Starting Off
I will be using IntelliJ IDEA paid version for the demontration of using Spring in my blog post.
src/main/resources.application.properties
- This is where you can edit your Spring settings that were set automatcially (changing default settings).
- It will also be used a lot when dealing with data bases.
Gradle
Gradle is a build automation tool primarily used for Java projects. It manages project dependencies, compiles code, runs tests, packages applications, and more. This post will be using gradle for demontration.
build.gradle
build.gradle is a Gralde based build script. This allows easy management of library and source code dependencies. It can be written in Kotlin or Groovy.
Server
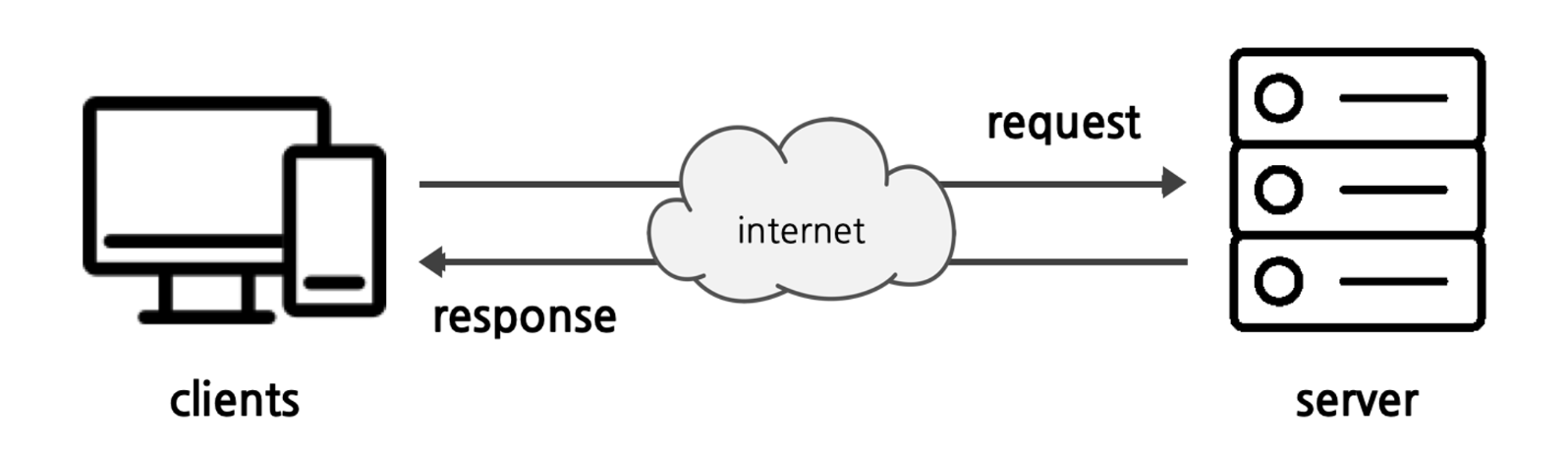
As shown in the simplified diagram below, clients request information to the server via internet. The client is able to make a request based on the address of the server which is called in IP (Internet Protocol address). While an IP address is like an address to a house a port is like doors to that house/building. And as we know, there can be multiple doors/entraces thus multiple ports exist per IP address.
Web Server
A web server is a specific type of server that delivers web pages to clients (like web browsers) over the internet or an intranet. It handles HTTP requests, serving static content like HTML, CSS, JavaScript files, and images, or dynamic content generated by web applications, making it a key component of any website or web-based application.
Application Programming Interface (API) & RESTful API
An API is a set of rules and protocols that allow one software application to interact with another. It defines the methods and data formats that applications use to communicate, enabling integration and functionality between different systems.
A RESTful API (Representational State Transfer API) is a specific type of API that adheres to REST principles. It uses standard HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE) and URIs to manipulate resources, typically represented in JSON or XML, ensuring stateless, scalable, and easy-to-understand web services.
💡 Statelessness means that each request from a client to a server is independent and contains all the information needed to understand and process the request. The server does not retain any information or state about previous requests from the same client.
💡Key Points of Statelessness
- No Session: The server does not retain any information about previous requests; each request is independent.
- Self-contained Requests: Every request must include all necessary information for processing, as the server does not remember past interactions.
- Scalability: Statelessness allows for easier scaling and load balancing since servers do not need to manage session data.
- Reliability: Each request is handled independently, improving reliability and fault tolerance since one server failure doesn't affect request processing.
Tools
Apache Tomcat
Apache Tomcat is an open-source web server and servlet container that implements Java Servlet and JavaServer Pages (JSP) specifications, enabling the deployment and execution of Java-based web applications. It handles HTTP requests, processes Java servlets, and generates dynamic web content based on JSPs, making it a key component for running Java web applications.
(Servlet container is to be explained later in this blog)!
Spring & Spring boot (check my previous blog)
What is Java? Spring VS. Spring-Boot
Lombok
Lombok is a Java library that automatically generates boilerplate code like getters, setters, constructors, and more through annotations, simplifying code and improving readability.
HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
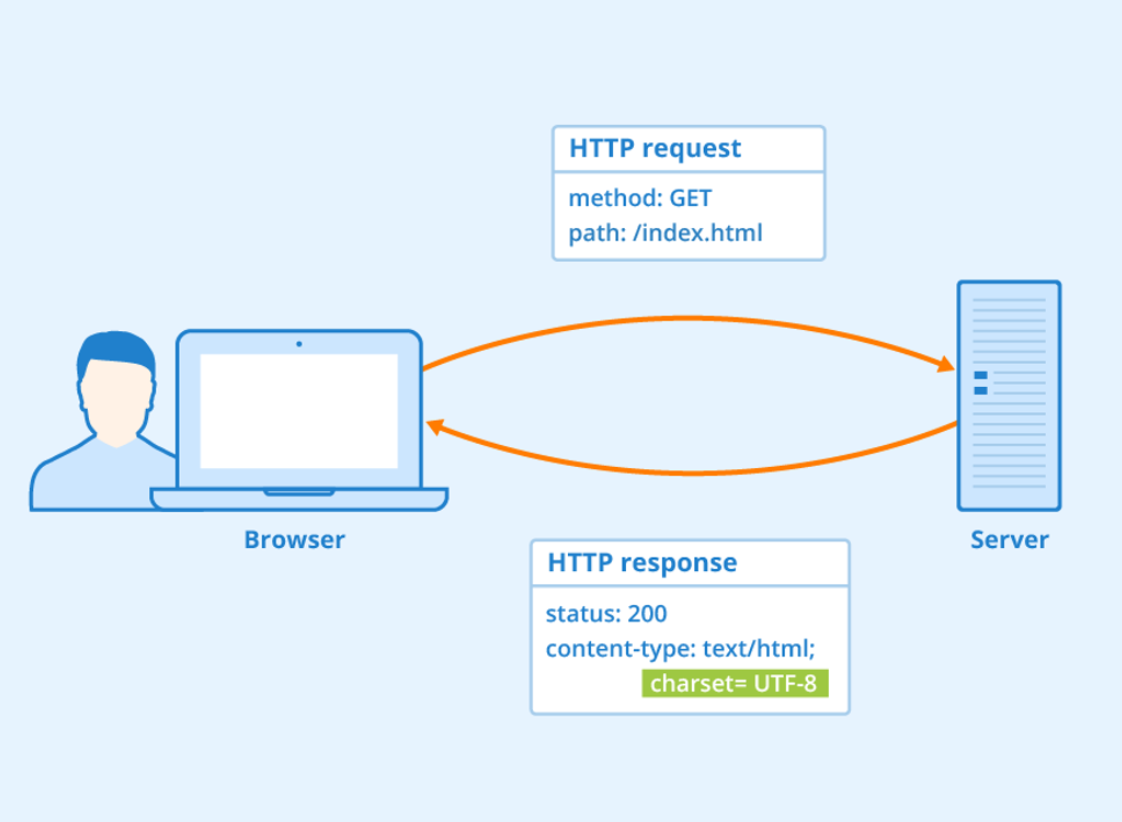
An HTTP request is a message sent by a client to a server over the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP). It is used to request resources or perform actions on a server. The client is usually a web browser, application, or any other service that can communicate over the HTTP protocol.
Headers of a HTTP browser request
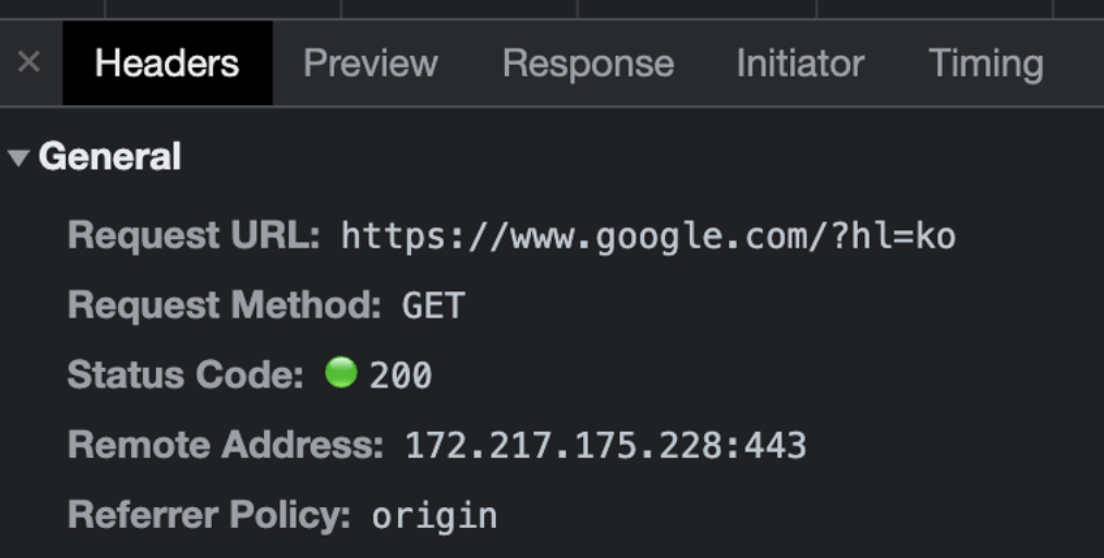
The current status code of 200 means that the request was successful. The other possible codes are the following:
- 1xx (Informational)
- requesst is recieved and is under process.
- 2xx (Successful)
- 3xx (Redirection)
- Client needs to undertake additional actions. Often times required to move to another page or redirection.
- 4xx (Client Error)
- There is an error in the client's request or authentication.
- 5xx (Server Error)
- There is an error in the server such as server overload.
- The most common one is 500, which indicates an inter problem in the server.
Request Headers
Request data from browser to the server.
Response Headers
Additional data that the server sent with the webpage data.
Payload
In the context of HTTP, a "payload" refers to the actual data that is being carried in the body of an HTTP request or response. The payload is the part of the message that contains the data intended to be transmitted between the client (such as a web browser or API client) and the server. According to general practices, except for the GET method, all other methods can send a payload.
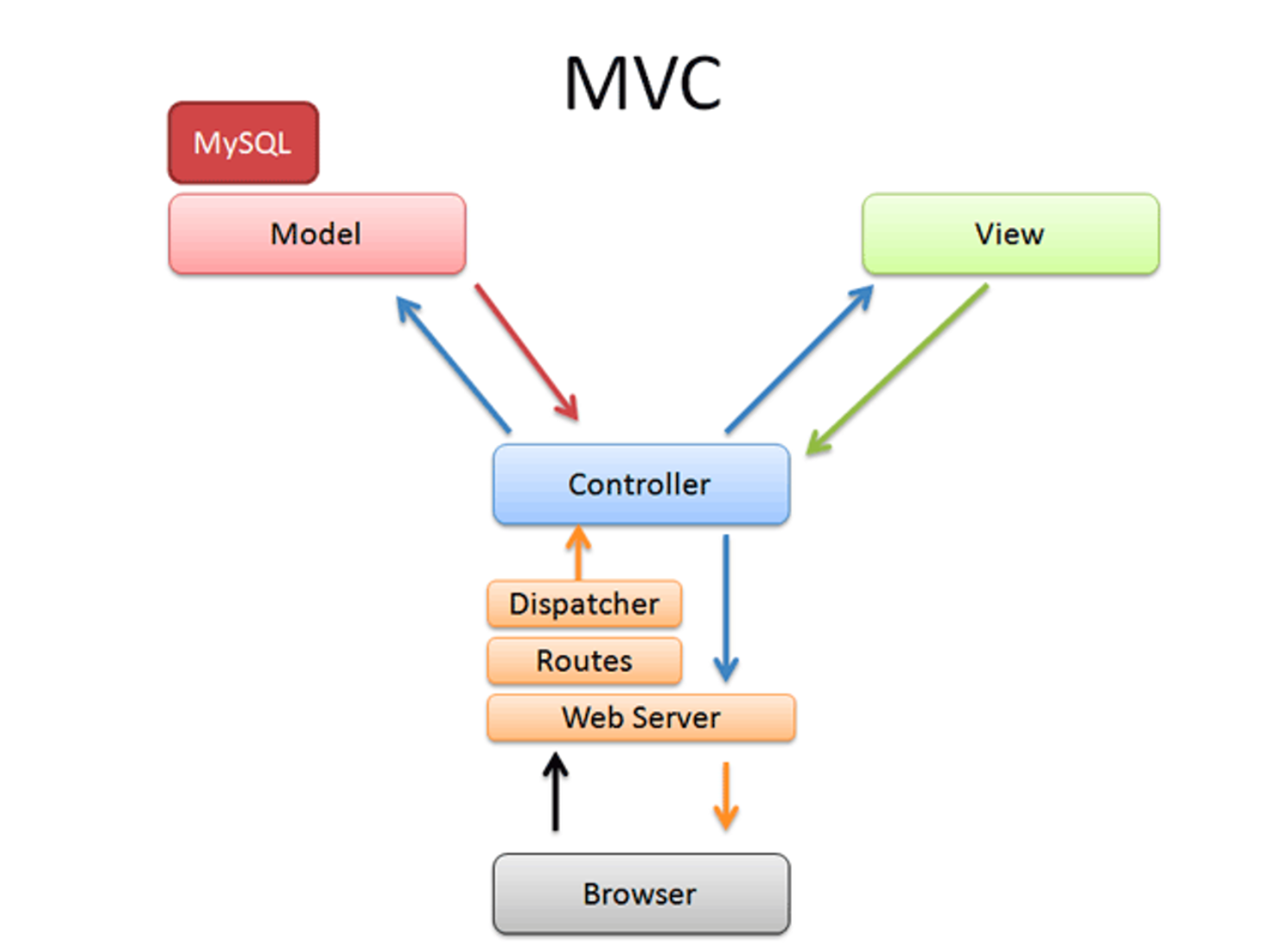
Model-View-Controller Design Pattern
-
Model: Manages the application's data and business logic, handling data retrieval, storage, and manipulation. It notifies the view of any changes to update the user interface.
-
View: Represents the presentation layer, displaying the data from the model to the user and providing an interface for user interaction. It updates dynamically based on changes in the model.
-
Controller: Acts as an intermediary between the model and view. It processes user input, manipulates data in the model, and updates the view accordingly.
This separation promotes modularity (design principle of dividing a system into distinct, self-contained components or modules, each responsible for a specific functionality), making the application easier to maintain, test, and scale.
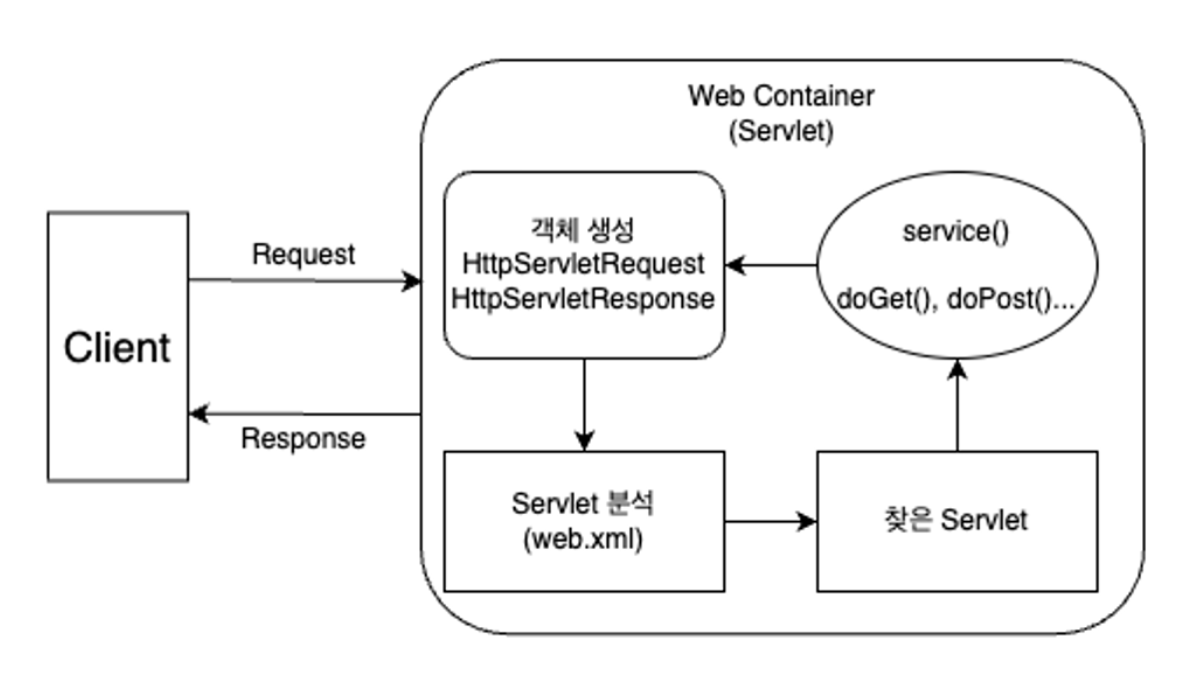
Servlet
A servlet is a Java programming language component that runs on a web server and handles HTTP requests and responses in a web application.
- step1: Client makes a request
- step2: HttpServletRequest object and HttpServletResponse object is created (These objects are designed to easily use the data contained in the HTTP request while adhering to the agreed-upon HTTP specifications).
- step3: Servlet analyzes what kind of request it is
- step4: After analysis, calls the service method
- step5: Depending on the request, calls the doGet or doPost method.
- step6: The results from the called methods are either returned directly or used to generate a dynamic page, which is then encapsulated in the HttpServletResponse object and sent back to the client (browser).
- step7: Once the response is complete, the created HttpServletRequest and HttpServletResponse objects are deconstructed.
💡 this sevrlet in java is not very easy to use!.. so we will use something called a 'Spring Controller' so we can easily contrcut a controller for our code.💡
Front Controller Pattern
A Front Controller Pattern design is an efficient way of handling request so that it is sent to the corresponding controller. DispatchServlet is a key element for such design in Java because the requests first come through the DispatchServlet which than "dispatches" it to the controller that it needs to go to.
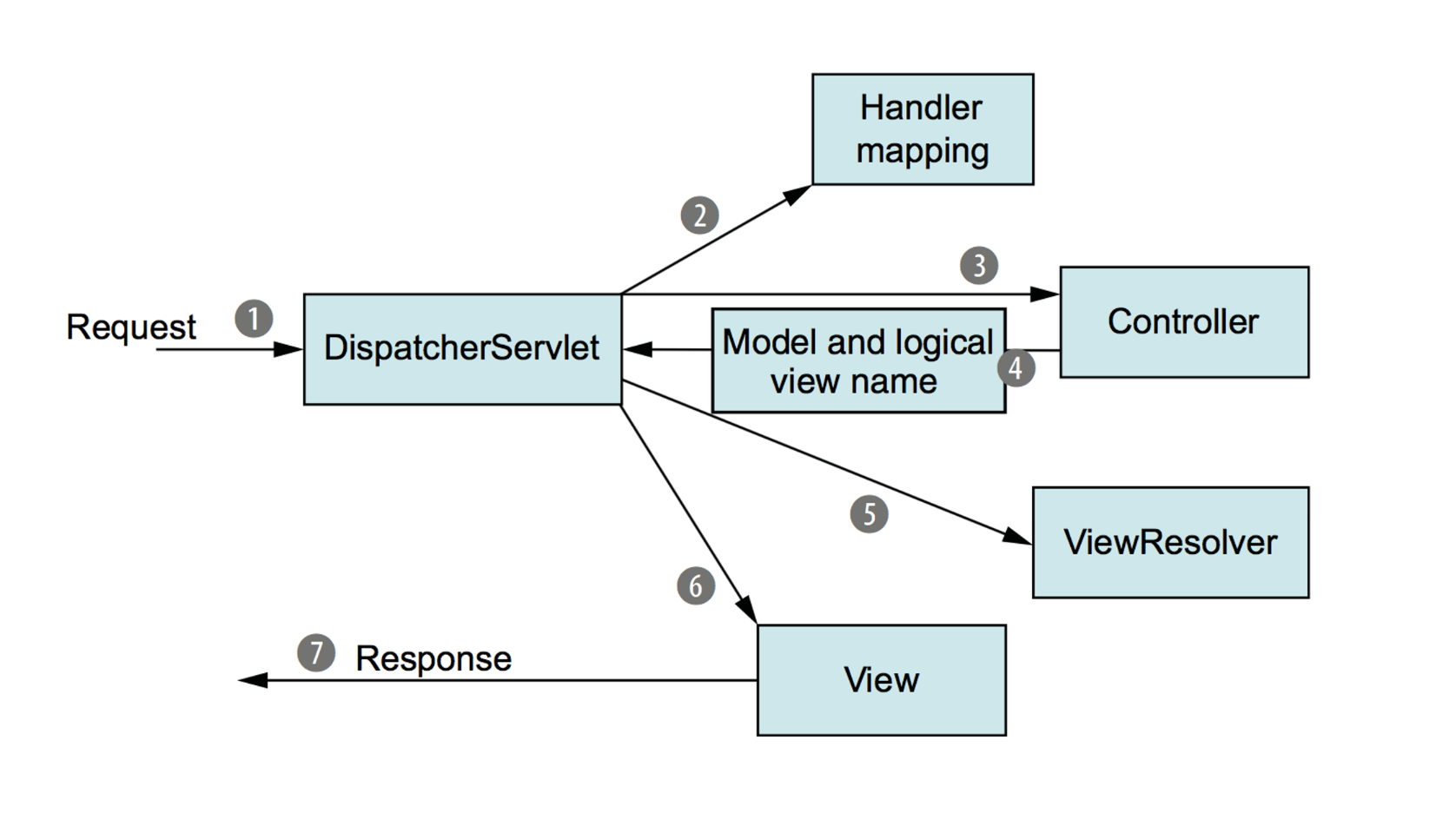
DispatcherServlet
DispatcherServlet acts as the central dispatcher or controller in the MVC architecture, managing and coordinating the handling of HTTP requests and responses.
Key Functions of DispatcherServlet:
-
Request Routing: It receives all incoming HTTP requests and routes them to the appropriate controllers based on URL patterns configured in the application.
-
Controller Coordination: It delegates the request to a specific controller, which processes the request, interacts with the model, and prepares a response.
-
View Resolution: After the controller processes the request and returns a model and view name, DispatcherServlet delegates the rendering of the view to a view resolver, which then renders the final response to the client.
-
Integration: DispatcherServlet integrates with other Spring components, such as HandlerMapping, HandlerAdapter, and ViewResolver, to provide a cohesive request handling process.
-
Exception Handling: It can handle exceptions and errors that occur during request processing, allowing for centralized error handling.
