EfficientViT: Multi-Scale Linear Attention for High-Resolution Dense Prediction : Review
PaperReview
Abstract
Computational cost makes deploying SOTA high-resolution dense prediction models on hardware devices difficult. Unlike prior models that rely on heavy softmax attention, hardware-inefficient large-kernel convolution, or complicated topology structure to obtain good performances, this multi-scale linear attention achieves the global receptive field and multi-scale learning(two desirable features for high-resolution dense prediction).
Introduction
High-resolution dense prediction has broad applications in the world. However, the computational cost is bad.
High-resolution dense prediction models require high-resolution images and storng context information extraction ablity to work well. Therefore, directly porting efficient model architectures
from image classification is unsuitable for high-resolution
dense prediction.
The core of EfficientViT is a new multi-scale linear attention module that enables the global receptive field and multi-scale learning with hardware-efficient operations.
Prior SOTA models demonstrate that the multi-scale learning and global receptive field are critical in improving models' performances. However, they dn'tt consider hardware efficency.(Ex, SegFormer-softmax attention into the backbone to have a global receptive field , SegNeXt- multi-branch module with large-kernel convolutions (Kernel size upto 21) to enable a large receptive field and multi-scale learning)
They propose substituting the inefficient softmax attention with lightweight ReLU linear attention to have the global receptive field.
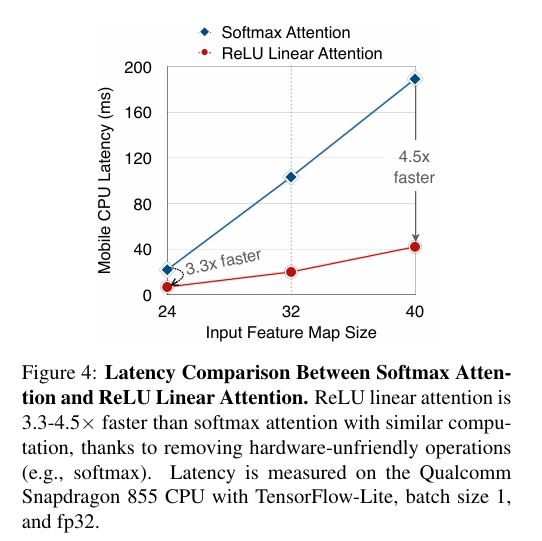
By leveraging the associative property of matrix multiplication,
ReLU linear attention can reduce the computational complexity from quadratic to linear while preserving functionality. In addition, it avoids hardware-inefficient operations like softmax, making it more suitable for hardware deployment.
However, Only using ReLU linear attention errupts limited capacity due to the lack of local information extraction and multi-scale learning ablity.
Therefore, They propose using convolution with ReLU linear attention and introduce the multi-scale linear attention module to address the capacity limitation of ReLU linear attention.
Specifically, they aggregate nearby tokens with small-kerel convolutions to generate multi-scale tokens. They perform ReLU linear attention on multi-scale tokens to combine the global receptive field with multi-scale learning. They also insert depth-wise convolutions into FFN layers to further improve the local feature extraction capacity.
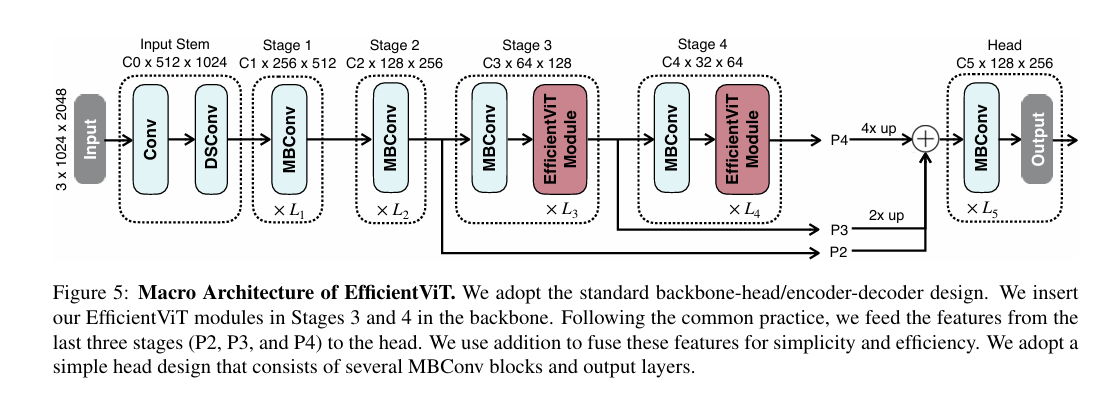
Method
this multi-scale linear attention simultanously achieves the global receptive field and multi-scale learning with only hardware-efficient operations. Then, based on the multi-scale linear attention, they present this model.
The glboal receptive field and multi-scale learning are essential from the performance perspective.
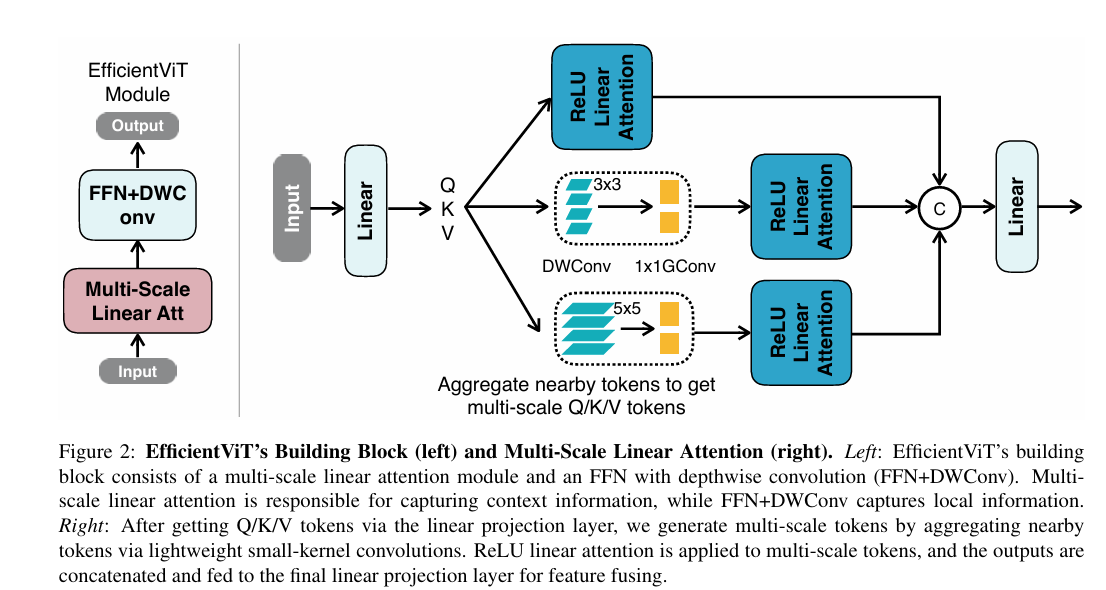
To use ReLU linear attention to enable the global receptive field instead of the heavy softmax attention. While ReLU linear attention and other linear attention modules have been explored in other domains, it has never been successfully applied to high-resolution dense prediction.
Enable Global Receptive Field with ReLU Linear Attention.
Given input x (in dimension Nxf), the generalized form of softmax attention can be written as:
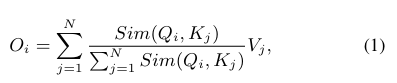
where 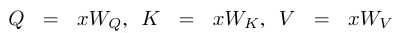
and,
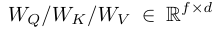
is the learnable linear projection matrix.
Sim(-,-) is the similarity function
In original softmax attention
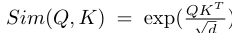
In this work, they use ReLU linear attention to achieve both the global receptive field and linear computational complexity.
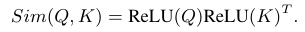
with ReLU Attention
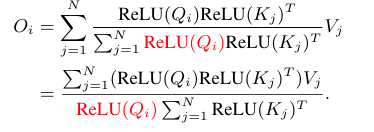
Then, it is useful that the associative property of matrix multiplication to reduce the computational complexty and memory footprint from quadratic to linear without changing its functionality