강의 복습 내용
[DAY 12] 최적화
[DLBasic] Optimization
-
Gradient Descent : First-order iterative optimization algorithm for finding a local minimum of a differentiable function.
-
Important Concepts in Optimization
- Generalization : How well the learned model will behave on unseen data.
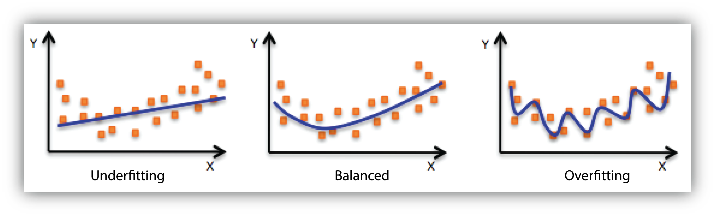
- Under-fitting vs. over-fitting
- Cross validation : Cross-validation is a model validation technique for assessing how the model will generalize to an independent (test) data set.
- Bias-variance tradeoff : We can derive that what we are minimizing (cost) can be decomposed into three different parts: bias^2, variance, and noise.
- Bootstrapping : Bootstrapping is any test or metric that uses random sampling with replacement.
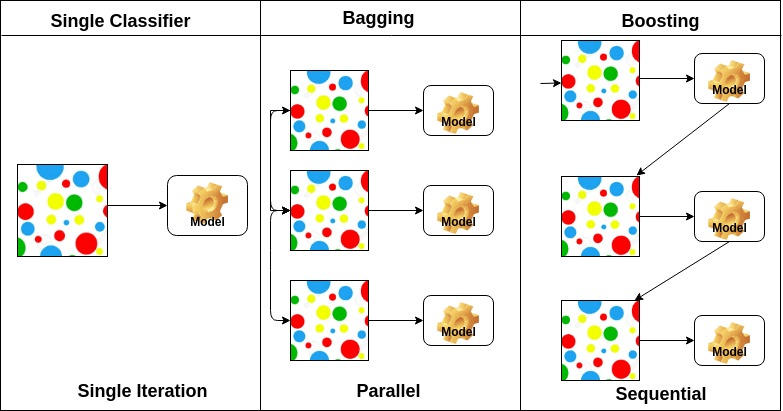
- Bagging and boosting
- Bagging (Bootstrapping aggregating) : Multiple models are being trained with bootstrapping.
- Boosting : It focuses on those specific training samples that are hard to classify. A strong model is built by combining weak learners in sequence where each learner learns from the mistakes of the previous weak learner.
-
Gradient Descent Methods
- Stochastic gradient descent : Update with the gradient computed from a single sample.
- Mini-batch gradient descent : Update with the gradient computed from a subset of data.
- Batch gradient descent : Update with the gradient computed from the whole data.
-
Gradient Descent
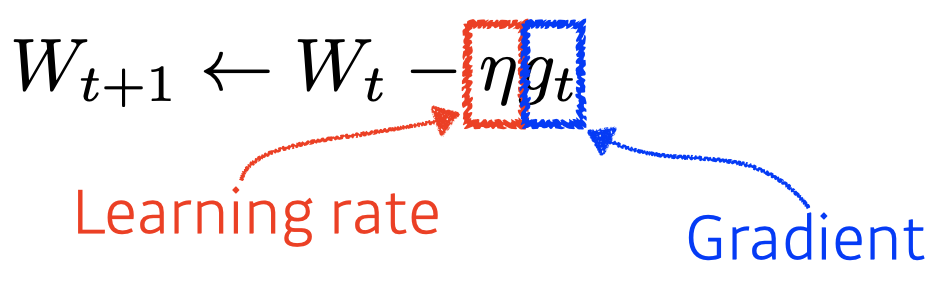
-
Momentum
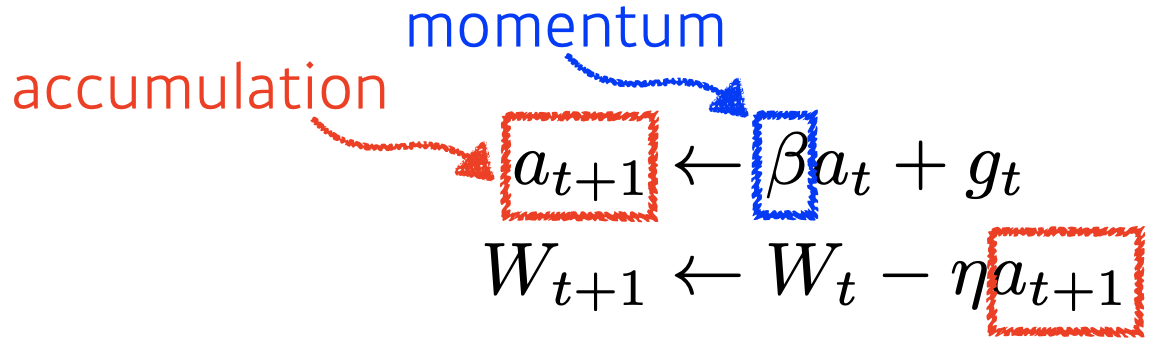
-
Nesterov Accelerated Gradient
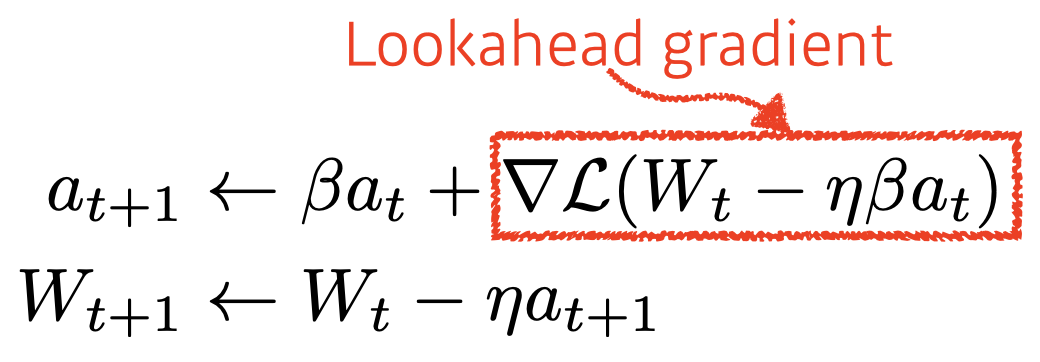
-
Adagrad
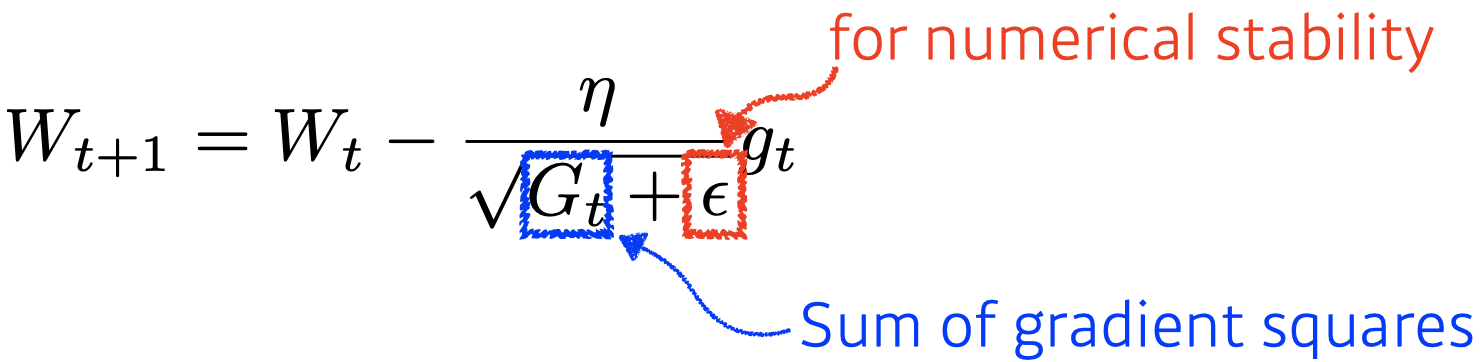
- Adagrad adapts the learning rate, performing larger updates for infrequent and smaller updates for frequent parameters.
-
Adadelta
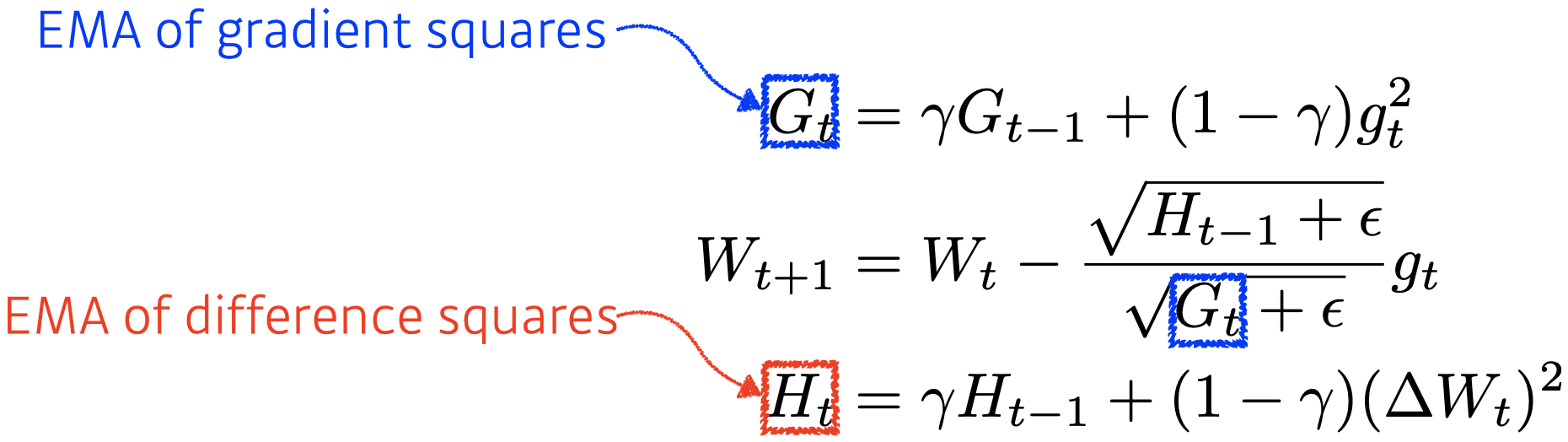
- Adadelta extends Adagrad to reduce its monotonically decreasing the learning rate by restricting the accumulation window.
- There is no learning rate in Adadelta.
-
RMSprop
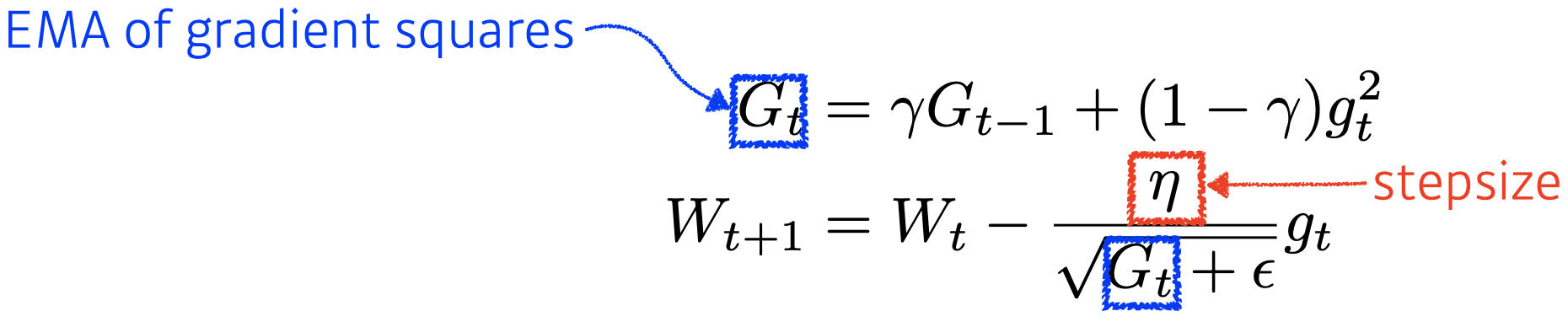
- RMSprop is an unpublished, adaptive learning rate method proposed by Geoff Hinton in his lecture.
-
Adam
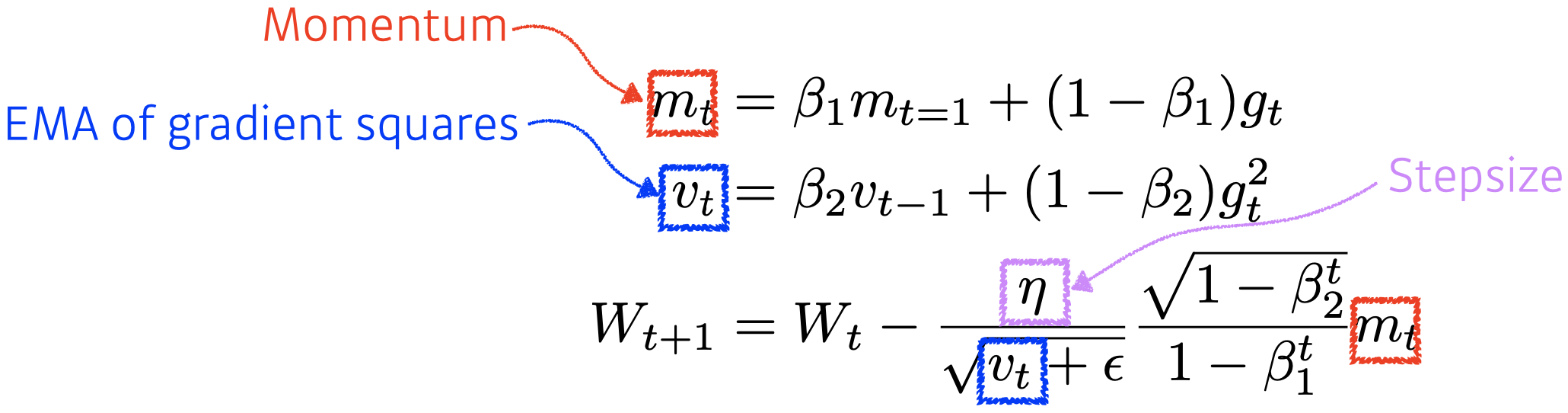
- Adaptive Moment Estimation (Adam) leverages both past gradients and squared gradients.
- Adam effectively combines momentum with adaptive learning rate approach.
-
Regularization
- Early Stopping : Note that we need additional validation data to do early stopping.
- Parameter Norm Penalty : It adds smoothness to the function space.
- Data Augmentation
- More data are always welcomed.
- However, in most cases, training data are given in advance.
- In such cases, we need data augmentation.
- Noise robustness : Add random noises inputs or weights.
- Label smoothing
- Mix-up constructs augmented training examples by mixing both input and output of two randomly selected training data.
- CutMix constructs augmented training examples by mixing inputs with cut and paste and outputs with soft labels of two randomly selected training data.
- Dropout : In each forward pass, randomly set some neurons to zero.
- Batch normalization
- Batch normalization compute the empirical mean and variance independently for each dimension (layers) and normalize.
- There are different variances of normalizations.
[AI Math 9강] CNN 첫걸음
- Convolution 연산 이해하기
- 지금까지 배운 다층신경망(MLP)은 각 뉴런들이 선형모델과 활성함수로 모두 연결된 (fully connected) 구조였습니다.
- Convolution 연산은 이와 달리 커널(kernel)을 입력벡터 상에서 움직여가 면서 선형모델과 합성함수가 적용되는 구조입니다.
- Convolution 연산의 수학적인 의미는 신호(signal)를 커널을 이용해 국소적 으로 증폭 또는 감소시켜서 정보를 추출 또는 필터링하는 것입니다.
- 커널은 정의역 내에서 움직여도 변하지 않고(translation invariant) 주어진 신호에 국소적(local)으로 적용합니다.
- Convolution 연산은 1차원뿐만 아니라 다양한 차원에서 계산 가능합니다.
- 2차원 Convolution 연산 이해하기
- 2D-Conv 연산은 이와 달리 커널(kernel)을 입력벡터 상에서 움직여가면서 선형모델과 합성함수가 적용되는 구조입니다.
- 입력 크기를 (H, W), 커널 크기를 (KH, KW), 출력 크기를 (OH, OW)라 하면 출력 크기는 다음과 같이 계산합니다.
- OH = H - KH + 1
- OW = W - KW + 1
- 3차원 Convolution 연산 이해하기
- 3차원 Convolution 의 경우 2차원 Convolution 을 3번 적용한다고 생각하면 됩니다.
- 텐서를 직육면체 블록으로 이해하면 좀 더 이해하기 쉽습니다.
- Convolution 연산의 역전파 이해하기
- Convolution 연산은 커널이 모든 입력데이터에 공통으로 적용되기 때문에 역전파를 계산할 때도 convolution 연산이 나오게 됩니다.
퀴즈 결과 회고
[AI Math 9강 퀴즈] CNN 첫걸음-1~5
- 다음 보기 중, 연속적인 변수에 대한 함수 f,g 사이의 convolution을 나타내는 수식으로 가장 적절한 것을 고르시오. (O)
- ans : 3
- 입력 벡터 x와 가중치 벡터 V가 다음과 같이 주어질 때, 다음 보기 중 올바른 h를 고르시오. (O)
- ans : 1
- 벡터 x와 h가 다음과 같이 주어질 때, y1 값을 구하시오. (X)
- ans : 4
- 틀린 이유 : 문제 오류
- 입력 행렬 X와 커널 K가 다음과 같이 주어질 때, Y1,2 값을 구하시오. (O)
- ans : 5
- 입력 행렬 X와 커널 K가 다음과 같이 주어질 때, Y2,2 + Y3,3 값을 구하시오. (O)
- ans : 9
Further Question
올바르게(?) cross-validation을 하기 위해서는 어떤 방법들이 존재할까요?
- Exhaustive cross-validation
- Leave-p-out cross-validation
- Leave-one-out cross-validation
- Non-exhaustive cross-validation
- k-fold cross-validation
- Holdout method
- Repeated random sub-sampling validation
- Nested cross-validation
- k*l-fold cross-validation
- k-fold cross-validation with validation and test set
Time series의 경우 일반적인 k-fold cv를 사용해도 될까요?
일반적인 K-fold Cross-Validation을 사용할 경우, 데이터가 뒤섞이기 때문에, Temporal Dependencies인 시계열 데이터에서는 사용해서는 안 됩니다.
따라서, 시계열 데이터에서는 Nested Cross-Validation을 사용하는 것이 좋습니다.
피어 세션 정리
강의 리뷰 및 Q&A
- [DLBasic] Optimization
- [AI Math 9강] CNN 첫걸음
과제 진행 상황 정리 & 과제 결과물에 대한 정리
[DLBasic] Optimization Assignment
Optimization에 대한 것으로, 어렵지 않게 해결했습니다.
총평
기본기가 많이 부족하다고 느낀 하루였습니다.
다음 주 설날을 맞아 휴강이라고 하니, 복습과 재정비의 시간을 가져야겠습니다.
오늘보다 더 성장한 내일의 저를 기대하며, 내일 뵙도록 하겠습니다.
읽어주셔서 감사합니다!
