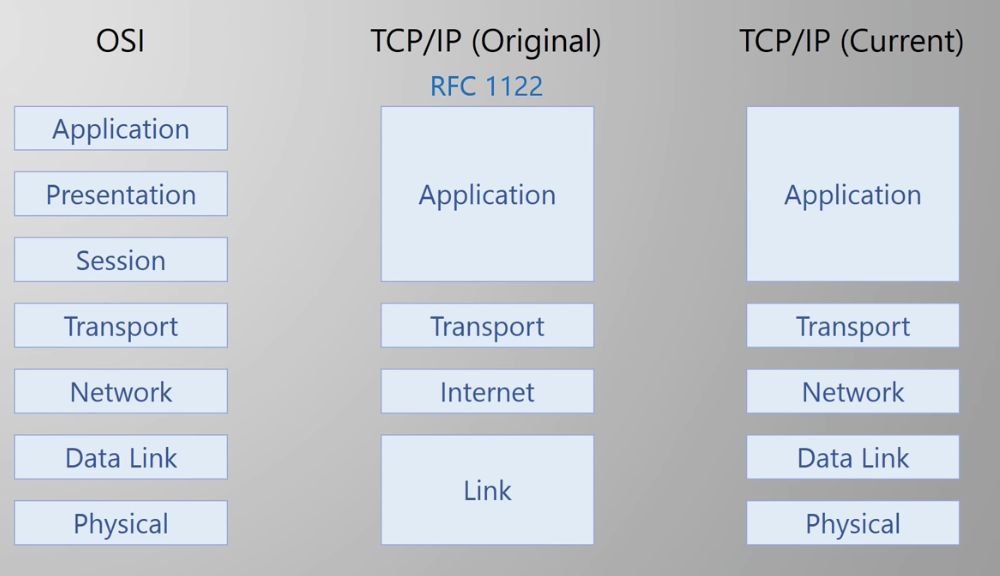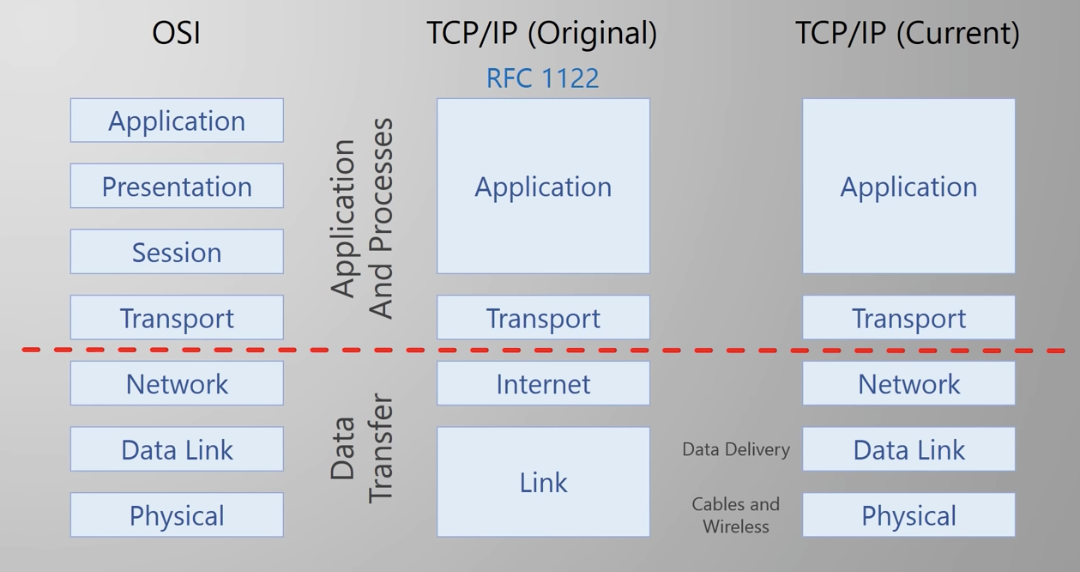
http : protocol that applications used to communicate
Application Web brower (client), Web server software (Server). HTTP DATA is added
Transport creates & maintains coversations between applications processes on hosts (TCP / UDP). Port Number is added
Network IP addresses. Data is broken into packets (manageable chunks of data). Source IP and Destination IP are added to every packet
Data Link Delivery of traffic on a single network segment or LAN. Delivery within a single subnet. (ex. Ethernet: MAC address is assigned). If two hosts are in the same subnet, just send. If in different subnet, it will be sent to a router, then router becomes the source and sent the message to the destination. If several routers are in the path, source addresses will change several times.
Physical Electrical, radio, light signal.(Fiber, copper ...)
TCP & UDP (Transport Layer)
Ports : address for application
Random Ports: 1024 ~ 65535 Well-Known Ports: 0-1023
For info about ports : https://www.iana.org/assignments/service-names-port-numbers/service-names-port-numbers.xhtml?&page=2
Using differerent ports allows multiplexing
Multiplexing allows several applications to access the network simultaneously.
Socket identifies which application the network data belongs to.
However, Single application can access the network many times at once. How with single port?
Now each conversation is truly unique!
TCP
- Additional Features
- Connection Oriented (connection has to be built before sending data and closed after done). This allows
- Error Recovery (Reliable)
- Windowing (Flow control)
- Ordered Data Delivery (Sequence number in the header to track the order that segments shoudl be processed in)
UDP
- Lightwieght & connectionless
- Does not care about errors. (Unreliable)
Ex. realtime application such asvideo streaming, phone cal, etc ...
Establishing TCP Connection (3-way Handshake)
1.SYN:1 Source Port:random Dst Port: server application port Sequence Number: random
2. Switch src and dst port, increment sequence number, set ACK:1 and SYN:1
3. Switch src and dst port, increment sequence number, set ACK:1 and SYN:1
Connection is established!
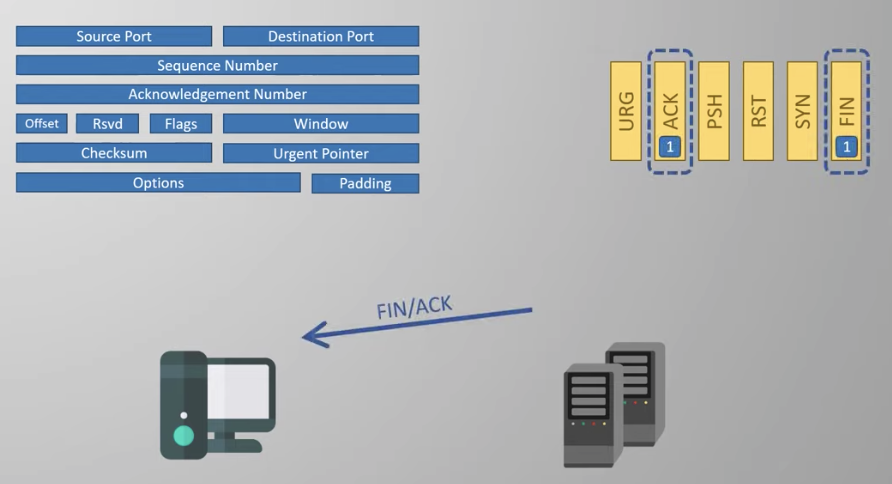
Closing the connection
1. First pair of messages to start the process
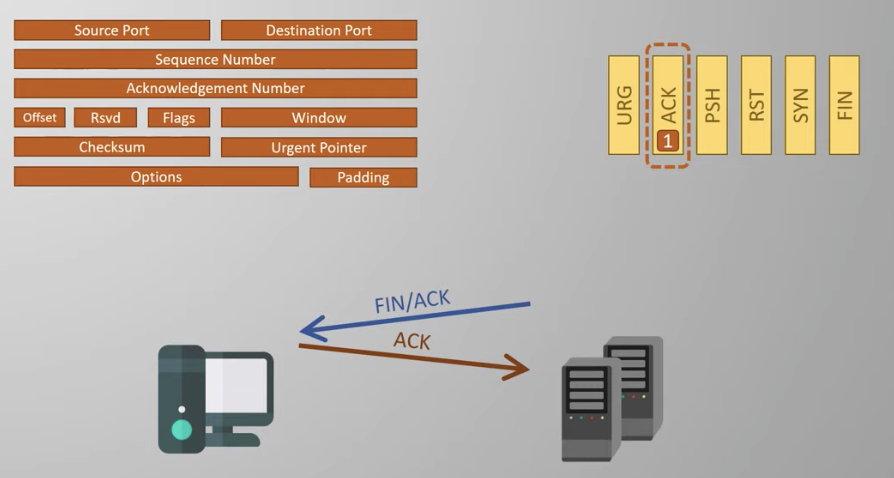
2. The application is notified, which may take a while
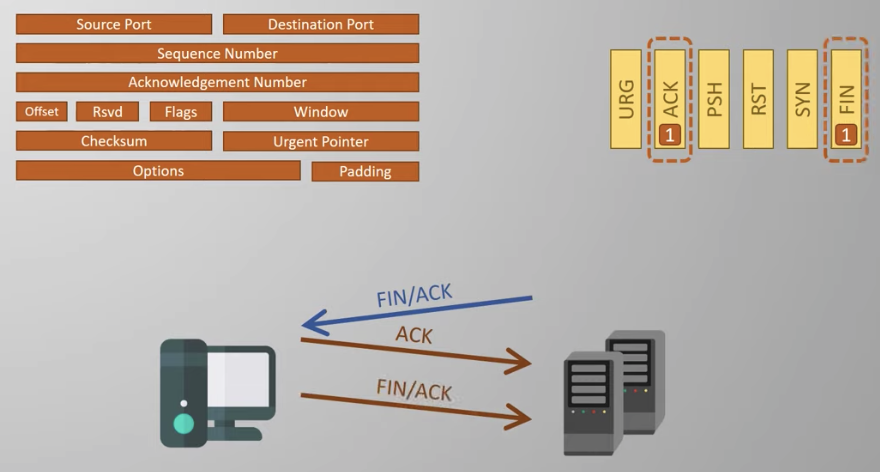
3. The second pair finished the process
You can just drop the connection by...
Only happens if there is an error. If a client is trying to connect to a server that is not open (no application using the port).
Thus, RST messages help with troubleshooting.
Windowing & Error Recovery
Sequence Number
- Counts the number of segment sent back and forth during handshake phase
- After handshake, it counts the number of bytes that have been sent.
Window size determines amount of data that can be acknolwedged in a single message (stored in window).
Sender can keep sending data without receiving ack from receiver untill window size is filled.
In the real world, receiver will not wait for window size to reach 0 before send ACK so that sender does not have to wait for ACK after sending.
Receiver detects missing data by recognizing incorrect sequence number in the message.
Possible solution:
- sends message with sequence number = 400, then sender will send all messages starting from 400 again.
- Selective Acnowledgement (SACK)
Flow Control
- Window size can change during communication. (Sliding Window)
- decrease window size if connection is loosing data, increase window size if connection is reliable and sending all data successfully.