재귀 Tree Traversal은 두가지 형태가 있다.
- 트리를 변경하거나 새로 생성하는 경우
Tree *dfs(...) {
root->left = dfs(...);
root->right = dfs(...);
return root;- 이미 만들어진 트리를 탐색하는 경우
void dfs(root) {
dfs(root->left);
dfs(root->right);270. Closest Binary Search Tree Value
문제
주어진 target값이 트리 노드중에 어떤값과 가장 가까운지 찾아라.
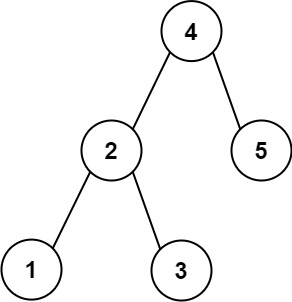
Input: root = [4,2,5,1,3], target = 3.714286
Output: 4해결
해당 값을 binary search하여 찾음. (해설 답안은 더 간결한데 확인해볼것 https://leetcode.com/problems/closest-binary-search-tree-value/solution/)
class Solution {
public:
int closestValue(TreeNode* root, double target) {
int left_most = -1;
int right_lest = -1;
TreeNode *node = root;
while (node) {
if (target < (double)node->val) {
right_lest = node->val;
node = node->left;
} else if ((double)node->val < target) {
left_most = node->val;
node = node->right;
} else { // node->val == target
return node->val;
}
}
if (left_most == -1 && right_lest != -1)
return right_lest;
else if (left_most != -1 && right_lest == -1)
return left_most;
// left_most target right_lest
double a = right_lest - (double)target;
double b = (double)target - left_most;
return a > b ? left_most : right_lest;
}
};814. Binary Tree Pruning
문제
0과1로 이루어진 이진트리에서 자식트리에 1이 없는 노드를 삭제해라.
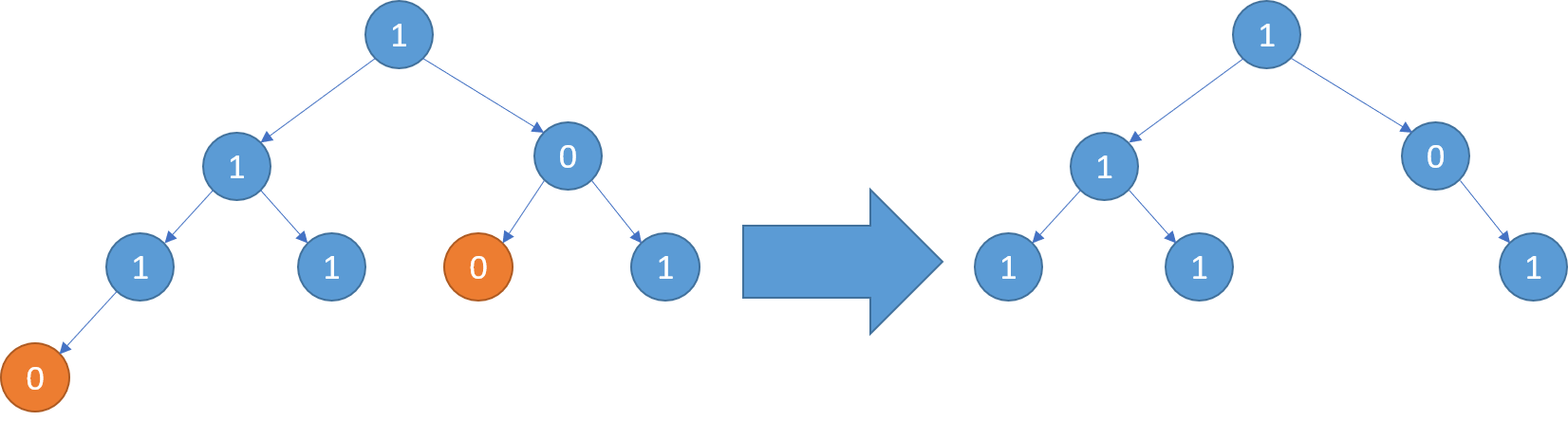
해결
0 ms, faster than 100.00% of C
leaf노드가 0일때 NULL을 리턴 -> 이걸 재귀적으로(후위 순회) 반복. 처음에 pre order 순으로 체크했다가 에러발생, post order로 해야함.
struct TreeNode* pruneTree(struct TreeNode* root){
if (root == NULL)
return NULL;
root->left = pruneTree(root->left);
root->right = pruneTree(root->right);
if (root && root->val == 0 && !root->left && !root->right)
return NULL;
return root;
}199. Binary Tree Right Side View
문제
주어진 트리를 우측에서 바라볼때 노드 값을 리턴하라.

해결
BFS로 순회. root부터 queue에 넣고, pop하면서 처음으로 height가 커질때마다 값들을 ret Vector에 저장. 아주 흥미로운 문제 였다.
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> rightSideView(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> ret;
queue<pair<TreeNode *, int>> q;
int cur_h = 0;
if (root)
q.push(make_pair(root, cur_h + 1));
while (!q.empty()) {
pair<TreeNode *, int> check = q.front();
q.pop();
TreeNode *node = check.first;
if (check.second > cur_h) {
ret.push_back(node->val);
cur_h = check.second;
}
if (node->right)
q.push(make_pair(node->right, cur_h + 1));
if (node->left)
q.push(make_pair(node->left, cur_h + 1));
}
return ret;
}
};99. Recover Binary Search Tree
문제
딱 한쌍의 노드를 swap해야 정상적인 BST가 되는 트리가 주어진다. 이 트리를 BST로 고쳐라.
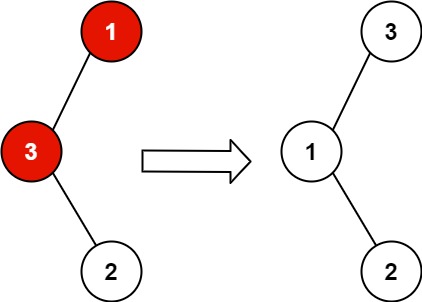
아이디어
- 기본적으로 tree를 inorder 순회
- 순회하면서 두개의 노드를 선정하는 방법.
- 잘못된 지점은 BST는 순회시 현재 노드가 이전노드보다 값이 작을 때.
- 순회시 첫번째로 발견된 지점과 마지막으로 발견된 지점이 최종 swap대상이다. 아래 코드는 이걸 찾는 알고리즘이다. (해설을 참고함)
- 순회 순서상 첫번째로 만나는 target 1은 처음 정렬상태가 어긋나는 노드이다. 이걸 찾고 고정한다(아래
if (n1 == NULL) n1 = prev;부분). 그 뒤 계속 순회를 하면서 target 1과 비교해서 정렬이 마지막으로 어긋나는 노드를 target2 로 선정. - 왜 처음과 마지막지점을 찾으면 답이 되는가? 이유는 딱 한쌍의 노드만 잘못배치되어 있기 때문이다.
- 결국 입력은 패턴이 있는데, 순회 순서가
5-2-3-4-14-2-3-15-3-11-3-2-4이런 종류만 트리의 입력으로 들어올 수 있음.정렬---(target1)---정렬----(target2)---정렬(정렬 지점은 없을수도 있음)
- 결국 입력은 패턴이 있는데, 순회 순서가
해결 O(N) / O(1)
struct TreeNode *n1 = NULL, *n2 = NULL, *prev = NULL;
void inorder(struct TreeNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
inorder(root->left);
//printf("%d ", root->val);
if (prev && root->val < prev->val) {
n2 = root; // search the final target 2
if (n1 == NULL) n1 = prev; // fix the target 1
else return;
}
prev = root;
inorder(root->right);
return;
}
void swap(struct TreeNode* a, struct TreeNode* b)
{
if (!a || !b)
fprintf(stderr, "failed to find targets\n");
int tmp = a->val;
a->val = b->val;
b->val = tmp;
}
void recoverTree(struct TreeNode* root){
n1 = NULL, n2 = NULL, prev = NULL;
inorder(root);
swap(n1, n2);
return;
}98. Validate Binary Search Tree
문제
주어진 트리가 BST(Binary Search Tree)를 만족하는지 확인하라
- left 자식트리의 모든 노드 값이 루트노드 보다 작아야한다.
- right 자식트리의 모든 노드 값이 루트노드 보다 커야한다.
- left, right 의 subtree 모두 BST를 만족한다.

해결 O(n) / O(2n)
정렬된 트리이니, Inorder 트리 순회를 하면서 값을 vector에 push_back(). vector의 마지막 값이 현재 노드의 값보다 크면 BST를 만족하지 못함. 문제는 공간복잡도가 콜스택 O(n)에 추가로 vector O(n)이다.
class Solution {
bool inorder(TreeNode* root, vector<int> &arr) {
if (root == NULL)
return true;
if (!inorder(root->left, arr))
return false;
//cout << root->val << " ";
if (!arr.empty() && arr.back() >= root->val)
return false;
arr.push_back(root->val);
if (!inorder(root->right, arr))
return false;
return true;
}
public:
bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> arr;
return inorder(root, arr);
}
};해결 O(n)/ O(n)
생각해보면 vector에 모든 값을 저장할 필요가 없음. prev변수 하나만 비교해도됨. 아래와 같이 코드 개선. 공간복잡도는 콜스택 O(n) 만 사용.
class Solution {
TreeNode* prev = NULL;
bool inorder(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL)
return true;
if (!inorder(root->left))
return false;
/* inorder traval */
if (prev && prev->val >= root->val)
return false;
prev = root;
return inorder(root->right);
}
public:
bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root) {
return inorder(root);
}
};102. Binary Tree Level Order Traversal
문제
트리를 순회하는데 동일한 level에 있는 노드끼리 분류해서 값을 리턴하라. 아래 output참고.

Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: [[3],[9,20],[15,7]]해결 (DFS)
dfs 순회 하면서 2차원 벡터의 level 인덱스에 값을 push_back()한다. 문제는 level인덱스가 없을때인데, 그 조건은 ret.size()가 level과 같거나 작다면 아직 level인덱스에 값이 없다는 뜻이다. 그 조건일때만 첫 벡터를 생성해서 push_back() 한다.
class Solution {
void level_order_travel(TreeNode *root, int level, vector<vector<int>> &ret) {
if (root == NULL)
return;
if (ret.size() <= level) { /* there is no ret[level], need to addsign a new vector */
vector<int> lv;
lv.push_back(root->val);
ret.push_back(lv);
} else {
ret[level].push_back(root->val);
}
level_order_travel(root->left, level + 1, ret);
level_order_travel(root->right, level + 1, ret);
}
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> ret;
level_order_travel(root, 0, ret);
return ret;
}
};해결 (BFS)
BFS순회를 하면서, 현재 높이를 기록해뒀다가 증가하면 저장.
https://velog.io/@soopsaram/Leetcode-199.-Binary-Tree-Right-Side-View 풀이와 동일하게 BFS순회 함.
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> ret;
if (root == NULL)
return ret;
vector<int> tmp;
queue<pair<TreeNode *, int>> q;
int prev_height = 0;
if (root)
q.push(make_pair(root, prev_height + 1));
while (!q.empty()) {
pair<TreeNode *, int> check = q.front();
q.pop();
TreeNode *node = check.first;
int cur_h = check.second;
if (cur_h == prev_height + 2) { // insert tmp to ret
ret.push_back(tmp);
prev_height++;
tmp.clear();
}
if (cur_h == prev_height + 1) { // make tmp (current height's vector)
tmp.push_back(node->val);
}
if (node->left) q.push(make_pair(node->left, cur_h + 1));
if (node->right) q.push(make_pair(node->right, cur_h + 1));
}
ret.push_back(tmp); // insert the last tmp
return ret;
}
};
589. N-ary Tree Preorder Traversal
문제
바이너리 트리가 아니라, 자식이 여러개인 트리를 preorder 순회하라.

Input: root = [1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6]
Output: [1,3,5,6,2,4]해결
사실 바이너리 트리랑 순회순서가 동일하다. 루트노드를 저장한뒤, 바이너리 트리가 left/right를 재귀로 순회했다면, 여기서는 child1,child2...childN 순차적으로 재귀를 호출하면 된다.
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
vector<Node*> children;
Node() {}
......
};
*/
class Solution {
void dfs_preorder(Node *root, vector<int> &ret) {
if (root == NULL)
return;
ret.push_back(root->val);
for (auto n: root->children) {
dfs_preorder(n, ret);
}
}
public:
vector<int> preorder(Node* root) {
vector<int> ret;
dfs_preorder(root, ret);
return ret;
}
};366. Find Leaves of Binary Tree
문제
아래 동작을 수행하는 코드를 작성해라.
- 리프노드를 출력하고
- 출력한 리프노드 제거
- 트리가 empty가 될때까지 반복
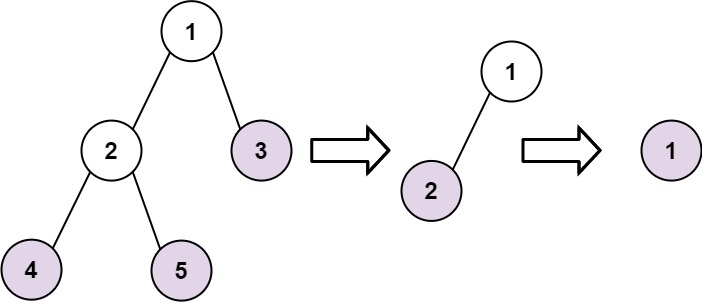
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5]
Output: [[4,5,3],[2],[1]]해결
현재 트리의 leef node를 출력하고 제거하는걸 계속 반복.
class Solution {
TreeNode *dfs(TreeNode *node, vector<int> &leef) {
if (!node)
return NULL;
if (!node->left && !node->right) {
leef.push_back(node->val);
return NULL;
}
node->left = dfs(node->left, leef);
node->right = dfs(node->right, leef);
return node;
}
public:
vector<vector<int>> findLeaves(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> ret;
TreeNode *n = NULL;
do {
vector<int> leef;
n = dfs(root, leef);
ret.push_back(leef);
} while(n);
return ret;
}
};114. Flatten Binary Tree to Linked List
문제
주어진 이진 트리를 링크드 리스트로 변환하라. 리스트의 순서는 트리의 preorder 순회 순서이다.
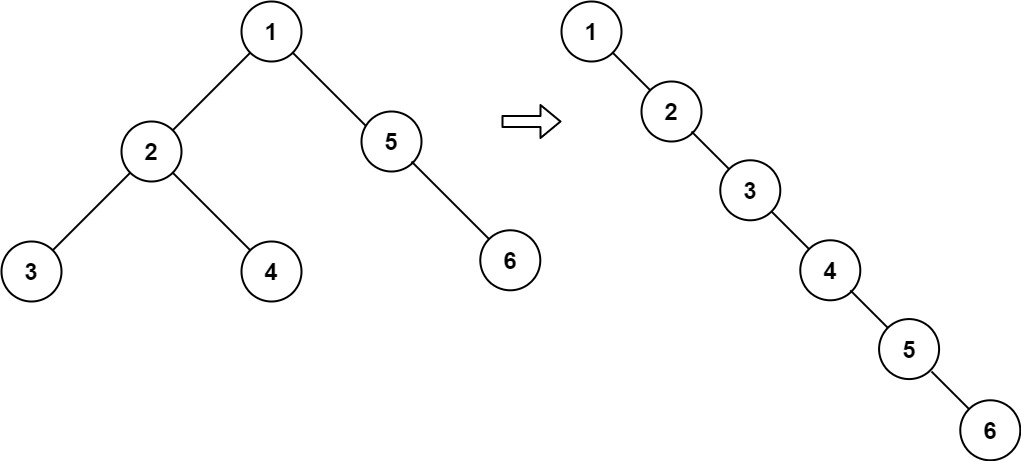
Input: root = [1,2,5,3,4,null,6]
Output: [1,null,2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6]https://leetcode.com/problems/flatten-binary-tree-to-linked-list/
해결 recursion
구조를 보면 root->right에 gen_list(root->left), 즉 root->left 통째로 리스트로 변환된 헤드를 등록하고. 기존 root->right는 tmp에 저장해두었다가, root->right의 가장 마지막 right에 gen_list(tmp)한것을 등록한다.
주의할 사항은 root->right노드가 위에서 저장했던 tmp노드와 동일하면 바로 gen_list(tmp)해야한다(아래 <- 이 부분).
좋은 문제였다!
struct TreeNode *gen_list(struct TreeNode *root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return NULL;
struct TreeNode *tmp = root->right;
if (root->left) {
root->right = gen_list(root->left);
root->left = NULL;
}
if (root->right) {
struct TreeNode *right_last = root->right;
if (right_last == tmp) { // <- 이 부분
right_last = gen_list(tmp);
} else {
for (; right_last->right != NULL; right_last = right_last->right)
;
right_last->right = gen_list(tmp);
}
}
return root;
}
void flatten(struct TreeNode* root){
root = gen_list(root);
}543. Diameter of Binary Tree
문제
주어진 이진트리의 Diameter(트리 내 존재하는 두 노드의 path중 가장 긴 path)를 구하라

https://leetcode.com/problems/diameter-of-binary-tree/
해결 O(N)
처음 접하는 유형의 문제였다. 단순히 루트노드에서 왼쪽깊이, 오른쪽깊이 두개를 더하면 오답이 나온다. 루트 이하 노드에서 더 긴 path가 나올 수도 있기 때문. 가령 아래같은 트리의 경우 root의 경우 최대길이는 1 + 5(왼쪽,오른쪽길이합) 이지만. root->right노드의 경우 4+4로 더 크다. 따라서 모든 노드를 순회하면서 노드마다 현재 노드의 max값을 갱신 하는 방식으로 풀어야한다.
o
o o
o o
o o o
o o
o o
그리고 트리순회의 시간복잡도는 N개의 노드를 한번씩 방문하므로 O(N)이다. 재귀호출이 2번일어난다고 O(2^N)이 아니다.
#define max(a,b) (((a) > (b)) ? (a) : (b))
int max_val;
int max_depth(struct TreeNode *node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return 0;
int L = max_depth(node->left);
int R = max_depth(node->right);
if (L + R > max_val)
max_val = L + R;
return max(L, R) + 1;
}
int diameterOfBinaryTree(struct TreeNode* root){
max_val = 0;
max_depth(root);
return max_val;
}230. Kth Smallest Element in a BST
문제
주어진 BST에서 k 번째로 작은 값을 출력하라.
Input: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,null,1], k = 3
Output: 3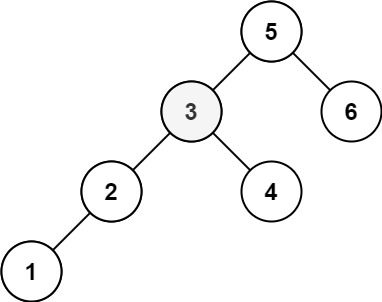
해결
BST이기 때문에 정렬이 되어있을것이고 inorder 순회를 하여 k번째 값을 출력하면 된다.
class Solution {
public:
void dfs_inorder(TreeNode *root, int k, vector<int> &nums) {
if (root == NULL && k < 0)
return;
if (root->left) dfs_inorder(root->left, k - 1, nums);
nums.push_back(root->val);
if (root->right) dfs_inorder(root->right, k - 1, nums);
return;
}
int kthSmallest(TreeNode* root, int k) {
vector<int> nums;
dfs(root, k, nums);
return nums[k - 1];
}
};추가로 dfs내에서 어떤 리턴값을 저장해야한다면, 어렵게 dfs함수의 리턴값으로 하지말고 그냥 매개변수 하나에 배열이나 벡터를 추가하자. 아래는 처음 풀었던 이상한 방식. 전역변수를 이상하게 사용함. 추천할수없는 방법!
class Solution {
public:
int kth = 0;
int ret = 0;
void dfs(TreeNode *root, int k) {
if (root == NULL && kth > k)
return;
if (root->left) dfs(root->left, k);
kth++;
if (kth == k) ret = root->val;
if (root->right) dfs(root->right, k);
return;
}
int kthSmallest(TreeNode* root, int k) {
dfs(root, k);
return ret;
}
};101. Symmetric Tree
문제
트리가 root를 기준으로 좌우 대칭인지 확인하기.
Input: root = [1,2,2,3,4,4,3]
Output: true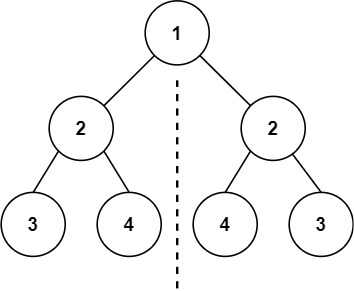
https://leetcode.com/problems/symmetric-tree/
해결
트리의 root->left를 invert_tree 해버리고, 그 후에 root->right와 동일한지 dfs해서 비교하여 해결
class Solution {
private:
TreeNode *invert_tree(TreeNode *root) {
if (root == NULL)
return NULL;
TreeNode *tmp = root->left;
root->left = invert_tree(root->right);
root->right = invert_tree(tmp);
return root;
}
bool dfs(TreeNode *n1, TreeNode *n2) {
if (n1 == NULL && n2 == NULL)
return true;
if ((!n1 && n2) || (n1 && !n2))
return false;
if (n1->val != n2->val)
return false;
if (!dfs(n1->left, n2->left))
return false;
if (!dfs(n1->right, n2->right))
return false;
return true;
}
public:
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
invert_tree(root->left);
return dfs(root->left, root->right);
}
};108. Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree
문제
정렬된 배열이 주어진다. 이것을 height balanced 이진탐색 트리로 변환하라.
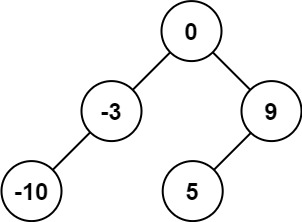
Input: nums = [-10,-3,0,5,9]
Output: [0,-3,9,-10,null,5]
Explanation: [0,-10,5,null,-3,null,9] is also accepted:https://leetcode.com/problems/convert-sorted-array-to-binary-search-tree/
해결
배열이 정렬된점 때문에 재귀함수 내에서 root-val 값을 항상 left/right 인덱스의 중앙값으로 하면 된다. 재귀형태의 tree traversal은 두가지 형태가 있는듯. 여러 Tree 문제 유형 확인하기 -> Leetcode - Tree & DFS 문제 (13)
- 트리를 새로 생성하는 경우
Tree *add_node() {
root->left = add_node();
root->right = add_node();
return root;- 이미 만들어진 트리를 탐색하는 경우
void dfs(root) {
dfs(root->left);
dfs(root->right);반드시 기억하자.. 트리 문제를 몇개를 풀었는데 아직도 첨 보면 햇갈림.
class Solution {
private:
vector<int> gnums;
TreeNode *gen_tree(int left, int right) {
if (left > right)
return NULL;
int mid = (left + right ) / 2;
TreeNode *root = new TreeNode;
root->val = gnums[mid];
root->left = gen_tree(left, mid - 1);
root->right = gen_tree(mid + 1, right);
return root;
}
public:
TreeNode* sortedArrayToBST(vector<int>& nums) {
gnums = nums;
return gen_tree(0, nums.size() - 1);
}
};1022. Sum of Root To Leaf Binary Numbers
문제
0/1로만 구성된 Tree에서 root부터 leef까지 이어지는 노드순서가 이진수값을 나타낸다고 할때, 주어진 트리에서 나타낼수 있는 모든 값의 총 합을 구하라.
Input: root = [1,0,1,0,1,0,1]
Output: 22
Explanation: (100) + (101) + (110) + (111) = 4 + 5 + 6 + 7 = 22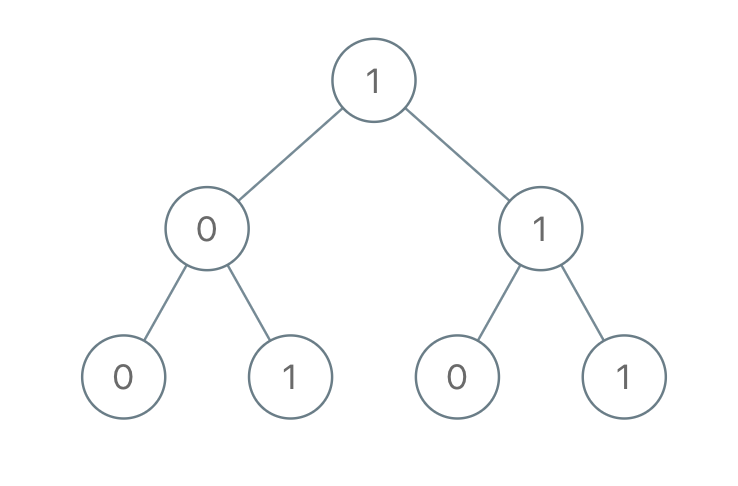
https://leetcode.com/problems/sum-of-root-to-leaf-binary-numbers/
해결
int recur(struct TreeNode* root, int val)
{
int sum = 0;
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
return val;
if (root->left)
sum += recur(root->left, root->left->val + val * 2);
if (root->right)
sum += recur(root->right, root->right->val + val * 2);
return sum;
}
int sumRootToLeaf(struct TreeNode* root){
return recur(root, root->val);
}226. Invert Binary Tree
문제
트리의 left, right를 서로 바꾸는 함수를 구현하라.
Input: root = [4,2,7,1,3,6,9]
Output: [4,7,2,9,6,3,1]
해결
root->left 에는 right로 invert된 결과를(그의 하위 자식들도 모두 invert가 된) 저장.
root->right에는 left로 invert된 결과 저장(swap이기 때문에 temp변수이용)
struct TreeNode* invertTree(struct TreeNode* root){
if (root == NULL)
return NULL;
struct TreeNode *temp = root->left;
root->left = invertTree(root->right);
root->right = invertTree(temp);
return root;
}아래는 TREE EASY문제들
94. Binary Tree Inorder Traversal
Inorder Traversal 하기
트리순회의 시간복잡도는 N개의 노드를 한번씩 방문하므로 O(N)이다. 재귀호출이 2번일어난다고 O(2^N)이 아니다.

Input: root = [1,null,2,3]
Output: [1,3,2]https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-tree-inorder-traversal/
int ret[101];
int nodecnt;
void travel(struct TreeNode *curr)
{
if (curr == NULL)
return;
travel(curr->left);
ret[nodecnt++] = curr->val;
travel(curr->right);
}
int* inorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize){
nodecnt = 0;
travel(root);
*returnSize = nodecnt;
return ret;
}144. Binary Tree Preorder Traversal
Preorder Traversal

Input: root = [1,null,2,3]
Output: [1,2,3]https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-tree-preorder-traversal/
int retcnt = 0;
void pre_travel(struct TreeNode* node, int *arr)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
arr[retcnt++] = node->val;
pre_travel(node->left, arr);
pre_travel(node->right, arr);
}
int* preorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize){
int *ret = (int *)calloc(101, sizeof(int));
retcnt = 0;
pre_travel(root, ret);
*returnSize = retcnt;
return ret;
}145. Binary Tree Postorder Traversal
Postorder Traversal

Input: root = [1,null,2,3]
Output: [3,2,1]https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-tree-postorder-traversal/
int retcnt;
void post_travel(struct TreeNode* node, int *arr)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
post_travel(node->left, arr);
post_travel(node->right, arr);
arr[retcnt++] = node->val;
}
int* postorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize){
int *ret = (int *)calloc(101, sizeof(int));
retcnt = 0;
post_travel(root, ret);
*returnSize = retcnt;
return ret;
}Tree Traversal
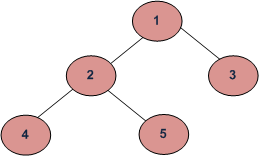
Depth First Traversals:
(a) Inorder (Left, Root, Right) : 4 2 5 1 3
(b) Preorder (Root, Left, Right) : 1 2 4 5 3
(c) Postorder (Left, Right, Root) : 4 5 2 3 1
Breadth-First or Level Order Traversal: 1 2 3 4 5 https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/tree-traversals-inorder-preorder-and-postorder/
938. Range Sum of BST
주어진 트리에서 특정 범위의 값의 총합 구하기
https://leetcode.com/problems/range-sum-of-bst/
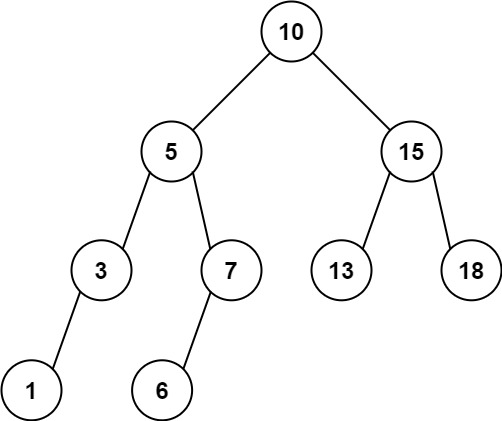
Input: root = [10,5,15,3,7,13,18,1,null,6], low = 6, high = 10
Output: 23
Explanation: Nodes 6, 7, and 10 are in the range [6, 10]. 6 + 7 + 10 = 23.int ret;
void inorder_travel(struct TreeNode *curr, int l, int h)
{
if (curr == NULL)
return;
inorder_travel(curr->left, l, h);
if (curr->val >= l && curr->val <= h)
ret += curr->val;
inorder_travel(curr->right, l, h);
}
int rangeSumBST(struct TreeNode* root, int low, int high){
ret = 0;
inorder_travel(root, low, high);
return ret;
}617. Merge Two Binary Trees
두 트리를 overlap해서 값을 합치기.

https://leetcode.com/problems/merge-two-binary-trees/
struct TreeNode* mergeTrees(struct TreeNode* root1, struct TreeNode* root2)
{
if (root1 == NULL)
return root2;
if (root2 == NULL)
return root1;
root1->val += root2->val;
root1->left = mergeTrees(root1->left, root2->left);
root1->right = mergeTrees(root1->right, root2->right);
return root1;
}104. Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
주어진 트리의 최대 깊이를 구하라.
Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: 3https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/

int max;
void dfs(struct TreeNode* root, int depth)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
if (depth > max)
max = depth;
dfs(root->left, depth + 1);
dfs(root->right, depth + 1);
}
int maxDepth(struct TreeNode* root){
max = 0;
dfs(root, 1);
return max;
}221001 다시 풀어본 풀이, 아래 코드가 훨씬 더 간결하고 좋은 풀이.
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root)
return 0;
return std::max(maxDepth(root->left), maxDepth(root->right)) + 1;
}
};111. Minimum Depth of Binary Tree
주어진 트리의 최소 깊이를 구하라.
Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: 2
Input: root = [2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6]
Output: 5주의사항
1
2
3
4
이런 트리의 경우 min depth는 1이 아니라 4임.
https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-depth-of-binary-tree/
#define min(a,b) (((a) < (b)) ? (a) : (b))
int minDepth(struct TreeNode* root){
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
int left = minDepth(root->left);
int right = minDepth(root->right);
if (!left && right)
return right + 1;
else if (left && !right)
return left + 1;
else
return min(left, right) + 1;
}221001 다시 풀어본 풀이, 위의것보다 이게 더 빠름
class Solution {
public:
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root)
return 0;
if (!root->left)
return minDepth(root->right) + 1;
if (!root->right)
return minDepth(root->left) + 1;
return std::min(minDepth(root->left), minDepth(root->right)) + 1;
}
};100. Same Tree
주어진 두 트리가 같으면 true 다르면 false 리턴.
https://leetcode.com/problems/same-tree/
Input: p = [1,2,1], q = [1,1,2]
Output: false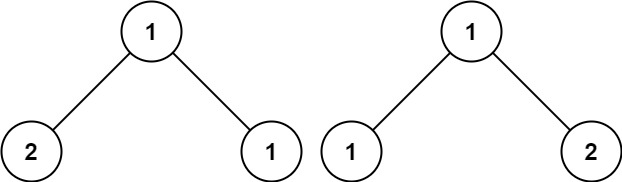
bool isSameTree(struct TreeNode* p, struct TreeNode* q){
/* base case */
if (p == NULL && q == NULL)
return true;
if (p == NULL && q)
return false;
if (q == NULL && p)
return false;
/* recursion */
if (p->val != q->val)
return false;
if (isSameTree(p->left, q->left) == false)
return false;
if (isSameTree(p->right, q->right) == false)
return false;
return true;
}110. Balanced Binary Tree
모든 노드의 좌우 자식노드의 깊이 차이가 1이하일때 트리의 height가 균형이 맞는다고 할때, 주어진 트리가 balanced 한지 아닌지 판단하라.
Input: root = [1,2,2,3,3,null,null,4,4]
Output: false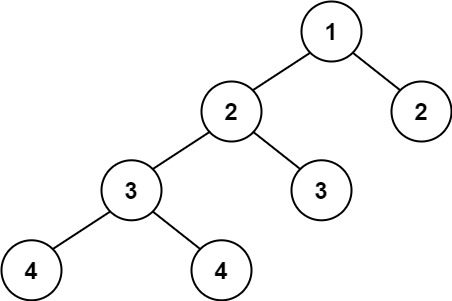
각각의 모든 노드에서 차이가 1이어야함. 문제 이해하는데 살짝 어려웠음. 각각의 노드의 좌우 자식노드의 깊이를 구해보면 됨. 가령 아래의 경우 균형이 맞지 않음.
1
2 2
3
4 https://leetcode.com/problems/balanced-binary-tree/
#define max(a,b) ((a) > (b)? (a): (b))
#define min(a,b) ((a) < (b)? (a): (b))
int height(struct TreeNode *node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return 0;
int left = height(node->left);
int right = height(node->right);
if (left == -1 || right == -1)
return -1;
if (left - right > 1 || left - right < -1)
return -1;
else
return max(left, right) + 1;
}
bool isBalanced(struct TreeNode* root){
if (height(root) == -1)
return false;
return true;
}112. Path Sum
트리내에서 루트부터 리프까지 노드의 합이 target인 path가 있다면 true 리턴.
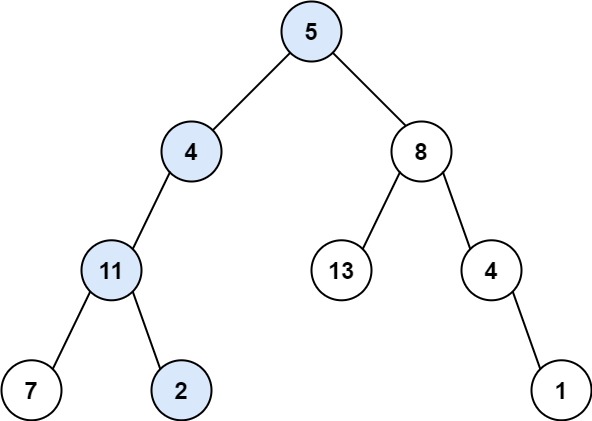
Input: root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,null,1], targetSum = 22
Output: truehttps://leetcode.com/problems/path-sum/
bool hasPathSum(struct TreeNode* root, int targetSum){
if (!root)
return false;
int newtarget = targetSum - root->val;
if (!root->left && !root->right) {
if (newtarget == 0)
return true;
return false;
}
if (hasPathSum(root->left, newtarget))
return true;
if (hasPathSum(root->right , newtarget))
return true;
return false;
}235. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Search Tree
이진탐색트리(정렬되어있음)에서 두 노드가 주어질때 가장 가까운 공통 조상노드를 리턴하기.
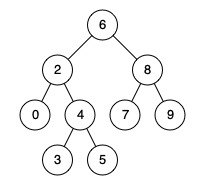
Input: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 8
Output: 6처음에 정렬되어있는 이진탐색트리라는걸 인지하지 못해서 해맷음. 그 뒤 힌트를 조금 참고함. 생각하기 어려웠던 문제였다.
해결 아이디어는 두 노드가 모두 현재root노드보다 작다면 root->left에서 재귀를 다시 시작하는것. 종료조건은 두노드가 모두 왼쪽에있지 않거나 오른쪽에 있지 않으면 현재 root노드가 답이라는 뜻이됨.
https://leetcode.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-search-tree/
struct TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(struct TreeNode* root, struct TreeNode* p, struct TreeNode* q) {
if (p->val < root->val && q->val < root->val)
return lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q);
else if (p->val > root->val && q->val > root->val)
return lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);
else
return root;
}257. Binary Tree Paths
주어진 이진트리에서 모든 root -> leaf까지 path를 문자열로 리턴하라.
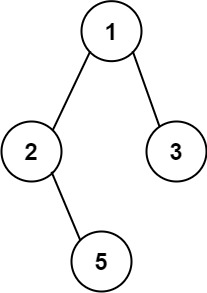
Input: root = [1,2,3,null,5]
Output: ["1->2->5","1->3"]https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-tree-paths/
char **ret;
int retcnt;
void recur(struct TreeNode* root, char *str)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
char newstr[300] = {'\0'};
strcpy(newstr, str);
if (!root->left && !root->right) {
sprintf(newstr, "%s%d", newstr, root->val);
ret[retcnt] = malloc(sizeof(char) * (strlen(newstr) + 1));
strcpy(ret[retcnt], newstr);
retcnt++;
return;
}
sprintf(newstr, "%s%d->", newstr, root->val);
recur(root->left, newstr);
recur(root->right, newstr);
}
char ** binaryTreePaths(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize){
ret = (char **)malloc(sizeof(char *) * 50);
char retstr[300] = {'\0'};
retcnt = 0;
recur(root, retstr);
*returnSize = retcnt;
return ret;
}404. Sum of Left Leaves
리프노드 중에서 모든 left 리프노드의 합을 구하라.
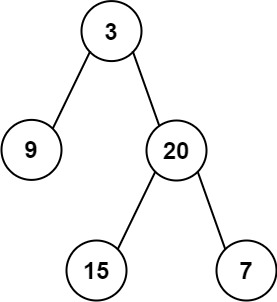
Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: 24https://leetcode.com/problems/sum-of-left-leaves/
int sumOfLeftLeaves(struct TreeNode* root){
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
int sum = sumOfLeftLeaves(root->left) + sumOfLeftLeaves(root->right);
if (root->left && !root->left->left && !root->left->right)
sum += root->left->val;
return sum;
}
897. Increasing Order Search Tree
BST를 정렬된 리스트로 만들기
https://leetcode.com/problems/increasing-order-search-tree/
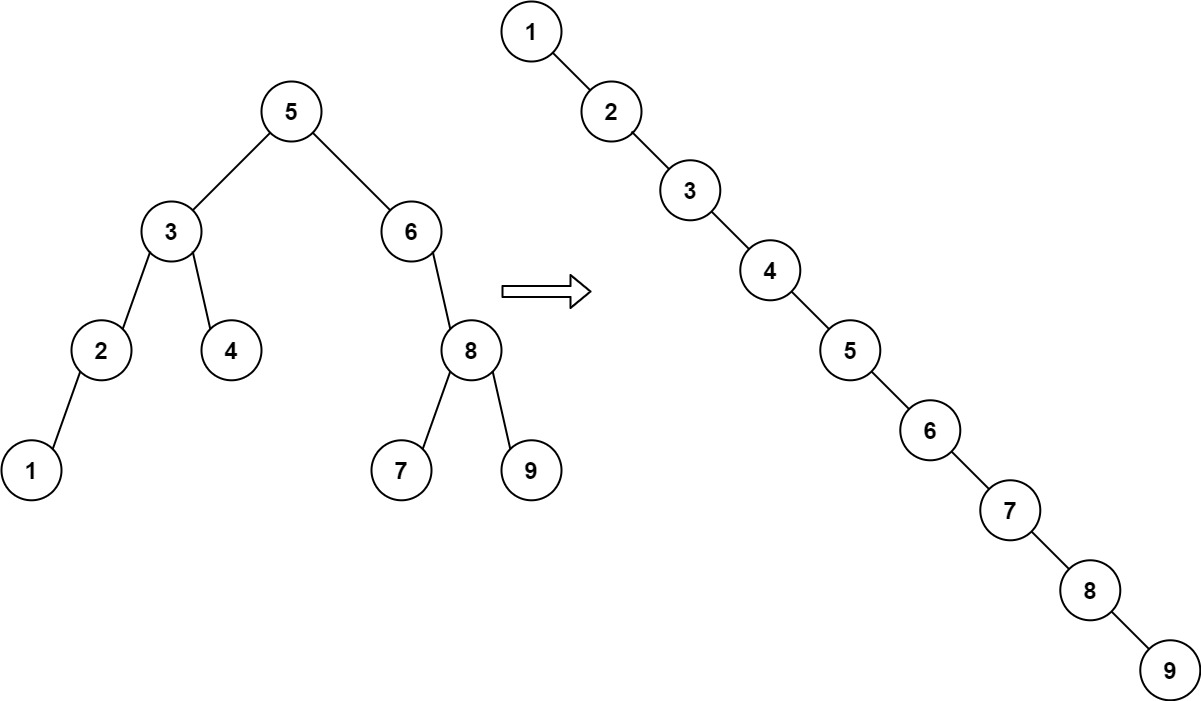
마지막에 new_leaf 의 left, right를 NULL로 안바꿔서 계속 Time Limit Exceeded 발생했었음.
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
struct TreeNode *new_head;
struct TreeNode *new_leaf;
void travel(struct TreeNode* curr)
{
if (curr == NULL)
return;
travel(curr->left);
printf("%d", curr->val);
if (new_head == NULL) {
new_head = curr;
new_leaf = curr;
} else {
new_leaf->right = curr;
new_leaf->left = NULL;
new_leaf = new_leaf->right;
}
travel(curr->right);
}
struct TreeNode* increasingBST(struct TreeNode* root){
new_head = NULL;
new_leaf = NULL;
travel(root);
new_leaf->left = NULL; /* without this line, It will be Time Out */
new_leaf->right = NULL;
return new_head;
}