잘 못가져온다.
- S4를 트랜스포머의 시작 레이어로 사용 → 글로벌 정보를 초기에 가져온 뒤 트랜스포머로 로컬 정보도 가져가자
- integration을 잘 하면 더 좋은 성능을 낼 수 있음을 시사함
Gated SSMs
- Mega
- 트랜스포머의 두가지 문제점 : inductive bias and quadratic attention complexity
- inductive bias : 토큰 간에 존재하는 상호작용 패턴에 대해 반영하지 못함
- Moving Average Equipped gated Attention
- gated attention : single-head
- classical EMA + gate → positional-level local dependency → position-agnostic attention
- Mega-chunk : linear space and time complexity while minimizing quality loss
- 트랜스포머의 두가지 문제점 : inductive bias and quadratic attention complexity
- Gated State Spaces (GSS)
- FFT에서의 계산복잡도를 낮추기 위한 gate mechanism 제시
- zero-shot generalization to longer input sequence
- 랜덤 초기화 사용, 근데 S4, Hippo 등 보다 (룰에 따른 초기화) 나은 성능
- 블록 트랜스포머보다 나은 성능, TPU에서 DSS보다 빠른 계산속도
- Toeplitz Neural Network (TNN)
- positional embedding 부분을 바꿔보자
- position-encoded Toeplitz matrix : capture relations btw input token pairs as a token mixer
- Toeplitz matrix vector production technique to reduce space-time complexity to O(NlogN)
- key feature : Relative Position encoder
- 고정된 파라미터 버짓에서 relative positional parameter을 만듦, toeplitz 행렬과 함께 사용해서 파라미터들을 시퀀스 길이에 독립이 되도록 만들었음.
- Mamba
- selective copying & induction head answpfmf gorufgka
- selection mechanism을 도입
- 하드웨어 기반 알고리즘을 제안
- gated MLP를 섞어서 더나은 결과를 얻을 수있도록
Recurrent SSMs
- Linear Recurrent Unit
- SSM 기저의 초기화 이론 등에 대해서 설명이 부족한 상황이었음. 이 때 LRU는 RNN에서 시작해서 SSM의 성능을 따라잡을 수있는지 살펴보기로 함
- Linear Recurrence : non-linearity를 없애고 linear RNN을 쌓아서 만듦
- Parameterization: RNN을 파라미터화, diagonal form으로 만들어서 병렬학습이 가능하게 함
- Stable Exponential Parametrization : diagonal recurrent matrix에 적용하여 학습 과정을 단순화
- normalization : hidden activation에 정규화 진행, 시간 안정성
- +) Griffin and Hawk : LRU에 추가 레이어 넣어서 더 나은 결과를 얻고자 함
- Griffin : LRU + MLP + residual blcok
- Hawk : LRU + MLP (global multi-query attention)
- SSM 기저의 초기화 이론 등에 대해서 설명이 부족한 상황이었음. 이 때 LRU는 RNN에서 시작해서 SSM의 성능을 따라잡을 수있는지 살펴보기로 함
- Hierarchically Gated Recurrent Neural network (HGRN)
- gated linear RNN , weight propagating from lower to upper
- short-term dependency handling : 저층 레이어
- long term dependency : 고층 레이어
- 은닉층 계산 복잡성 해결을 위해서 element-wise linear recurrent layer를 사용 → 비선형성 제거
- linear RNN : EMA + gating schemes
- S4, RWKV, S4nd, Mega, LRU 모두 EMA 사용하나 decay rate는 data independent (static)
- HGRN은 forget gate를 사용해서 dyn\amic decaying을 가능케함
- 여러 벤치마크에서 좋은 성능을 보였으며 특히 perplexity gap을 잘 줄인 특징이 있음
Miscellaneous SSMs
- Mixture of Experts : LLM 성능 향상을 위하 주로 쓰이는 방법
- SSM에 적용한 경우 : Balckmamba, MoE mamba, Jamba
- BlackMamba : self attention to mamba SSM + MoE-Transformer architecture.
- activation on only one sparse parameter set
- router mechanism
- MoE-Mamba : Black Mamba와 비슷한 아키텍처, attention to Mamba SSM + MoE TRransformer
- Jamba : hybrid architecture : Mamba layers + Transformer layers
- 특히 commonsense reasoning에 특화
- 몇몇 벤치마크에서 Mistral-8X-7B보다 나은 성능을 보였음
- 256K까지 input seq length 늘림
- MambaByte : HW efficient algorithm으로 만들자!!
- 고정된 메모리 공간안에 최적화된 디코딩 테크닉을 가져오자.
- context length에 독립적으로 설계
- 524K까지 긴 길이를 처리할 . 수있음
- lower perplexity & improved performance가 가능함을 보여줌
- BlackMamba : self attention to mamba SSM + MoE-Transformer architecture.
- SSM and In-context learning
- ICL : relationship btw task performance and the information present within the training data
- 특정 function class를 가져와 사용하는데 적합한가?
- 트랜스포머에서도 in context learning 하기 위해서는 적절히 학습이 필요하고 이것은 대부분 inference 시간안에 일어남.
- mamaba도 standard scenario에서 이것을 . 잘할 . 수있다.
- MambaFormer : 다양한 태스크에서 Mamba가 잘 할수 있음을 보여줬으나 Quadratic performance를 보였음.. ← 더 읽어봐야할 듯!
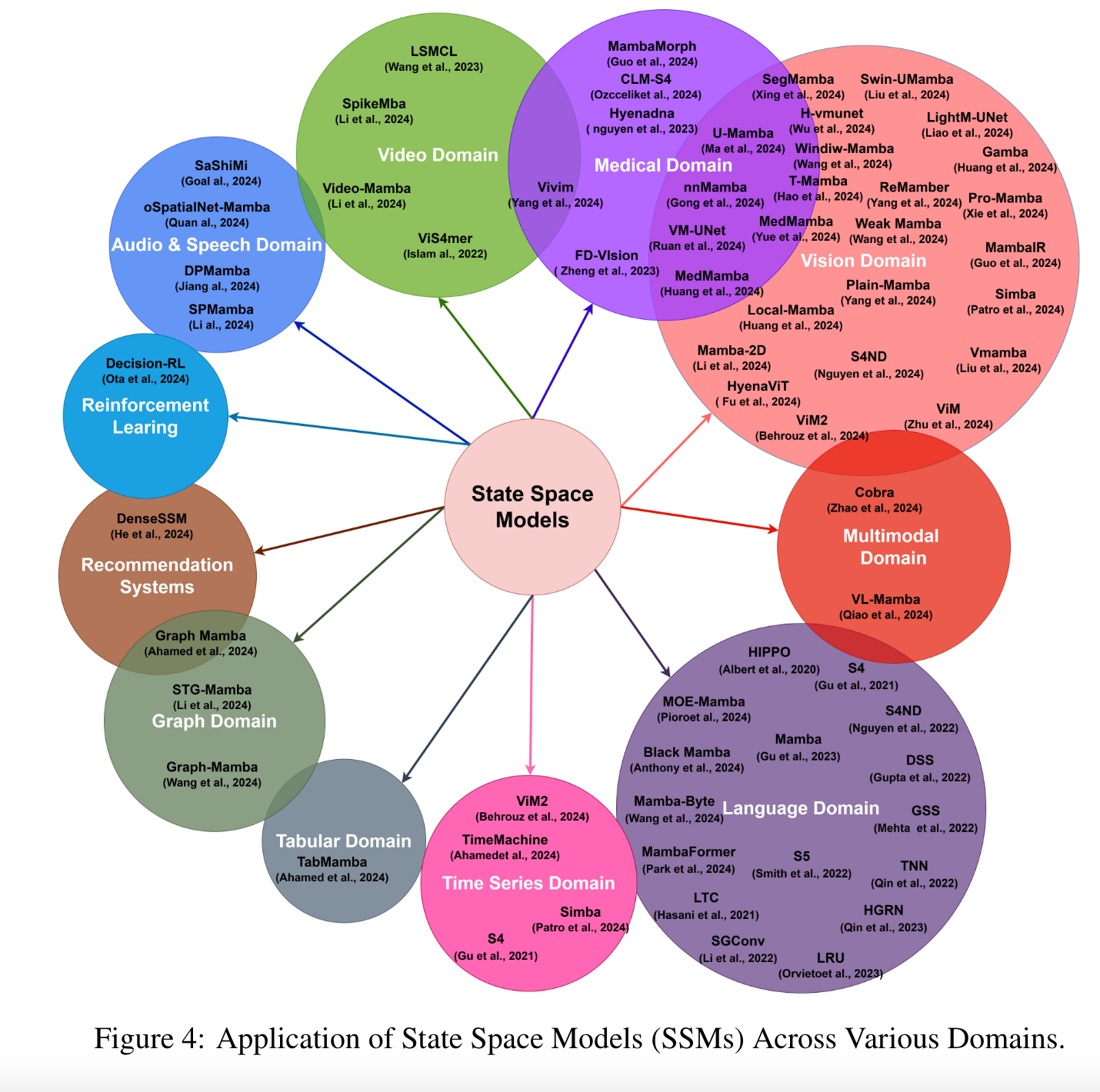
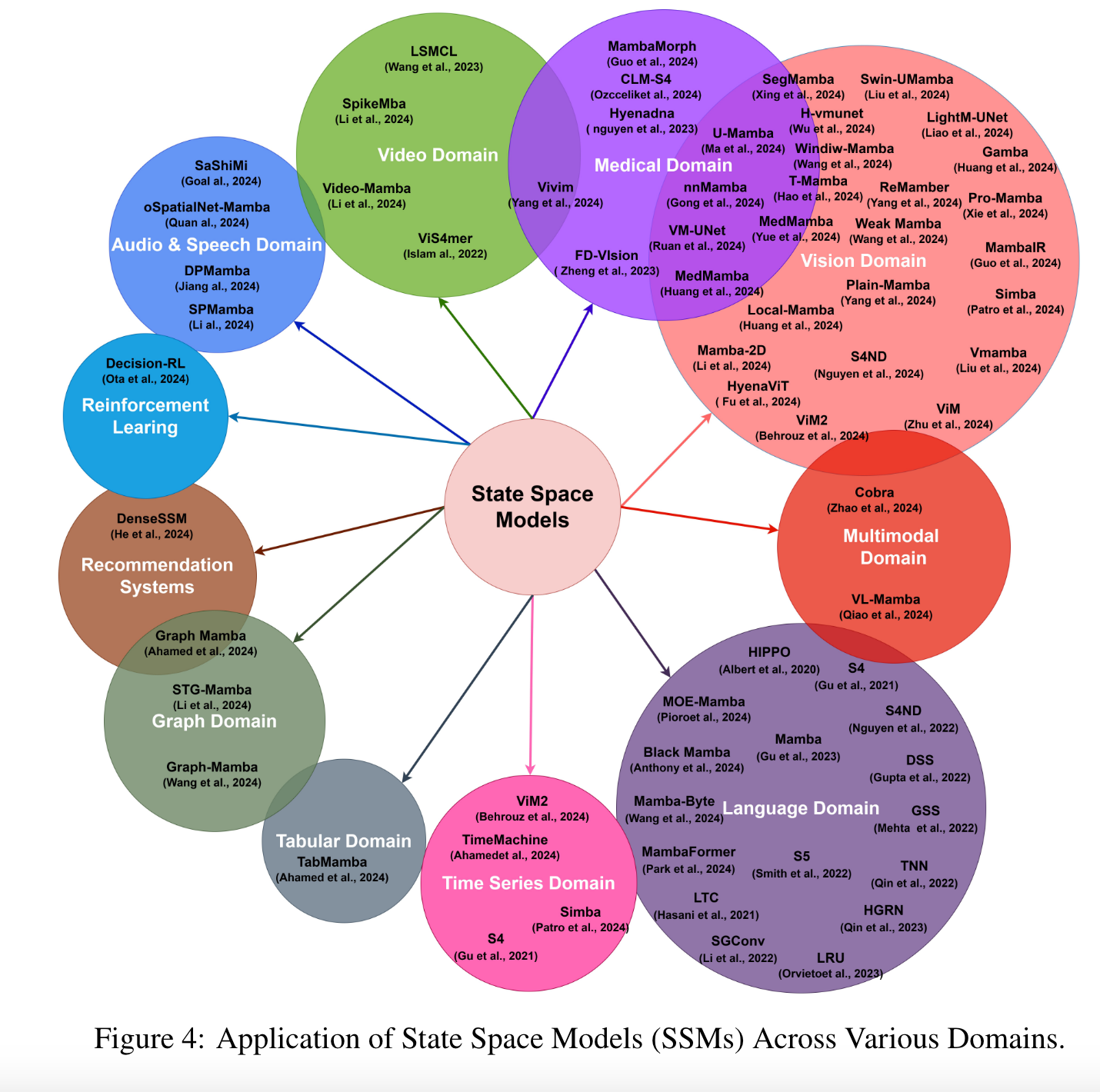
Applications of State Space Models
Language domain
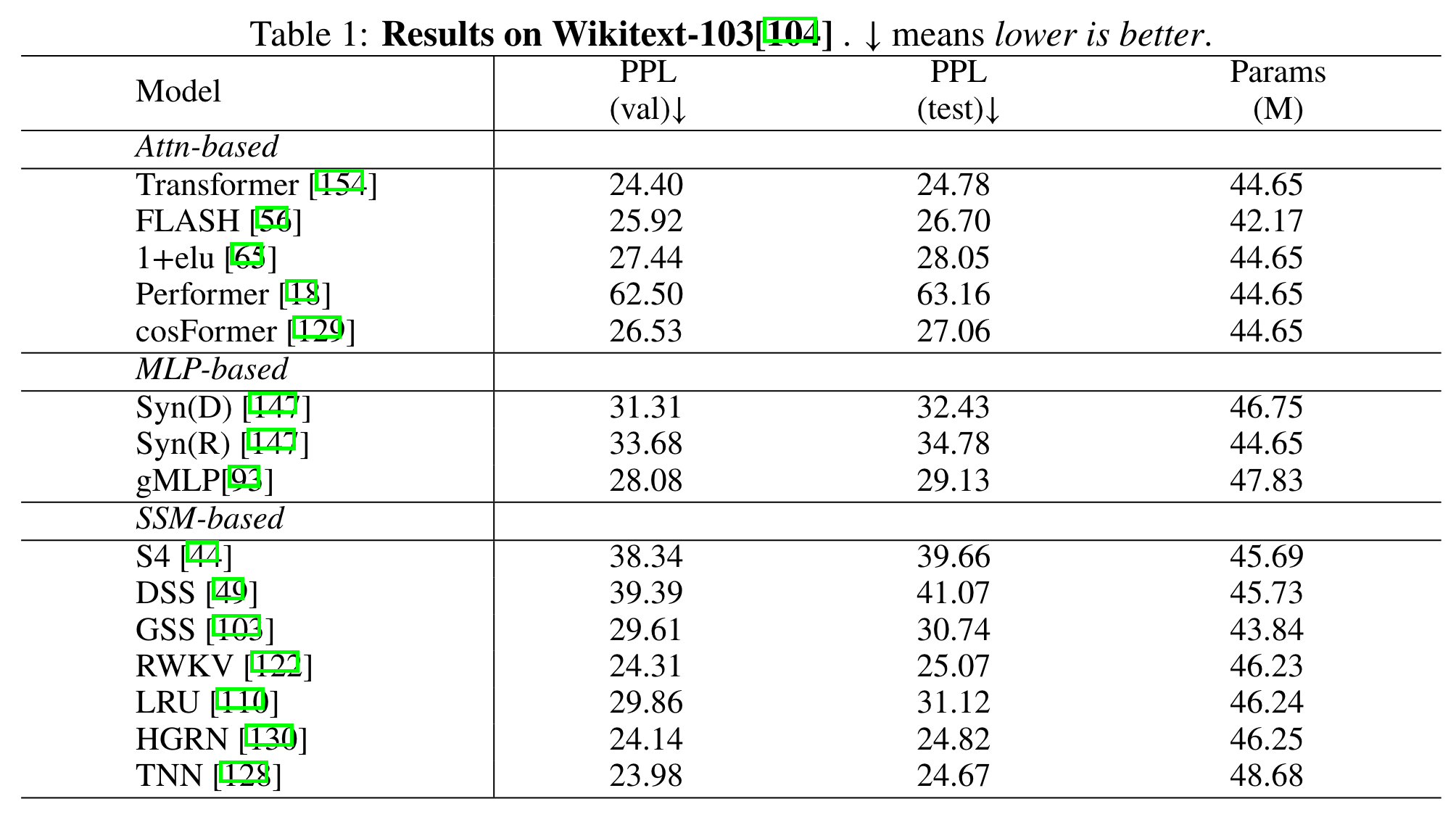
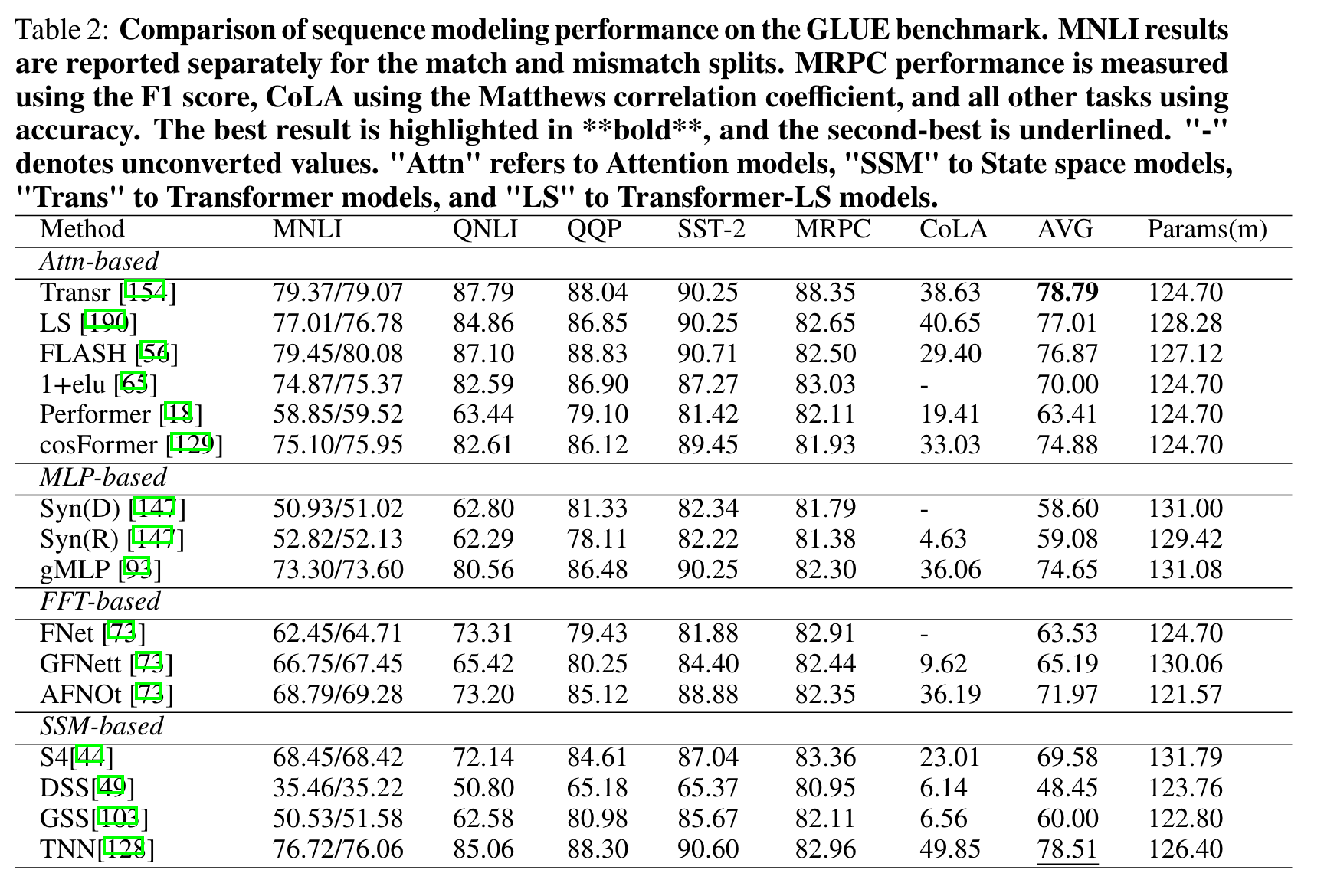
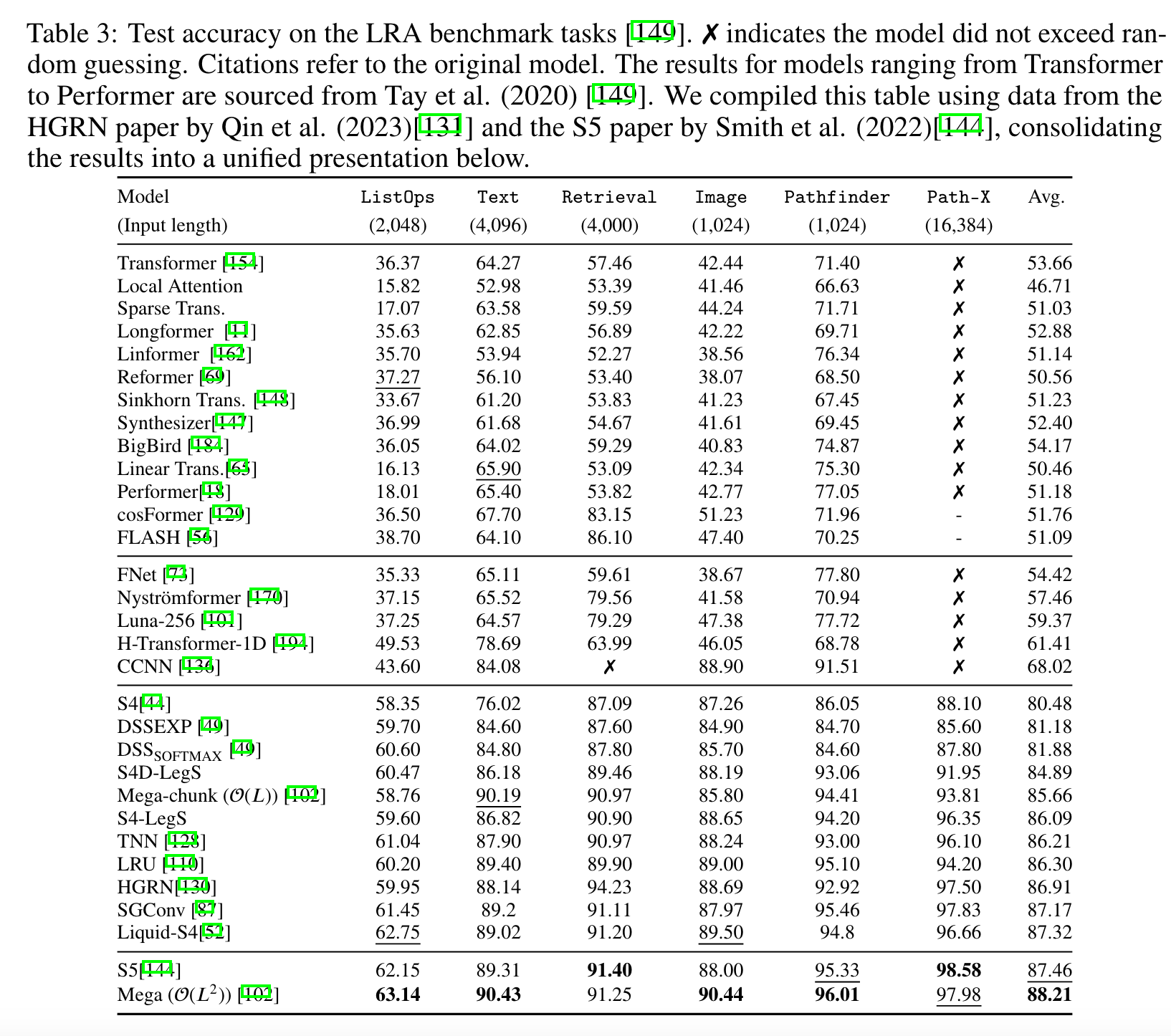
- perplexity score 거의 비슷하게 따라옴
- LRA에서는 더 좋은 성과
- 기본 LM task에서는 트랜스포머보다 좋지 않은 성능, 그러나 아직 Mamba가 저 표에 없어서 여지가 있음(실제로 Mamba만 비교한 결과 살펴보면 더 좋아짐)
Vision domain
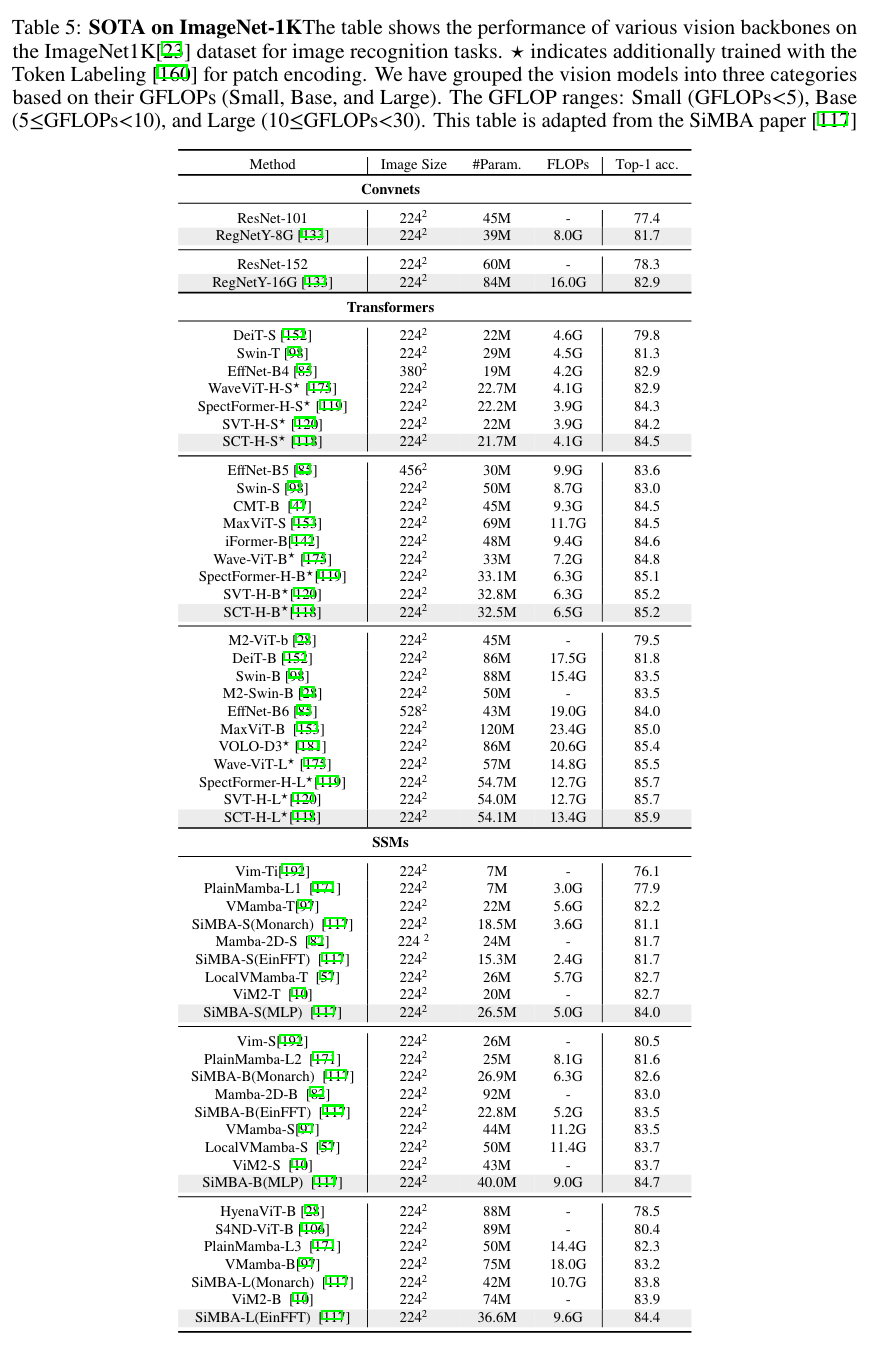
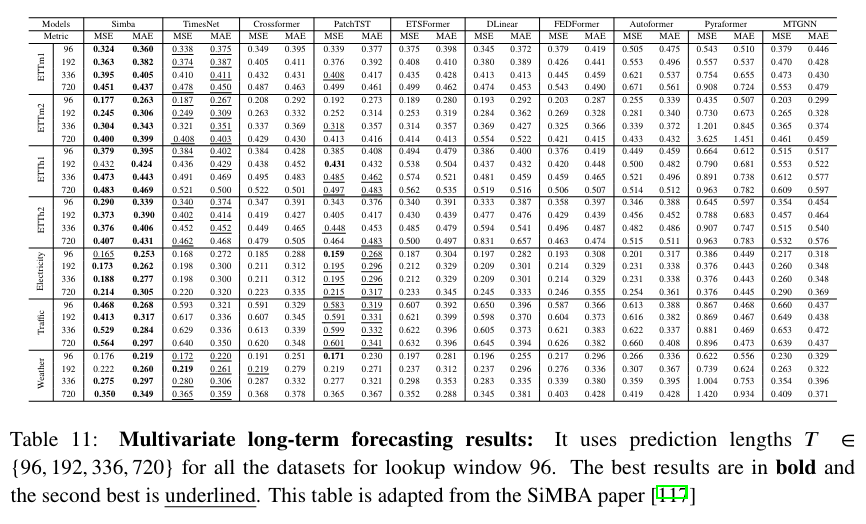
- SiMBa: bidirectional and visual state space model
- SiMBA [117] aims to bridge this gap by incorporating Mamba for token mixing, replacing attention networks, and leveraging Einstein FFT (EinFFT) for channel mixing. SiMBA introduces the Einstein blending method for channel mixing, providing a novel approach without the constraints of requiring perfect square dimensions for sequence length and channel dimensions. Furthermore, SiMBA adopts the pyramid version of the transformer architecture, leading to significant performance improvements, especially on benchmarks like ImageNet and time series tasks.
Medical domain (skip)
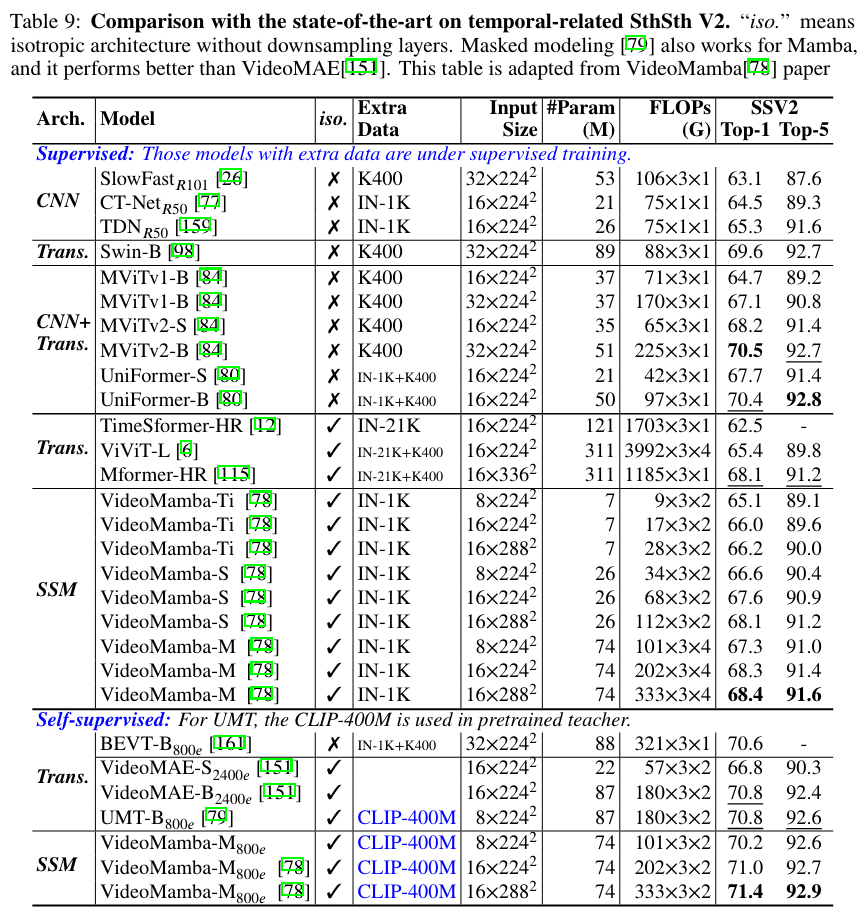
Video domain
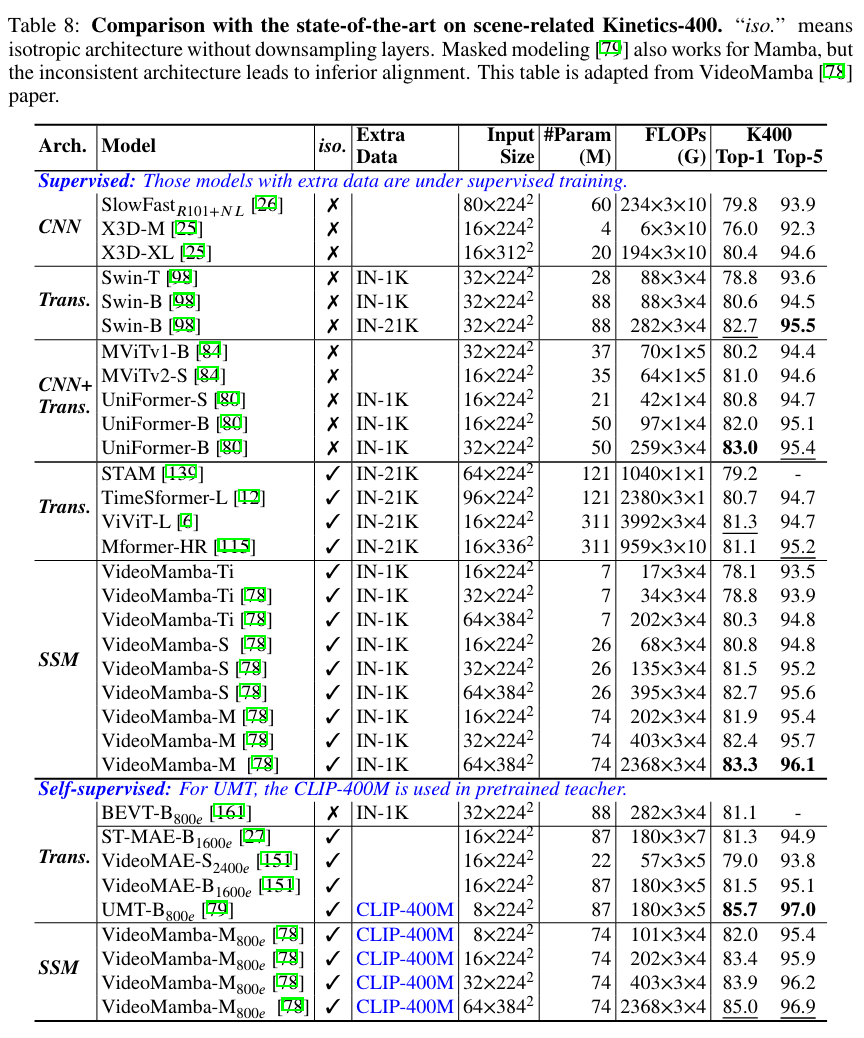
Time Series
Tabular/Graph/Recommendation System/Audio&Speech
State of the Arts Results
Dataset Details (skip)
- LRA, Multivariate Time series, Video, Multimodal LLM datasets 에서 좋은 성능을 보였음. 기타 자세한 데이터셋 설명은 생략
Results
- LRA : 트랜스포머 등 기타 모델이 ListOPs, Text, Retrieval, Image, Pathfinder, Path-X 등에서 그닥 좋지 않은 성능을 거둠 (계산 복잡도 때문에) SSM이 . 더나은 결과를 보이며 S4의 변형들이 좋은 결과를 보임. 다만 왜 S5와 Mega가 SOTA 성능을 보이는지는 알 수 없음. 이러한 설명 해석이 또하나의 연구 주제일수도
- Language domain
- GLUE 결과에서는 SSM 카테고리가 나머지 셋보다 그닥 좋은 결과를 얻지 못했다. 그나마 TNN이 따라잡을 가능성을 보여주긴 했다.
- WikiText에서도 괄목할만한 성과를 거두지 못했으며, 여전히 attention-based transformer 들이 더 좋은 결과를 냈다. (perplexity score for next word prediction)
- Pile에서는 HGRN만이 comparable한 결과를 보였다.
- Vision domain
- LocalVMamba, PlainMamba-L3, VMamba-T 등이 주목할만한 성능을 보임. 특히 SiMBA-S, SiMBA-B, SiMBA-L등 변형들이 좋은 결과를 보였음.
- Time Series forecasting
- SiMBA의 성능이 주목할만함. robust performance and effectively modeling benchmarks
Conclusion
- 다양한 모델들을 3가지 카테고리로 분류하여 정리함
- Transformer와 SSM을 혼합하여 더 좋은 성능을 보이는 모델을 확인할 수 있었음
- SSM을 larger scale로 만드는 것 역시 여전히 중요한 쟁점 중 하나이며 안정성 유지 또한 중요한 문제이다.(특히 컴퓨터 비전에서)
- 또한 in-context learning 부분에서도 발전의 여지가 충만하므로 이 부분도 살필 필요가 있다.
