파이썬을 이용한 진법 변환!
오늘은 진법의 정의와 파이썬으로 진법을 표현하는 방법에 대해 알아보겠습니다.
진법 : 진법이란, 특정 숫자 몇 개를 사용하여 수를 표시하는 방법입니다.
예를 들어, 2진법은 0,1 2개를 사용하고, 8진법은 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7이 될 것입니다.
우리가 가장 흔하게 사용하는 진법은 10진법입니다.
10진수를 2진수로 변환은?
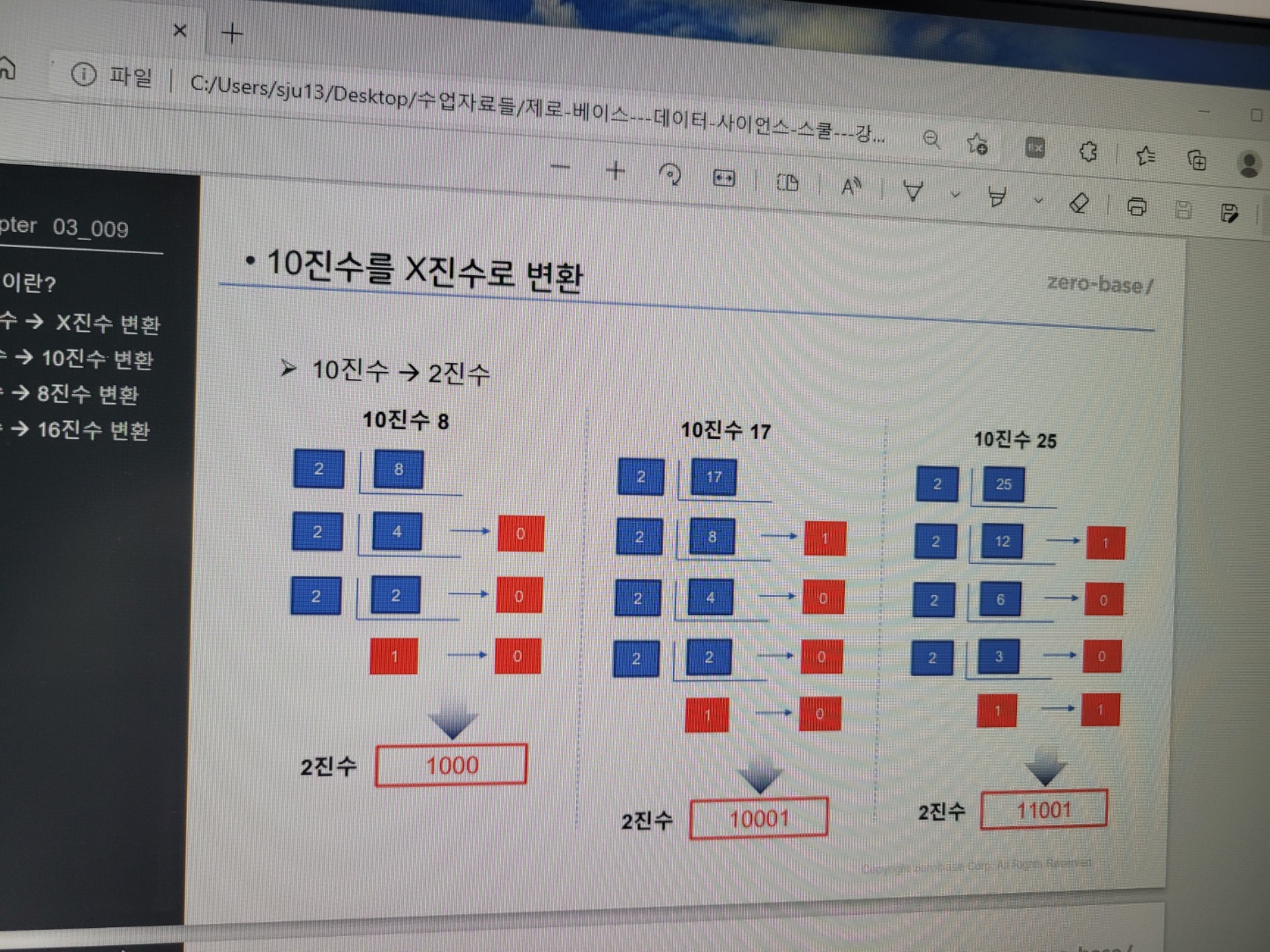
이그림을 참고하면 좋을 것입니다.
10진수를 8진수로 변환은?
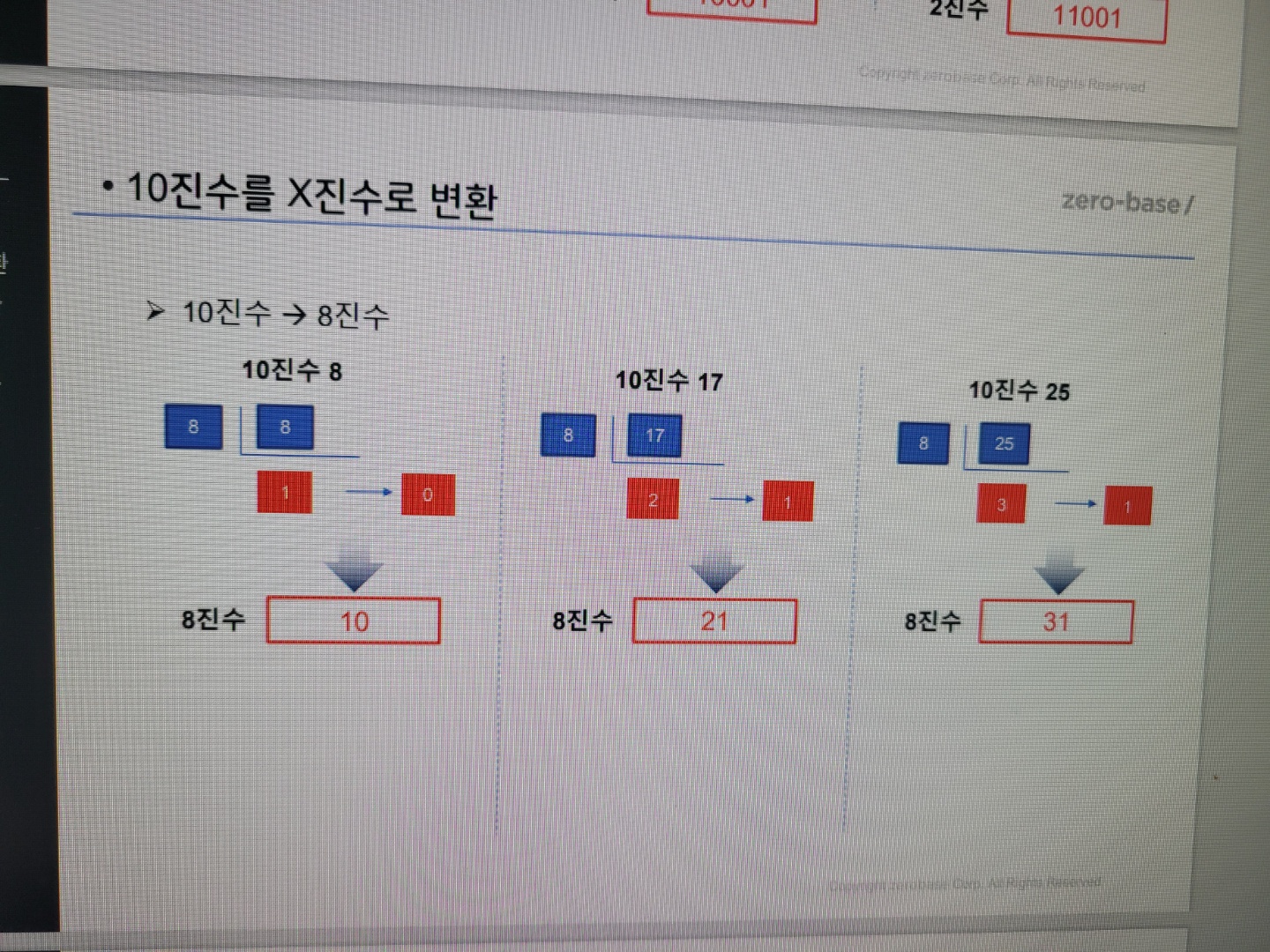
이그림을 참고하면 좋을 것입니다.
10진수를 16진수로 변환은?
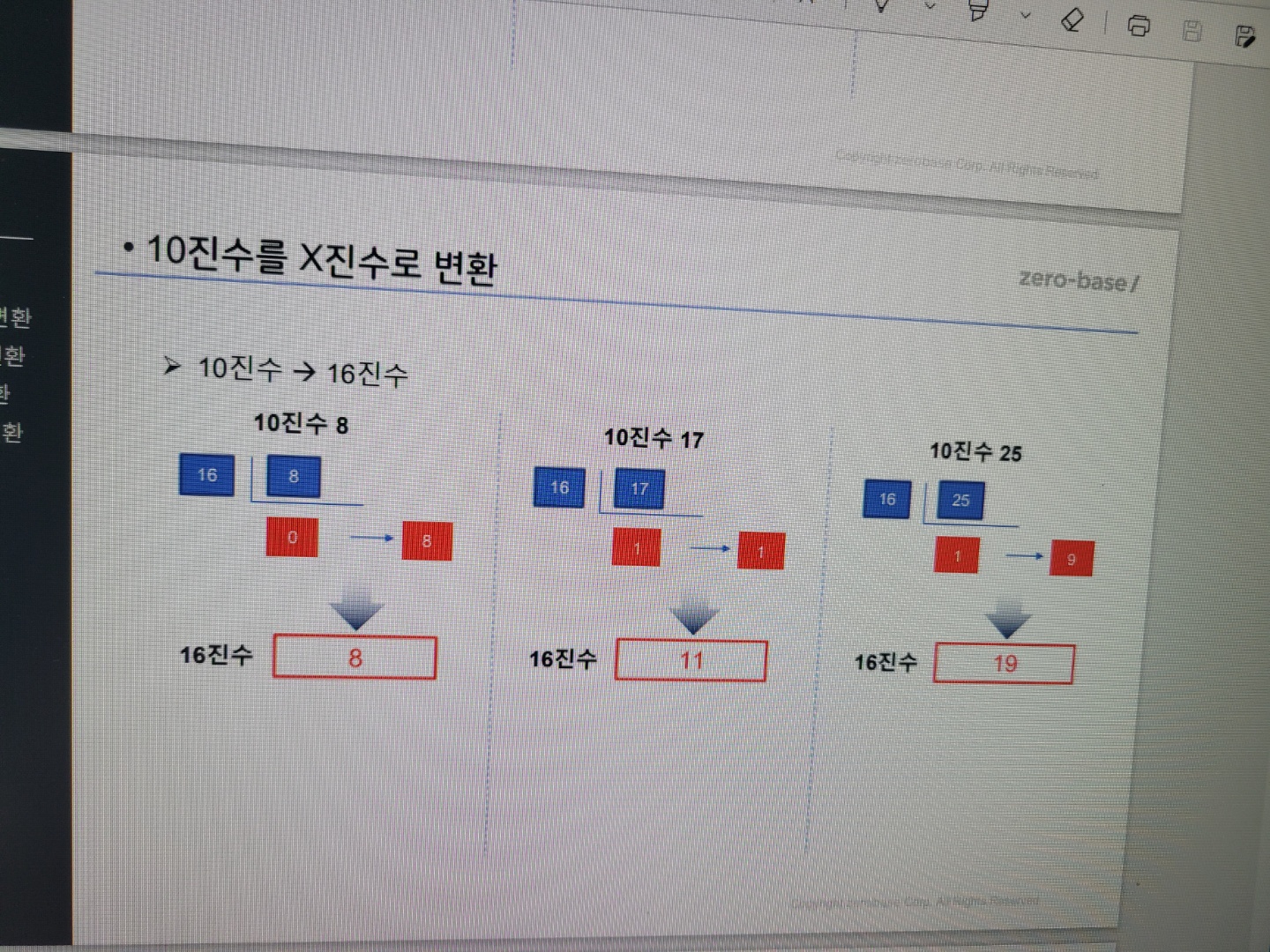
이 그림을 참고하면 좋을 것입니다.
그럼 반대로 X진수를 10진수로 변환 할때는 어떻게 하면 좋을까요?
2진수를 10진수로 변환은?
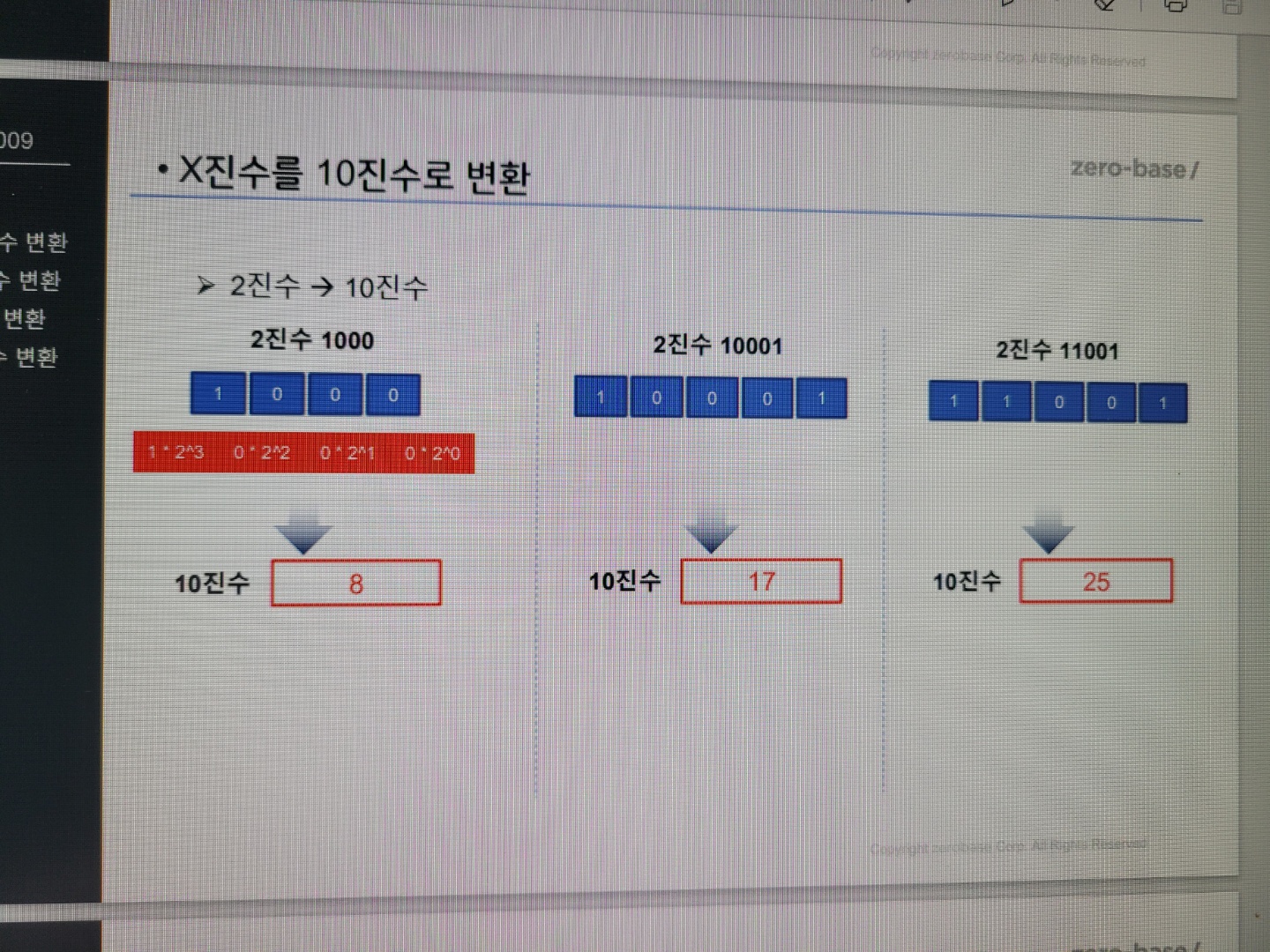
이그림을 참고하면 좋을 것입니다.
8진수를 10진수로 변환은?
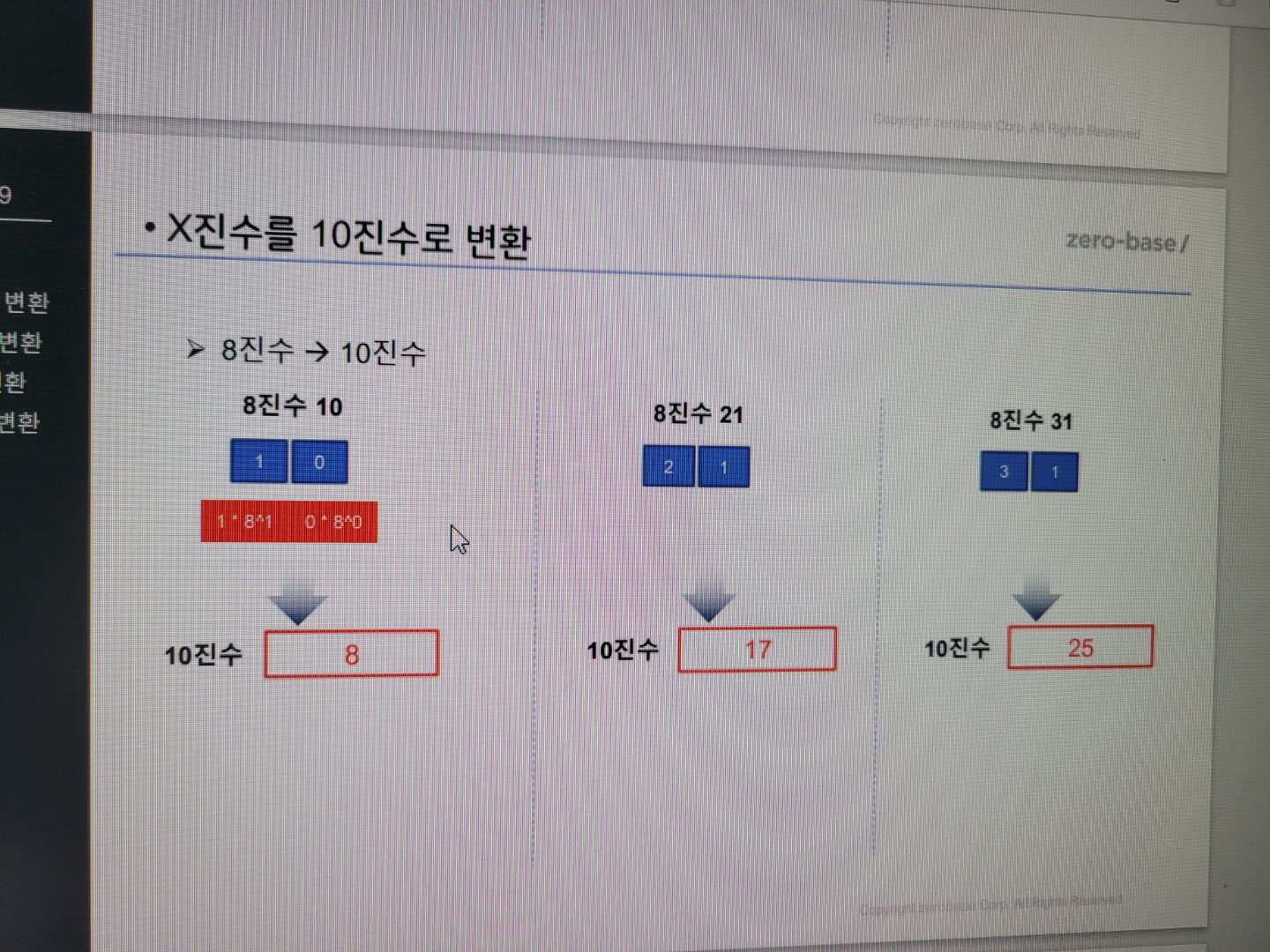
이그림을 참고하면 좋을 것입니다.
**그럼 이제 파이썬으로 진수를 표현하도록 하겠습니다.
10진수 ==> 2진수 , 8진수, 16진수
binary : bin() ====> print('2진수: {}'.format(bin(dNum))
octal : oct() ====> print('8진수: {}'.format(oct(dNum))
Hexadecimal : hex() ===> print('16진수: {}'.format(hex(dNum))
=====> 2진수 : 0b1110
8진수 : 0o36
16진수 : 0x1e
10진수 -> 2진수, 8진수, 16진수
print('Type of bin(dNum): {}'.format(type(bin(dNum))))
print('Type of oct(dNum): {}'.format(type(oct(dNum))))
print('Type of hex(dNum): {}'.format(type(hex(dNum))))
===> 그러면 Type of bin(dNum): <class 'str'>
Type of oct(dNum): <class 'str'>
Type of hex(dNum): <class 'str'> ===> 셋다 변환 결과는
문자열!!
10진수
print('2진수: {}'.format(format(dNum, '#b')))
print('8진수: {}'.format(format(dNum, '#o')))
print('16진수: {}'.format(format(dNum, '#x')))
print('Type of bin(dNum): {}'.format(type(format(dNum, '#b'))))
print('Type of oct(dNum): {}'.format(type(oct(dNum, '#o'))))
print('Type of hex(dNum): {}'.format(type(hex(dNum, '#x'))))
=====> 2진수 : 0b11110 , 8진수 : 0o36 , 16진수 0x1e
Type of bin(dNum) : <class 'str'>
Type of oct(dNum) : <class 'str'>
Type of hex(dNum) : <class 'str'>
x진수를 10진수로 변환
x진수 -> 10진수
print('2진수(0b11110) -> 10진수({})'.format(int('ob11110', 2)))
print('8진수(0o36) -> 10진수({})'.format(int('0o36', 8)))
print('16진수(0x1e) -> 10진수({})'.format(int('0x1e', 16)))
===> 2진수(0b11110) -> 10진수(30)
8진수(0o36) --> 10진수(30)
16진수(ox1e) ---> 10진수(30)
**** x진수를 x진수로 변환
1) 2진수를 x진수로!
print('2진수(0b11110) -> 8진수({})'.format(oct(0b11110)))
print('2진수(0b11110) -> 10진수({})'.format(int(0b11110)))
print('2진수(0b11110) -> 16진수({})'.format(hex(0b11110)))
===> 2진수(0b11110) -> 8진수(0o36)
2진수(0b11110) -> 10진수(30)
2진수(0b11110) -> 16진수(0x1e)
2) 8진수를 x진수로!
print('8진수(0o36) -> 2진수({})'.format(bin(0o36)))
print('8진수(0o36) -> 10진수({})'.format(int(0o36)))
print('8진수(0o36) -> 16진수({})'.format(bin(0o36)))
===> 8진수(0o36) -> 2진수(0b11110)
8진수(0o36) -> 10진수(30)
8진수(0o36) -> 16진수(0x1e)
3) 16진수를 x진수로!
print('16진수(0x1e) -> 2진수({})'.format(bin(0x1e)))
print('16진수(0x1e) -> 8진수({})'.format(oct(0x1e)))
print('16진수(0x1e) -> 10진수({})'.format(int(0x1e)))
===> 16진수(0x1e) -> 2진수(ob11110)
16진수(ox1e) -> 8진수(0o36)
16진수(ox1e) -> 10진수(30)
