
This is the first practical module for the bootcamp.
Time Consumed: 60 minutes
Difficulty level: 3/5
Summary: Syntax of Kotlin functions
Because I had some programming experience this did module did not take me long but because I took notes in between, it actually took me more than 60 minutes. The quiz was easy and straight forward, consisting of only 10 questions.
Notes
Val vs Var - variable types
In the code below there are errors... can you find what it is?
fun main() {
val discountPercentage: Int = 0
val offer: String = ""
val item = "Google Chromecast"
discountPercentage = 20
offer = "$discountPercentage% discount on $item!"
printlen(offer)
} The main problem is that in Kotline,
'val': immutable, read-only variables
'var': mutable/modifiable variables
Why would anyone use ‘val’ instead of ‘var’?
Val: Once assigned, value cannot change! This provides safey against accidental reassignment.
Var: Offers flexibility when values need to be updated.
Typecasting & Concatenation
Typecasting Method 1
fun main() {
val numberOfAdults = "20"
val numberOfKids = "30"
// Convert strings to integers
val adults = numberOfAdults.toInt()
val kids = numberOfKids.toInt()
// Perform numerical addition
val total = adults + kids
println("The total party size is: $total")
}Typecasting Method 2
fun main() {
val numberOfAdults = "20"
val numberOfKids = "30"
// Perform numerical addition
val total = numberOfAdults.toInt() + numberOfKids.toInt()
println("The total party size is: $total")
} Contatenation
fun main() {
val baseSalary = 5000
val bonusAmount = 1000
val totalSalary = "$baseSalary + &bonusAmount"
printlen($totalSalary)
}Function syntax
- note the way the data type of function parameters are return values are written.
- also for void functions, you don't need to state the return data type. It will be set to 'Unit' by default.
fun add(a: Int, b: Int): Int {
val c = a+b
return c
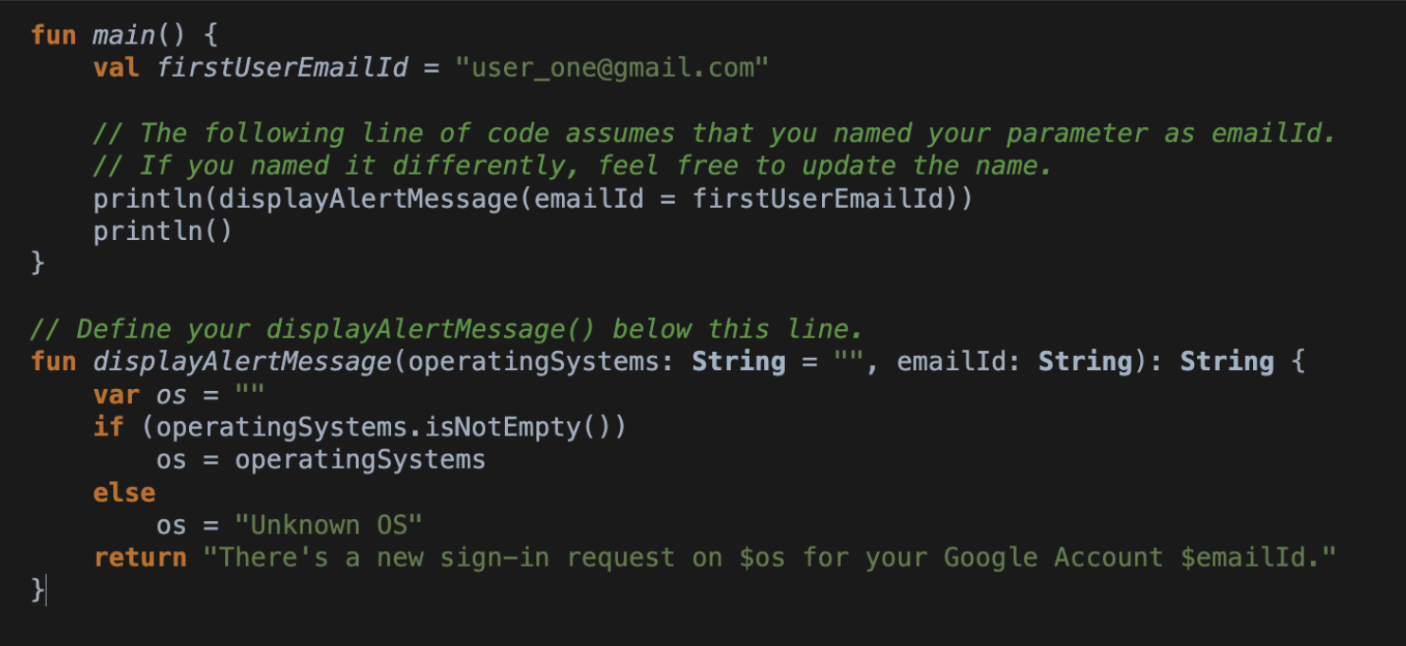
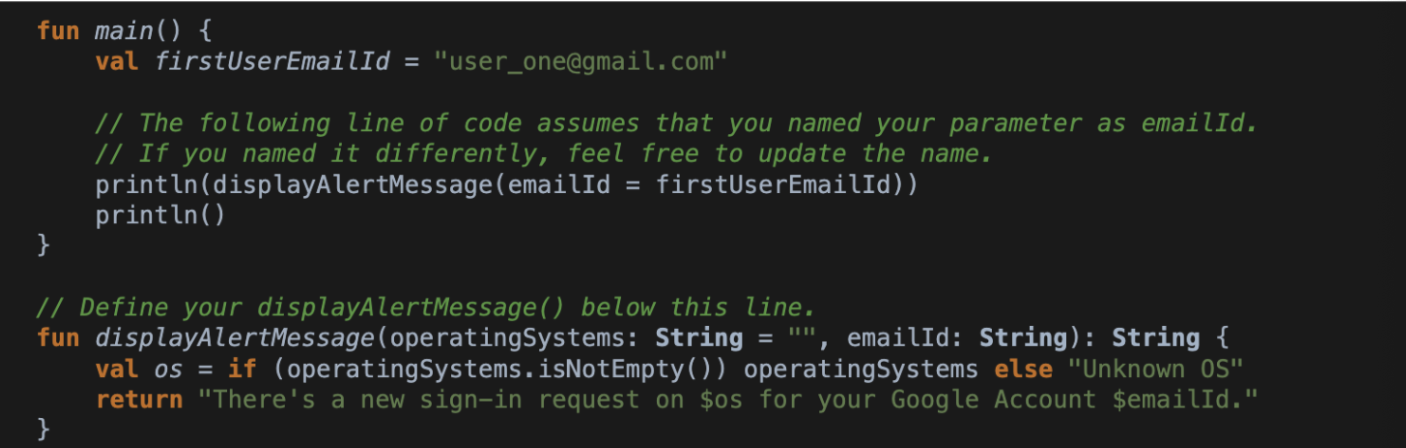
}Addressing a function's empty parameters
Method 1
Method 2
Following Best Practice in Writing Code
The code here does not follow Kotlin's naming conventions. Let's try fixing it up!

This is isn’t something that’s technical but important on a professional level. You will want your naming follows conventions and that your code is readable.
- Now, the variable name starts with a lower case letter and capitalized for any keywords that come after.
- there should be no whitespaces in the names.
fun main() {
val steps = 4000
val caloriesBurned = pedometerStepsToCalories(steps)
println("Walking $steps steps burns $caloriesBurned calories")
}
fun pedometerStepsToCalories(numberOfSteps: Int): Double {
val caloriesBurnedForEachStep = 0.04
val totalCaloriesBurned = numberOfSteps * caloriesBurnedForEachStep
return totalCaloriesBurned
}
[FYI] Double is the data type for floating-point numbers with double precision (compared to float), occupying 64 bits
Boolean Functions
Here we have a simple boolean function and its sample output. The function returns true when the phone usage time today is greater than yesterday.

Named Arguments
Calling a function with named arguments allows us to change the order of the parameters.
my_function(age = 25, name = "John", city = "New York")