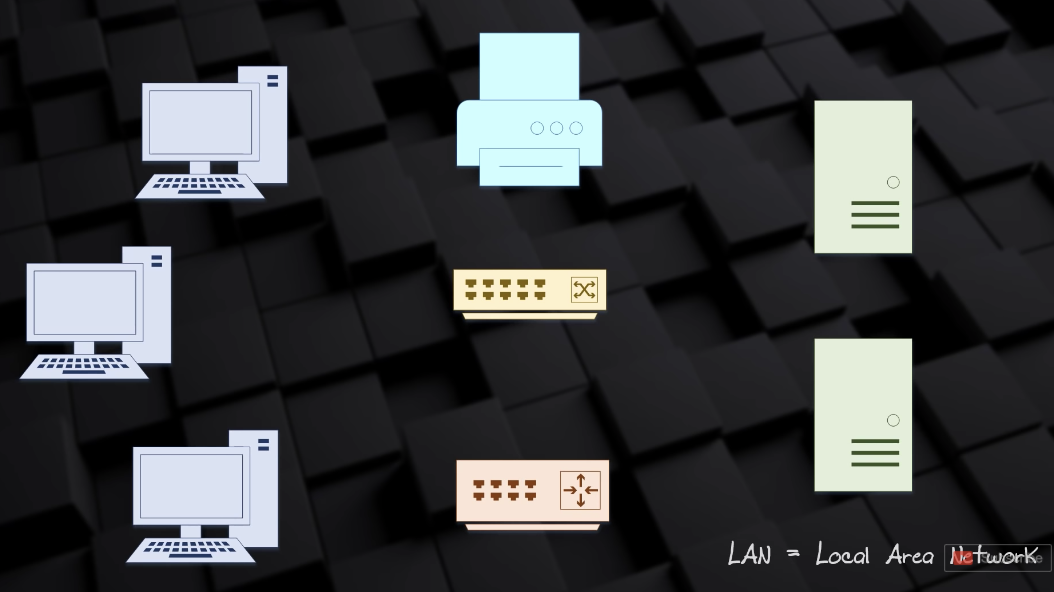
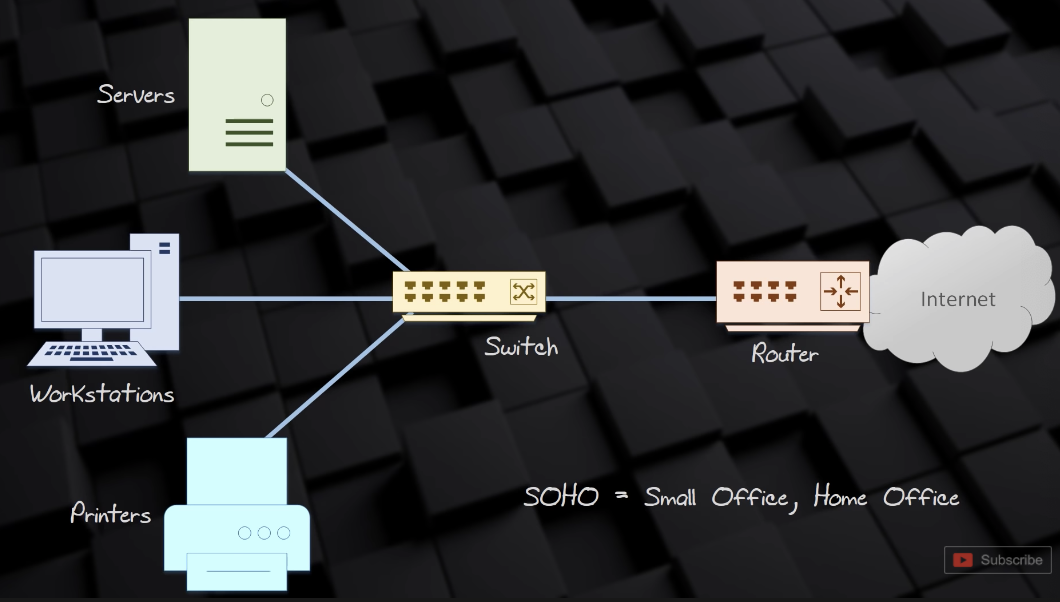
- Networks connect devices
- Devices share information
- To share information, they must speak the same language (Protocol)
Types of Network
SOHO (Small Office, Home Office)
LAN (Local Area Network)
WAN (Wide Area Network)
Cables
Copper
- used for short distances
- uses electric signals
- affected by interference
Fiber
- Made from glasses and more expensive
- uses light signals, thus suitable for long distance
- not affected by outer interference
Ethernet
Media Access Control How data should be formatted and sent
Physical controls speed and volume

Purpose of layering: devices with different cables and different speed still can communicate with each other.
Code number
802 LAN technologies
802.3 Ethernet
i 10Mbps u100Mbps ab1Gbps an10Gbps
For more info:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IEEE_802.3
Copper (UTP-Unshielded Twisted)
- if wires run in parallel, it will create magnetic field and create electricity, affecting signals (crosstalk).
- cables are thus twisted to prevent crosstalk.
Straigh Through Cable
Used to connect host to a switch
Crossover Cable
Used to connect host to host
Auto MDI-X
detecs the cable type and adapts if needed.
2TXs/2RXs. Require Auto MDI-X
4TXs/4TXs. Require Auto MDI-X
Fibers
Full Duplex Send and receive data simultaneously (Dure Core)
Half Duplex Send or Receive at one time (Single Core)
Single Mode Fibre Laser Light, >2km, more expensive
Multi Mode Fibre LED Light, 500m, cheaper
- Only can be bend so far before Attenuation
Attenuation - Degrading Signal or signal loss