정보보안의 기초와 실제 구현
1. 데이터 무결성 검증: 이름 궁합과 Checksum의 이해
체크섬(Checksum)이란?
데이터의 무결성을 검증하는 가장 기본적인 방법입니다.
전송된 데이터가 올바른지 확인하는 간단한 방법입니다.
public class ChecksumExample {
public static int calculateChecksum(String input) {
int checksum = 0;
for (char c : input.toCharArray()) {
checksum += c;
}
return checksum % 256; // 8비트 체크섬
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String message = "Hello, World!";
int checksum = calculateChecksum(message);
System.out.println("Message: " + message);
System.out.println("Checksum: " + checksum);
}
}2. 단방향 암호화의 핵심: 해시 함수의 이해
해시(Hash)의 주요 특징
import java.security.MessageDigest;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
public class HashExample {
public static String calculateSHA256(String input) {
try {
MessageDigest digest = MessageDigest.getInstance("SHA-256");
byte[] hash = digest.digest(input.getBytes());
StringBuilder hexString = new StringBuilder();
for (byte b : hash) {
String hex = Integer.toHexString(0xff & b);
if (hex.length() == 1) hexString.append('0');
hexString.append(hex);
}
return hexString.toString();
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}해시(Hash)의 주요 특징과 각각의 의미, 활용 사례에 대해 자세히 설명해드리겠습니다.
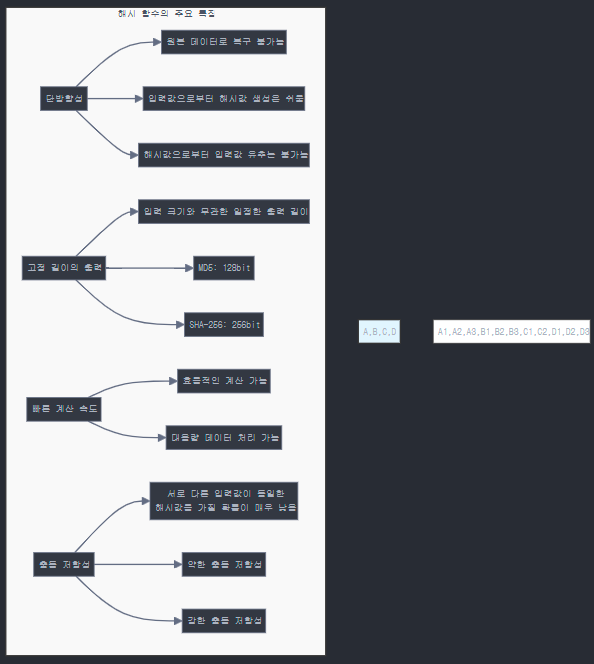
1. 단방향성: 원본 데이터로 복구 불가능
특징
- 해시 함수로 생성된 해시값에서 원본 데이터를 복원할 수 없습니다.
- 입력값으로부터 해시값을 계산하는 것은 쉬습니다.
- 해시값으로부터 입력값을 찾는 것은 계산적으로 불가능 합니다.
활용 사례
- 패스워드 저장: 데이터베이스에 평문 대신 해시값 저장
- 디지털 서명: 메시지의 무결성 검증
- 블록체인: 이전 블록의 해시값을 포함하여 체인 형성
구현 예시
import java.security.MessageDigest;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
public class PasswordHasher {
/**
* 문자열을 SHA-256으로 해싱하고 16진수 문자열로 반환
* @param input 해싱할 문자열
* @return 16진수 형태의 해시값
*/
public static String sha256Hash(String input) throws NoSuchAlgorithmException {
MessageDigest digest = MessageDigest.getInstance("SHA-256");
// 입력 문자열을 바이트 배열로 변환하여 해싱
byte[] hash = digest.digest(input.getBytes());
// 바이트 배열을 16진수 문자열로 변환
StringBuilder hexString = new StringBuilder();
for (byte b : hash) {
String hex = Integer.toHexString(0xff & b);
if (hex.length() == 1) {
hexString.append('0');
}
hexString.append(hex);
}
return hexString.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
String password = "myPassword123";
String hashedPassword = sha256Hash(password);
System.out.println("Original: " + password);
System.out.println("Hashed: " + hashedPassword);
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}이 코드의 주요 특징:
- MessageDigest 클래스를 사용하여 SHA-256 해싱 구현
- 바이트 배열을 16진수 문자열로 변환하는 로직 포함
- 예외 처리를 통한 안전한 구현
사용 예시:
String password = "myPassword123";
String hashedPassword = PasswordHasher.sha256Hash(password);주의사항:
-
이 구현은 기본적인 해싱만 수행하며, 실제 패스워드 저장 시에는 솔트(salt)를 추가하고 더 강력한 해싱 알고리즘(예: PBKDF2, BCrypt)을 사용하는 것이 좋습니다.
-
보안이 중요한 프로덕션 환경에서는 이전에 보여드린 PBKDF2 구현을 사용하는 것을 권장합니다.
2. 고정 길이의 출력 (Fixed Output Length)
특징
입력 데이터의 크기와 관계없이 항상 동일한 길이의 해시값 생성 합니다.
알고리즘별 고정된 출력 길이:
- MD5: 128비트 (16바이트)
- SHA-1: 160비트 (20바이트)
- SHA-256: 256비트 (32바이트)
- SHA-512: 512비트 (64바이트)
활용 사례
- 체크섬(Checksum): 파일 무결성 검증
- 데이터 인덱싱: 고정 길이로 인한 효율적인 저장 및 검색
- 메시지 다이제스트: 통신 프로토콜에서의 메시지 검증
3. 빠른 계산 속도 (Fast Computation)
특징
- 입력값에 대한 해시값 계산이 매우 빠름
- 하드웨어 구현이 용이
- 대용량 데이터 처리에 적합
활용 사례
- 실시간 데이터 무결성 검증
- 대용량 파일 시스템의 중복 검사
- 데이터베이스 인덱싱
- 캐시 키 생성
4. 충돌 저항성 (Collision Resistance)
약한 충돌 저항성 (Weak Collision Resistance)
- 주어진 입력값 x에 대해, 같은 해시값을 가지는 다른 입력값 y를 찾기 어려움
- 첫 번째 역상 저항성(First Pre-image Resistance)이라고도 함
강한 충돌 저항성 (Strong Collision Resistance)
- 같은 해시값을 가지는 서로 다른 두 입력값을 찾기 어려움
- 두 번째 역상 저항성(Second Pre-image Resistance)이라고도 함
활용 사례
- 디지털 서명: 문서의 무결성 보장
- 블록체인: 트랜잭션의 유일성 보장
- 데이터 중복 제거: 파일의 유일성 확인
(*) 보안 고려사항
1.솔트(Salt) 사용
import javax.crypto.SecretKeyFactory;
import javax.crypto.spec.PBEKeySpec;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
import java.security.SecureRandom;
import java.security.spec.InvalidKeySpecException;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Base64;
public class PasswordHasher {
private static final int SALT_LENGTH = 32; // 솔트 길이 (바이트)
private static final int HASH_LENGTH = 256; // 해시 길이 (비트)
private static final int ITERATIONS = 100000; // 반복 횟수
private static final String ALGORITHM = "PBKDF2WithHmacSHA256";
/**
* 비밀번호를 해싱하고 솔트와 함께 반환
* @param password 해싱할 비밀번호
* @return 솔트와 해시를 합친 byte 배열
*/
public static byte[] hashPassword(String password) throws NoSuchAlgorithmException, InvalidKeySpecException {
// 랜덤 솔트 생성
SecureRandom random = new SecureRandom();
byte[] salt = new byte[SALT_LENGTH];
random.nextBytes(salt);
// 비밀번호 해싱
PBEKeySpec spec = new PBEKeySpec(
password.toCharArray(),
salt,
ITERATIONS,
HASH_LENGTH
);
SecretKeyFactory factory = SecretKeyFactory.getInstance(ALGORITHM);
byte[] hash = factory.generateSecret(spec).getEncoded();
// 솔트와 해시 합치기
byte[] combined = new byte[salt.length + hash.length];
System.arraycopy(salt, 0, combined, 0, salt.length);
System.arraycopy(hash, 0, combined, salt.length, hash.length);
return combined;
}
/**
* 저장된 해시값과 비밀번호가 일치하는지 검증
* @param password 검증할 비밀번호
* @param storedHash 저장된 해시 (솔트 + 해시)
* @return 일치 여부
*/
public static boolean verifyPassword(String password, byte[] storedHash)
throws NoSuchAlgorithmException, InvalidKeySpecException {
// 저장된 해시에서 솔트 추출
byte[] salt = new byte[SALT_LENGTH];
System.arraycopy(storedHash, 0, salt, 0, salt.length);
// 저장된 해시값 추출
byte[] hash = new byte[storedHash.length - SALT_LENGTH];
System.arraycopy(storedHash, SALT_LENGTH, hash, 0, hash.length);
// 입력된 비밀번호를 같은 솔트로 해싱
PBEKeySpec spec = new PBEKeySpec(
password.toCharArray(),
salt,
ITERATIONS,
HASH_LENGTH
);
SecretKeyFactory factory = SecretKeyFactory.getInstance(ALGORITHM);
byte[] testHash = factory.generateSecret(spec).getEncoded();
// 해시값 비교
return Arrays.equals(hash, testHash);
}
/**
* Base64로 인코딩된 문자열로 변환
*/
public static String toBase64(byte[] data) {
return Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(data);
}
/**
* Base64 문자열을 byte 배열로 디코딩
*/
public static byte[] fromBase64(String data) {
return Base64.getDecoder().decode(data);
}
// 사용 예시
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// 비밀번호 해싱
String password = "myPassword123";
byte[] hashedPassword = hashPassword(password);
String base64Hash = toBase64(hashedPassword);
System.out.println("Hashed password: " + base64Hash);
// 비밀번호 검증
boolean isValid = verifyPassword(password, hashedPassword);
System.out.println("Password is valid: " + isValid);
// 잘못된 비밀번호 검증
boolean isInvalid = verifyPassword("wrongPassword", hashedPassword);
System.out.println("Wrong password is valid: " + isInvalid);
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException | InvalidKeySpecException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}1. 주요 특징
- PBKDF2WithHmacSHA256 알고리즘 사용
- 32바이트(256비트) 랜덤 솔트
- 100,000회 반복
- 256비트 해시 출력
2. 추가 기능
- 비밀번호 검증 메소드 포함
- Base64 인코딩/디코딩 지원
- 상세한 예외 처리
3. 사용 예시
String password = "myPassword123";
byte[] hashedPassword = PasswordHasher.hashPassword(password);
String base64Hash = PasswordHasher.toBase64(hashedPassword);
// 데이터베이스에 base64Hash 저장
// 나중에 비밀번호 검증시
boolean isValid = PasswordHasher.verifyPassword(
inputPassword,
PasswordHasher.fromBase64(storedHash)
);4.보안 고려사항
- SecureRandom 사용으로 안전한 난수 생성
- 충분한 반복 횟수로 무차별 대입 공격 방지
- 일정한 시간 실행으로 타이밍 공격 방지
- 모든 중간 데이터는 byte[]로 처리
3. 대칭키 암호화 시스템의 이해
AES(Advanced Encryption Standard) 구현 예시
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;
import java.util.Base64;
public class AESExample {
private static final String ALGORITHM = "AES";
public static String encrypt(String value, String key) throws Exception {
SecretKeySpec secretKey = new SecretKeySpec(key.getBytes(), ALGORITHM);
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(ALGORITHM);
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, secretKey);
byte[] encryptedBytes = cipher.doFinal(value.getBytes());
return Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(encryptedBytes);
}
public static String decrypt(String encrypted, String key) throws Exception {
SecretKeySpec secretKey = new SecretKeySpec(key.getBytes(), ALGORITHM);
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(ALGORITHM);
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, secretKey);
byte[] decryptedBytes = cipher.doFinal(Base64.getDecoder().decode(encrypted));
return new String(decryptedBytes);
}
}4. 비대칭키 암호화 시스템의 구현
RSA 암호화 예시
import java.security.*;
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
public class RSAExample {
public static KeyPair generateKeyPair() throws Exception {
KeyPairGenerator generator = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance("RSA");
generator.initialize(2048);
return generator.generateKeyPair();
}
public static byte[] encrypt(String message, PublicKey publicKey) throws Exception {
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("RSA");
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, publicKey);
return cipher.doFinal(message.getBytes());
}
public static String decrypt(byte[] encrypted, PrivateKey privateKey) throws Exception {
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("RSA");
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, privateKey);
byte[] decrypted = cipher.doFinal(encrypted);
return new String(decrypted);
}
}5. 디지털 서명: 전자서명의 이해와 구현
디지털 서명 구현 예시
import java.security.*;
public class DigitalSignatureExample {
public static byte[] createDigitalSignature(String message, PrivateKey privateKey) throws Exception {
Signature signature = Signature.getInstance("SHA256withRSA");
signature.initSign(privateKey);
signature.update(message.getBytes());
return signature.sign();
}
public static boolean verifyDigitalSignature(String message, byte[] signedMessage, PublicKey publicKey) throws Exception {
Signature signature = Signature.getInstance("SHA256withRSA");
signature.initVerify(publicKey);
signature.update(message.getBytes());
return signature.verify(signedMessage);
}
}6. PKI(Public Key Infrastructure) 시스템과 SSL/TLS
SSL 인증서 검증 예시
import javax.net.ssl.*;
import java.security.cert.X509Certificate;
public class SSLExample {
public static void setupSSLContext() throws Exception {
SSLContext sslContext = SSLContext.getInstance("TLS");
TrustManager[] trustManagers = new TrustManager[] {
new X509TrustManager() {
public X509Certificate[] getAcceptedIssuers() { return null; }
public void checkClientTrusted(X509Certificate[] certs, String authType) {}
public void checkServerTrusted(X509Certificate[] certs, String authType) {}
}
};
sslContext.init(null, trustManagers, new SecureRandom());
SSLContext.setDefault(sslContext);
}
}PKI 시스템의 주요 구성요소
PKI(Public Key Infrastructure) 시스템과 SSL/TLS 동작 과정을 자세히 설명해드리겠습니다.
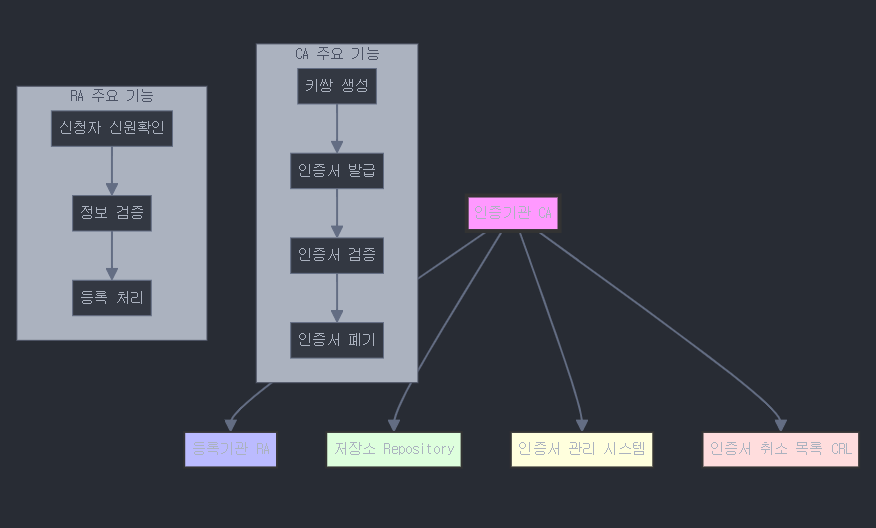
1. 인증기관(CA, Certificate Authority)
- 디지털 인증서를 발급하고 관리하는 최상위 기관
- 공개키 기반의 디지털 인증서를 생성, 발급, 폐기하는 역할 수행
- 신뢰성 있는 제3자 기관으로서 인증서의 무결성과 신뢰성을 보장
예: Verisign, GlobalSign, Let's Encrypt 등
2. 등록기관(RA, Registration Authority)
- CA의 인증서 발급 업무를 대행하는 기관
- 신청자의 신원을 확인하고 인증서 발급 요청을 검증
- 인증서 신청자와 CA 사이의 중개자 역할 수행
- 부하 분산과 효율적인 인증서 관리를 위해 활용
3. 저장소(Repository)
- 발급된 인증서와 인증서 관련 정보를 저장하고 공개
- LDAP(Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) 등을 통해 접근 가능
- 인증서 검증에 필요한 정보를 실시간으로 제공
- 인증서 상태 정보의 투명한 관리를 지원
4. 인증서 관리 시스템
- 인증서의 전체 라이프사이클을 관리하는 시스템
- 인증서 발급, 갱신, 폐기, 관리 등의 기능 제공
- 키 쌍 생성 및 보관 기능 포함
- 인증서 정책 관리 및 감사 기능 지원
5. 인증서 취소 목록(CRL, Certificate Revocation List)
- 폐기되거나 효력이 정지된 인증서 목록
- 주기적으로 업데이트되어 배포
- OCSP(Online Certificate Status Protocol)를 통한 실시간 검증 지원
- 인증서의 유효성을 확인하는 중요한 메커니즘
SSL/TLS 동작 과정 상세 설명
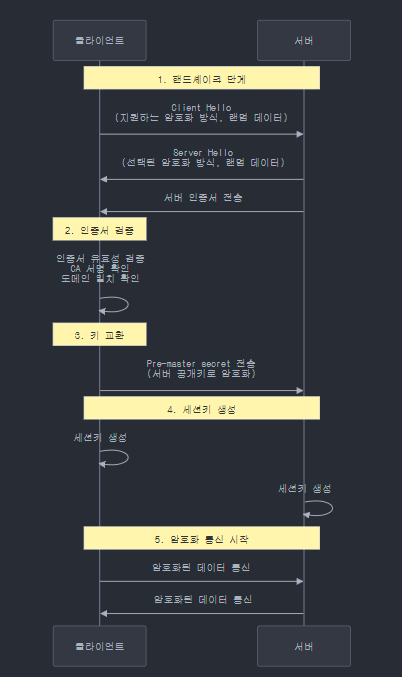
1. 클라이언트 Hello
- 클라이언트가 서버에 연결을 시도하며 다음 정보를 전송
- 지원하는 SSL/TLS 버전
- 지원하는 암호화 알고리즘(Cipher Suite)
- 랜덤 데이터(클라이언트 난수)
2. 서버 Hello 및 인증서 전송
- 서버는 클라이언트의 요청에 응답
- 사용할 SSL/TLS 버전 선택
- 사용할 암호화 알고리즘 선택
- 서버의 디지털 인증서 전송
- 서버 랜덤 데이터 전송
3. 클라이언트의 인증서 검증
- 클라이언트는 서버 인증서의 유효성을 검증
- CA의 서명 확인
- 인증서 유효기간 확인
- 도메인 이름 일치 확인
- CRL/OCSP를 통한 폐기 여부 확인
4. 세션키 교환
- Pre-master secret 생성 및 교환
- 클라이언트가 pre-master secret 생성
- 서버의 공개키로 암호화하여 전송
- 양측에서 동일한 세션키 생성
5. 암호화된 통신 시작
- 생성된 세션키를 사용하여 대칭키 암호화 통신 시작
- 이후의 모든 데이터는 협상된 암호화 알고리즘으로 암호화
- 통신의 기밀성과 무결성 보장
이러한 PKI 시스템과 SSL/TLS 프로토콜은 현대 인터넷 보안의 근간이 되며, 특히 전자상거래, 온라인 뱅킹 등 보안이 중요한 서비스에서 필수적으로 사용됩니다.
