Gradle
Is an automatic build tool that converts java source code to an executable .jar file.
build.gradle
build.gradle is a Gradle based build script. You can easily manage library dependencides and this can be written in groovy or kotlin. The dependencies shown below are automatically downloaded by Gradle from external repositories.
More on Gradle and other tools can be found here
Web Server & WAS
Web Server
A Web Server is a system that serves static content (like HTML, CSS, and images) to clients over HTTP/HTTPS. It handles incoming requests from web browsers and delivers the requested resources. Common web servers include Apache, Nginx, and Microsoft IIS.
Web Application Server (WAS)
A Web Application Server (WAS) handles dynamic content and application logic. It processes requests that require backend operations, such as interacting with databases and executing server-side code (e.g., Java, Python). Examples include Apache Tomcat, JBoss/WildFly, and Oracle WebLogic.
Key Differences
- Web Server: Primarily serves static content.
- WAS: Handles dynamic content and executes business logic.
How They Work Together
In a web application, the web server handles static files and forwards dynamic requests to the WAS, which processes them and returns a response. This setup allows for efficient content delivery and scalable architectures.
Sending Reponses to the Client
💡 Previously, servers have sent back to the client the actual website like html, but the shifting trend is for servers to only send 'data' and the client then changing the html accordingly on their side.
Spring Grammar
annotations (@)
They are form of metadata that provide data about a program but are not part of the program itself. They can be used by the compiler, at runtime, or by frameworks and libraries to influence how your code behaves.
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/response/rest")
public class ResponseRestController {
@GetMapping("/json/string")
public String helloStringJson() {
return "{\"name\":\"Robbie\",\"age\":95}";
}Jackson library
The Jackson library is a popular Java-based framework used for converting Java objects to JSON (serialization) and JSON to Java objects (deserialization). It's widely used in Spring applications to automatically handle JSON data binding in RESTful web services.
Serialization Example (objects to JSON)
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
User user = new User("John", 30);
String jsonString = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(user);
System.out.println(jsonString);
Output: {"name":"John","age":30}
Deserialization Example (JSON to objects)
String jsonString = "{\"name\":\"John\",\"age\":30}";
User user = objectMapper.readValue(jsonString, User.class);
System.out.println(user.getName()); // Output: John
@RestController = @Controller + @ResponseBody
In Spring, @RestController, @Controller, and @ResponseBody are annotations that play a crucial role in handling web requests and responses. Here’s a breakdown of each:
1. @Controller
-
Purpose: The
@Controllerannotation is used to define a controller class in a Spring MVC (Model-View-Controller) application. A class annotated with@Controlleris responsible for processing incoming web requests, preparing a model, and returning a view to be rendered as a response. -
View Resolution: By default, methods in a
@Controllerclass return a view name, which is resolved by a view resolver (like Thymeleaf, JSP, etc.) to render an HTML page or another view. -
Example:
@Controller public class MyController { @GetMapping("/hello") public String hello(Model model) { model.addAttribute("message", "Hello, World!"); return "hello"; // Returns a view named "hello" which would be hello.html } }
2. @ResponseBody
-
Purpose: The
@ResponseBodyannotation indicates that the return value of a method should be written directly to the HTTP response body (typically as JSON or XML), rather than being interpreted as a view name. -
Direct Response: When a method is annotated with
@ResponseBody, Spring will convert the returned object to JSON (or another format) using an appropriate message converter and write it directly to the HTTP response. -
Example:
@Controller public class MyController { @GetMapping("/api/hello") @ResponseBody public String hello() { return "Hello, World!"; // Written directly to the response body } }
3. @RestController
-
Purpose: The
@RestControllerannotation is a specialized version of@Controller. It combines the functionality of@Controllerand@ResponseBody. -
Simplified API Development: When you annotate a class with
@RestController, you no longer need to annotate each method with@ResponseBody. Every method in the class will automatically have its return value written directly to the HTTP response body. -
Example:
@RestController public class MyRestController { @GetMapping("/api/hello") public String hello() { return "Hello, World!"; // Automatically written to the response body } }
💡FUN FACT: the annotations that we have been using were constantly simplified! 💡
💡LOOK BELOW!💡
@Controller
//@RequestMapping("/hello/request")
public class RequestController {
// @GetMapping("/form/html")
@RequestMapping(value = "/hello/request/form/html", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String helloForm() {
return "hello-request-form";
}
}is the same as
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/hello/request")
public class RequestController {
@GetMapping("/form/html")
// @RequestMapping(value = "/hello/request/form/html", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String helloForm() {
return "hello-request-form";
}
}Path Variable vs. Request Param
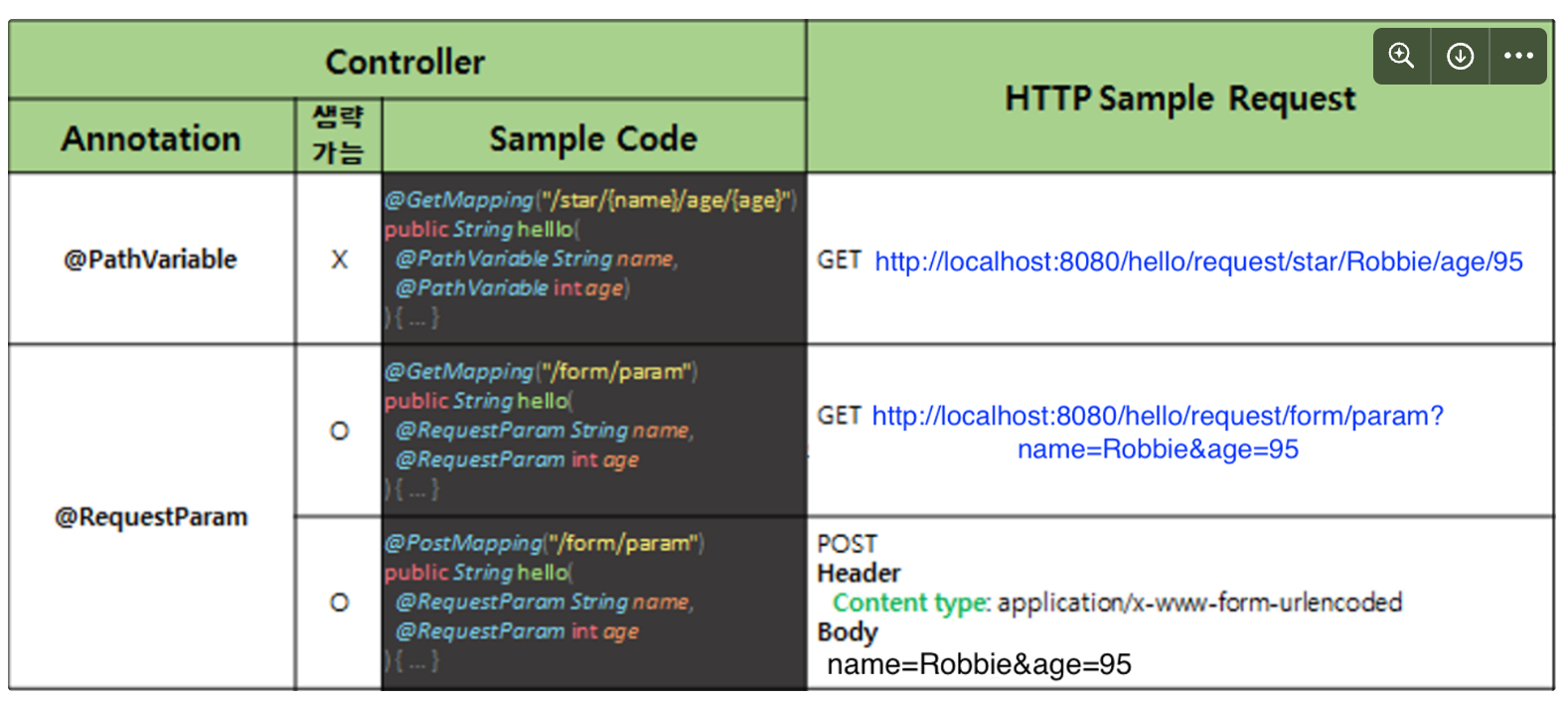
Making HTTP Requests
@ModelAttribute
@RequestBody
Using DTOs
even though memo class and the memoDto class our almost identical, we still create a seperate memoDto class. This is because DTOs are simple objects used specifically to transfer data whereas our domain object is a core to the code/business logic and is often linked with other important classes. Thus using DTO objects are safer. Also, its better in terms of security because DTOs only expose necessary information.
