S3 Security 종류
User-Based
- IAM policies
- which API calls should be allowed for a specific user from IAM
- IAM policies
Resource-Based
- Bucket Policies
- bucket wide rules from the S3 console
- allows cross account
- Object Access Control List(ACL)
- finer grain(can be disabled)
- Bucket Access Control List(ACL)
- les conmmon(can be disabled)
- Bucket Policies
Object Encryption
- encrypt objects in Amazon S3 using encryption keys
MFA Delete
NOTE!
IAM principal can access an S3 object if
- the user IAM permissions ALLOW it OR the resource policy ALLOW it
- AND there's no explicit DENY
S3 Bucket Policies
- JSON based policies
- Principal (=누구에게): the account or user to apply the policy to
- Resources (=무엇을): buckets and objecs
- Actions (=어떤 행동 하는 것을): Set of API to Allow or deny
- Effect (=허용/거부): Allow/Deny

- Use S3 bucket for policy to
- grant public access to the bucket
- force objects to be encrypted at upload
- grant access to another account (Cross Account)
S3 Object Encryption
can encrypt objects using 4 methods
Server-Side Encryption (SSE)
-
Server-Side Encryption with Amazon S3-Managed Keys (SSE-S3)
- default
- encryption using keys handled, managed, and owned by AWS
- encryption type is AES-256
- must set header "x-amx-servier-side-encryption": "AES256"

-
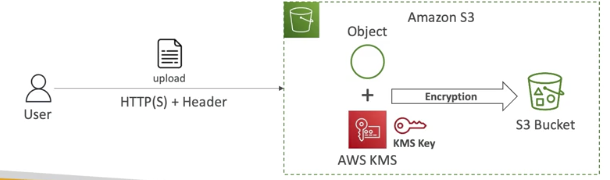
Server-Side Encryption with KMS keys sotred in AWS KMS(SSE-KMS)
- encryption using keys handled and managed by AWS KMS(key management service)
- KMS advantages: user control + audit key usage using CloudTrail
- must set header "x-amx-servier-side-encryption": "aws:kms"
-
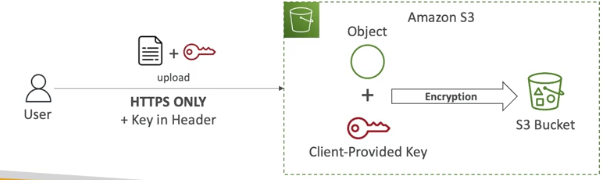
Server-Side Encryption with Customer-Provided keys (SSE-C)
- encryption using keys fully managed by the customer oustide of AWS
- S3 does NOT store the encryption key you provide
- HTTPS must be used
- Encryption key must be provided in HTTP headers, for every HTTP request made
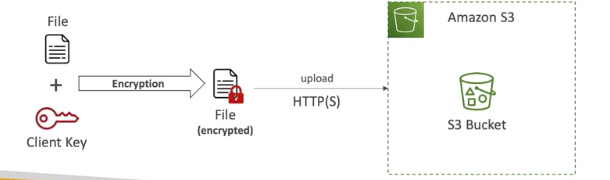
Client-Side Encryption
- use clieng libraries such as Amazon S3 Cliend-Side Encryption Library
- clients must encrypt data themsleves before sending to S3
- clients must decrypt data themselves when retrieving from S3
- customer fully manages the keys and encryption cycle
S3 CORS
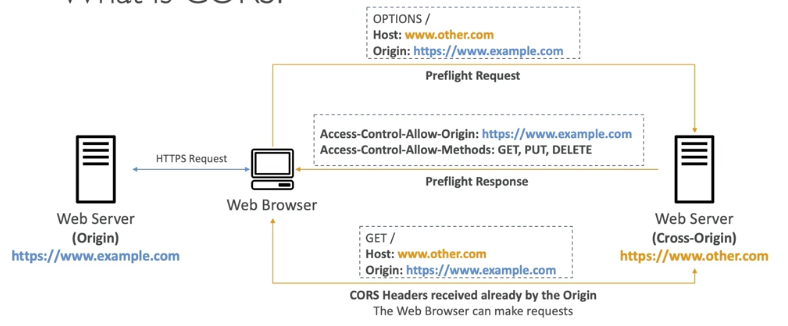
What is CORS?
CORS, or Cross-Origin Resource Sharing, is a security feature implemented by web browsers that allows or restricts web pages from making requests to a different domain than the one that served the web page. In other words, it's a mechanism that allows requests to other origins while visiting the main origin
Origin
= scheme(protocol) + host(domain) + port
- same origin: http://example.com/app1 & http://example.com/app2
- different origins: http://example.com & http://other.com
CORS and S3
if a client makes a cross-origin request on our S3 bucket, we need to enable the correct CORS headers. you can allow for a specific origin or for * (all origins)

MFA Delete
This is an extra layer of protection to deleting obejcts in S3.
- MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication): force users to generate a code on a device (usually a mobile phone or hardware) before doing important operations on S3
- MFA will be required to
- permanently delete an object version
- suspend versioning on the bucket
- MFA won't be required to
- enable versioning
- list deleted versions
- to use MFA Delete, Versioning must be enabled on the bucket
- only the bucket owner(root account) can enable/disable MFA Delete
