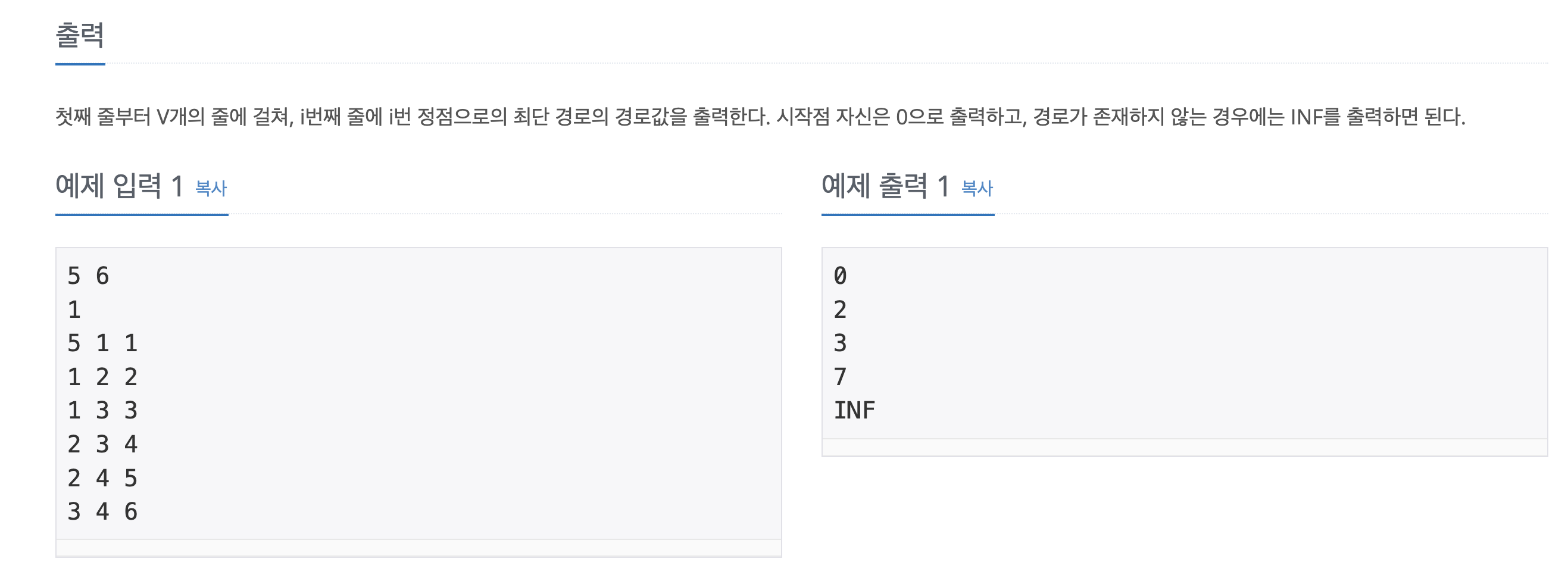
🌱 문제
🌱 풀이
최단경로 문제 푸는 방법
- 가중치 개념이 없는 단순 최소 경로 문제 →
BFS- 가중치 개념이 있고, 한 노드 기준으로 다른 노드까지의 최소 경로를 구하는 문제 →
다익스트라✅- 가중치 개념이 있고, 모든 노드 기준으로 다른 노드까지의 최소 경로를 구하는 문제 →
플로이드 와샬
풀이 과정
(1 ≤ V ≤ 20,000, 1 ≤ E ≤ 300,000)정점 갯수 크기가 꽤나 크기 때문에 인접행렬 대신 인접리스트에 간선 정보를 저장하였다.
- 인접리스트를 만들고, 초기 거리 배열을 최댓값으로 초기화 한다.
- 주어진 시작 정점에서 bfs를 시작한다.
- 다음 지점을 갈 때, 현재 지점을 거쳐서 가는 경우가 더 최단경로라면 최댓값 배열을 갱신하고 이 경우에만 queue에 넣는다. ⇒ 이것이
다익스트라방식이다.
주의할 점
- 처음에는 그냥 Queue를 통해 다익스트라를 진행했는데 시간초과가 났다.
- 그래서 PriorityQueue를 통해 가중치가 작은 순으로 큐에 들어가게 함으로써 해결했다.
1. 인접 리스트 생성하고, 거리 배열 초기화 하기
edges = new ArrayList[V+1];
for(int i=0; i<=V; i++) {
edges[i]= new ArrayList<Info>(); // 리스트배열 초기화
dist[i]=Integer.MAX_VALUE; // 거리배열 최댓값으로 초기화
}
for(int i=0; i<E; i++) {
int from, to, w;
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
from= Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
to=Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
w=Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
edges[from].add(new Info(to, w)); // 인접리스트 생성
}2. 다익스트라 진행
dist[K]=0; // 시작지점에서 시작지점까지의 거리는 0이다.
PriorityQueue<Info> queue = new PriorityQueue<Info>((o1,o2)->o1.w-o2.w); // 가중치 기준 오름차순 정렬
// Queue<Integer> queue= new ArrayDeque<Integer>(); // 그냥 queue는 시간초과 발생
queue.add(new Info(K,0));
while(!queue.isEmpty()) { // 다익스트라 시작
Info cur = queue.poll();
for(int i=0; i<edges[cur.to].size(); i++ ) {
Info next= edges[cur.to].get(i);
if(dist[next.to]>dist[cur.to]+next.w) {// 다음 정점을 갈 때, 현재 정점을 거쳐서 가는경로가 최단경로일 경우, 거리값 갱신하고 queue에 넣기.
dist[next.to]=dist[cur.to]+next.w;
queue.add(new Info(next.to,dist[next.to]));
}
}
}3. 정답 출력
- 거리값 배열이 처음 초기화한 그래도 최댓값이라면 경로가 없는것이기 때문에 INF 출력
- 출력이 많아지면
sysout으로는 시간초과가 날 수 있으므로StringBuilder를 이용하였다.
for(int i=1; i<=V; i++) {
if(dist[i]==Integer.MAX_VALUE)
sb.append("INF").append("\n");
else
sb.append(dist[i]).append("\n");
}
System.out.println(sb);🌱 코드
package Dec_week04;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
//1753. 최단 경로
public class boj_1753 {
static class Info{
int to; // 경로의 도착지점 번호
int w; // 경로의 가중치
public Info(int to, int w) {
this.to=to;
this.w=w;
}
}
static int V,E,K; // 정점 갯수, 간선 갯수, 시작 번호
static ArrayList<Info> edges[];
static int dist[];
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
V=Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
E=Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
K=Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
dist= new int[V+1];
edges = new ArrayList[V+1];
for(int i=0; i<=V; i++) {
edges[i]= new ArrayList<Info>(); // 리스트배열 초기화
dist[i]=Integer.MAX_VALUE; // 거리배열 최댓값으로 초기화
}
for(int i=0; i<E; i++) {
int from, to, w;
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
from= Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
to=Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
w=Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
edges[from].add(new Info(to, w)); // 인접리스트 생성
}
dist[K]=0;
PriorityQueue<Info> queue = new PriorityQueue<Info>((o1,o2)->o1.w-o2.w); // 가중치 기준 오름차순 정렬
// Queue<Integer> queue= new ArrayDeque<Integer>(); // 그냥 queue는 시간초과 발생
queue.add(new Info(K,0));
while(!queue.isEmpty()) { // 다익스트라 시작
Info cur = queue.poll();
for(int i=0; i<edges[cur.to].size(); i++ ) {
Info next= edges[cur.to].get(i);
if(dist[next.to]>dist[cur.to]+next.w) {// 다음 정점을 갈 때, 현재 정점을 거쳐서 가는경로가 최단경로일 경우, 거리값 갱신하고 queue에 넣기.
dist[next.to]=dist[cur.to]+next.w;
queue.add(new Info(next.to,dist[next.to]));
}
}
}
for(int i=1; i<=V; i++) {
if(dist[i]==Integer.MAX_VALUE)
sb.append("INF").append("\n");
else
sb.append(dist[i]).append("\n");
}
System.out.println(sb);
}
}
참고한 블로그 - https://bangu4.tistory.com/276
