1. all method
all method도 then method처럼, 새로운 promise 객체를 리턴하긴 하지만, 인자(argument)로 들어온 배열 내 모든 promise 객체가 pending 상태에서 fulfilled 상태가 될 때까지 기다렸다가, 각 promise 객체의 작업 성공 결과들로 이루어진 배열을 작업 성공 결과로 갖게 된다는 차이점이 있다.
때문에, all method는 여러 promise 객체의 작업 성공 결과를 기다렸다가 모두 한 번에 취합해야 하는 상황에서 유용하다.
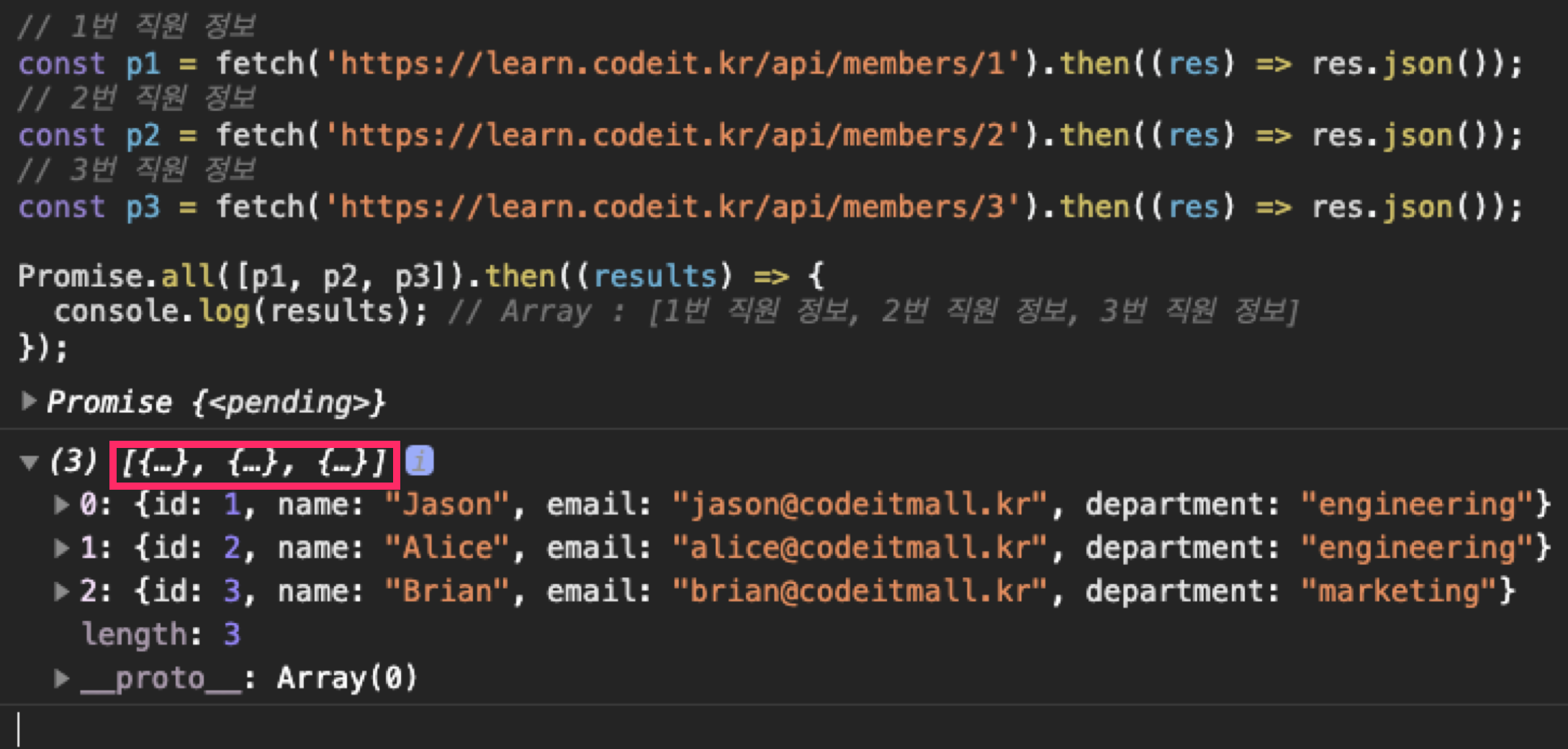
// 1번 직원 정보
const p1 = fetch('https://learn.codeit.kr/api/members/1').then((res) => res.json());
// 2번 직원 정보
const p2 = fetch('https://learn.codeit.kr/api/members/2').then((res) => res.json());
// 3번 직원 정보
const p3 = fetch('https://learn.codeit.kr/api/members/3').then((res) => res.json());
Promise
.all([p1, p2, p3])
.then((results) => {
console.log(results); // Array : [1번 직원 정보, 2번 직원 정보, 3번 직원 정보]
});
그렇다면, 객체들 중 하나라도 rejected 상태가 된다면 어떻게 될까?
이 경우, all method가 리턴한 promise 객체는 rejected 상태가 되고, 그와 동일한 작업 실패 정보를 가져오게 된다.
즉, 하나의 promise 객체라도 rejected 사앹가 되면, 전체 작업이 실패한 것으로 간주되는 것이다.
만약, 이를 해결하고 싶다면, 아래 코드와 같이, catch method를 붙여주면 된다.
// 1번 직원 정보
const p1 = fetch('https://learn.codeit.kr/api/members/1').then((res) => res.json());
// 2번 직원 정보
const p2 = fetch('https://learn.codeit.kr/api/members/2').then((res) => res.json());
// 3번 직원 정보
const p3 = fetch('https://learnnnnnn.codeit.kr/api/members/3').then((res) => res.json());
Promise
.all([p1, p2, p3])
.then((results) => {
console.log(results); // Array : [1번 직원 정보, 2번 직원 정보, 3번 직원 정보]
})
.catch((error) => {
console.log(error);
});2. race method
race method도, all method와 마찬가지로, 여러 promise 객체들이 있는 배열을 인자(argument)로 받고 promise 객체를 리턴하지만, 적용 원리에 차이가 있다.
race method가 리턴한 promise 객체는 argument로 들어온 배열의 여러 promise 객체들 중에서 가장 먼저 fulfilled 상태 또는 rejected 상태가 된 promise 객체와 동일한 상태와 결과를 갖게 된다.
예를 들자면, 아래와 같은 코드에서는, p1 객체가 가장 먼저 fulfilled 상태가 될 것이기 때문에, race method가 리턴한 promise 객체는 p1 객체와 동일한 상태와 결과를 갖게 된다.
const p1 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => resolve('Success'), 1000);
});
const p2 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => reject(new Error('fail')), 2000);
});
const p3 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => reject(new Error('fail2')), 4000);
});
Promise
.race([p1, p2, p3])
.then((result) => {
console.log(result); // hello 출력
})
.catch((value) => {
console.log(value);
});3. allSettled method
allSettled method도, promise 객체 배열을 argument로 받고 promise 객체를 리턴한다는 점은 동일하다.
다만, allSettled method는, 배열 내의 모든 promise 객체가 fulfilled 또는 rejected 상태가 되기까지 기다리고, pending 상태의 promise 객체가 하나도 없게 되면, allSettled method가 리턴한 promise 객체의 상태값은 fulfilled 상태가 되고, 그 작업 성공 결과로 하나의 배열을 갖게 된다.
이 배열에는, argument로 받았던 배열 내의 각 promise 객체의
- 최종 상태를
status프로퍼티로, - 그 작업 성공 결과는
value프로퍼티로, - 작업 실패 정보는
reason프로퍼티에
담은 객체들이 요소로 존재하게 된다.
[
{status: "fulfilled", value: 1},
{status: "fulfilled", value: 2},
{status: "fulfilled", value: 3},
{status: "rejected", reason: Error: an error}
]fulfilled 상태와 rejected 상태를 묶어서 settled 상태라고 하는데, allSettled method는 말 그대로, 배열 속 모든 Promise 객체들이 settled 상태가 되기만 하면 되는 것이라고 이해하면 된다.
4. any method
any method도, promise 객체 배열을 argument로 받고 promise 객체를 리턴한다는 점은 동일하다.
다만, 여러 promise 객체들 중에서, 가장 먼저 fulfilled 상태가 된 promise 객체의 상태와 결과가 any method가 리턴한 promise 객체에도 동일하게 반영된다.
만약, 모든 promise 객체가 rejected 사아태가 되어버리면, AggregateError라고 하는 에러를 작업 실패 정보를 갖고 rejected 상태가 되어버린다.
