async · await
<script>
async function doSomething() => {
const r1 = await promise();
const r2 = await promise2(r1);
const r3 = await promise3(r1, r2);
···
return r3;
});
dosomething()
.then(r3 => console.log(r3)
);
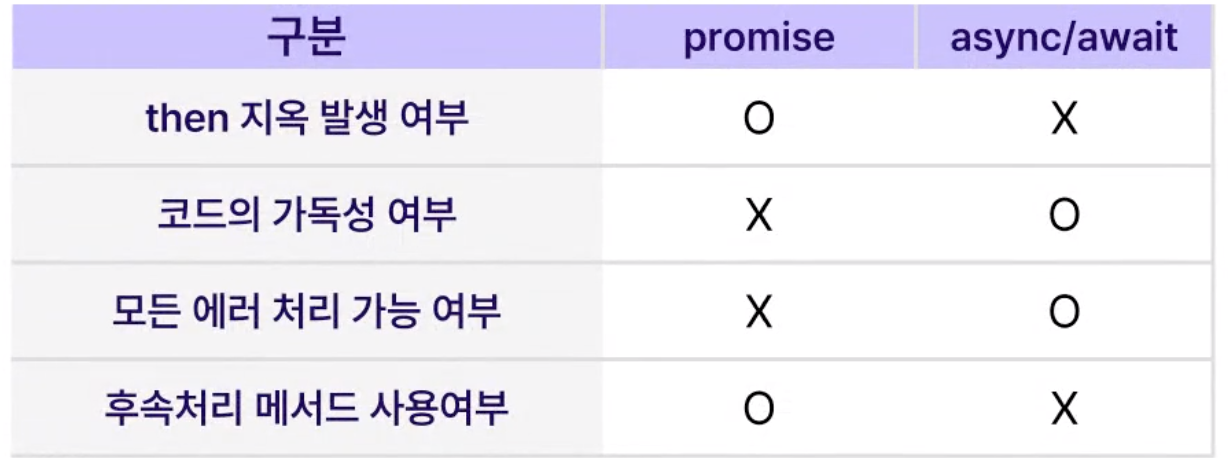
</script>· 기존의 비동기식 처리인 콜백 함수, promise 의 단점을 보완
· async-await 은 promise 의 다른 문법
· Promise 를 활용한 비동기 코드를 "간결하게" 작성하는 문법
· "에러 파악"에 용이
👉 promise 는 객체 내부에서 발생한 에러를 catch 로 처리하여, 외부에서 찾기 어려움
👉 async·await 은 모든 동기·비동기 에러를 try-catch 로 처리 가능하여 에러 파악이 용이
async
· 항상 function 앞에 위치함
· async 함수의 "return"은 Promise
👉 return 시 암묵적으로 Promise.resolve() 로 반환
👉 return Promise.resolve(1) = return 1
· 함수 안에 await 사용 가능
👉 promise 함수의 결과는 await 으로 받음
👉 await 한 promise 함수가 완료될 때까지 다음 라인으로 넘어가지 않음
<script>
async function asyncFunc() {
let data = await fetchData()
let user = await fetchUser(data) {
return user
}
}
</script>⚪ fetchUser, fetchData
Promise 를 리턴하는 함수
await
· JS 는 await 키워드를 만나면 Promise 가 처리될 때까지 대기 후 결과는 그 이후에 반환
· 함수를 호출한 후 함수 본문 중 await 를 사용하면, 실행이 잠시 중단되었다가 promise 가 처리된 후 결과와 함께 실행이 재개됨
· await 는 promise.than 보다 좀 더 가독성 있고 세련되게 result 값을 얻을 수 있음.
주의점
· async 함수 없이 단독으로 전역 영역에서의 await 은 syntax error 발생
👉 await 키워드는 반드시 async 함수 안에서만 사용
· async 와 await 키워드를 이용하여 "즉시실행 함수"로 호출 시 에러 없이 동작
<script>
(async() => {
let response = await fetch('http://~');
let data = await response.json();
console.log(data);
alert(data);
})();
</script>실행 순서
<script>
async function asyncFunc() {
let data1 = await fetchData1()
let data2 = await fetchData2(data1)
let data3 = await fetchData3(data2)
return data3
}
<< 같음 >>
function promiseFunc() {
return fetchData1()
.than(fetchdata2)
.than(fetchdata3)
}
</script>⚪ await
< then 메서드 체인 > 을 연결한 것처럼 "순서대로" 동작
👉 비동기 코드에 쉽게 순서를 부여 가능
에러 처리
<script>
<< catch 메서드 >>
function fetchData1() {
return request()
.then((response) => response.requestData )
.catch(error => {
// error 발생
})
}
<< try-catch 구문 >>
async function asyncFunc() {
try {
let data1 = await fetchData1()
return fetchData2(data1)
} catch(e) {
console.log("실패: ", e)
}
}
<< try-catch 구문 2 >>
// try-catch 세분화 가능
async function asyncFunc() {
try {
let data1 = await fetchData1()
return fetchData2(data.id)
} catch(e) {
console.log("id load 실패: ", e)
}
try {
let data2 = await fetchData1()
return fetchData1(data.address)
} catch(e) {
console.log("address load 실패: ", e)
}
}
</script>⚪ catch
promise 를 리턴하는 함수의 경우, < catch 메서드 > 를 이용하여 에러를 처리
⚪ try-catch
< async·await > 형태의 비동기 코드 에러 처리가 가능
· catch(e)
parameter ' e ' 는 promise 의 catch 메서드가 받는 반환 값과 동일
async 클래스 메서드
· 메서드 이름 앞에 async 를 추가하면, async 클래스 메서드 선언 가능
👉 async 메서드와 async 함수는 promise 를 반환하고, await 사용 가능
<script>
class Waiter {
async wait() {
return await 1;
}
};
new Waiter().wait().then(alert);
</script>async·await 에러 핸들링
· await 에서 던진 에러는 바로 try-catch 문을 통해서 처리가 가능
<script>
<< try-catch >>
async function errorHandling() {
try {
let res = await fetch('http://~');
let data = await res.json()'
} catch (error) {
// fetch 와 res.json 에서 발생한 에러 모두 처리 가능
alert(error);
}
}
errorHandling();
<< catch >>
async function errorHandling2() {
let res = await fetch('http://~');
};
errorHandling2().catch(alert) // reject 가 반환되어 catch 처리
</script>async·await vs Promise
· async·await 사용 시 await 이 대기 처리, .then 구문 필요 x
· catch 대신 try-catch 사용 가능
· 문법의 제약으로 인해 async 함수 바깥의 최상위 레벨 코드에서는 await 불가
· .then / catch 를 통해 최종 결과나 처리되지 못한 error 핸들링
async 가 아닌 함수에서 async 호출
<script>
async function wait() {
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 1000));
return 10;
}
function solution() {
wait().then(result => alert(result));
}
solution();
</script>