Key point
- 리플렉션
- Object.GetType()메소드, Type 클래스 역할
- 리플렉션을 통한 객체 생성
- 애트리뷰트
16.1 리플렉션
- 객체의 형식(Type) 정보를 들여다보는 기능
형식 정보 읽기
Object.GetType() 메소드 & Type 클래스
GetType()- 메소드 모든 데이터 형식의 조상인
Object의
Type() 형식의 결과를 반환하는 기능을 가진다. - 모든 데이터 형식은 이 메소드를 통해 객체의 형식 정보를 얻어낼 수 있다.
- 메소드 모든 데이터 형식의 조상인
Type 형식- .NET에서 사용되는 데이터 형식의 모든 정보를 담고 있다.
- 형식 이름
- 소속된 어셈블리 이름
- 프로퍼티 목록
- 메소드 목록
- 필드 목록
- 이벤트 목록
- 형식이 상속하는 인터페이스의 목록
- .NET에서 사용되는 데이터 형식의 모든 정보를 담고 있다.
// Object.GetType()메소드와 Type 형식 사용 방법
int a = 0;
Type type = a.GetType(); // Type
FieldInfo[] fields = type.GetFields(); // 필드 목록
System.Type의 주요 메소드-
다양한 정보를 뽑아낼 수 있음
-
메소드 검색 옵션
System.Reflection.BindingFlas열거형 이용
Type type = a.GetType(); // public 인스턴스 필드 조회 var fields1 = type.GetFields(BindingFlags.Public | BindingFlags.Instance); // 비 public 인스턴스 필드 조회 var fields2 = type.GetFields(BindingFlags.NonPublic | BindingFlags.Instance); // public 정적 필드 조회 var fields3 = type.GetFields(BindingFlags.Public | BindingFlags.Static); // 비 public 정적 필드 조회 var fields4 = type.GetFields(BindingFlags.NonPublic | BindingFlags.Static);
-
예제
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
using System.Reflection; // System.Reflection.BindingFlas - 메소드 검색 옵션
namespace GetType
{
class MainApp
{
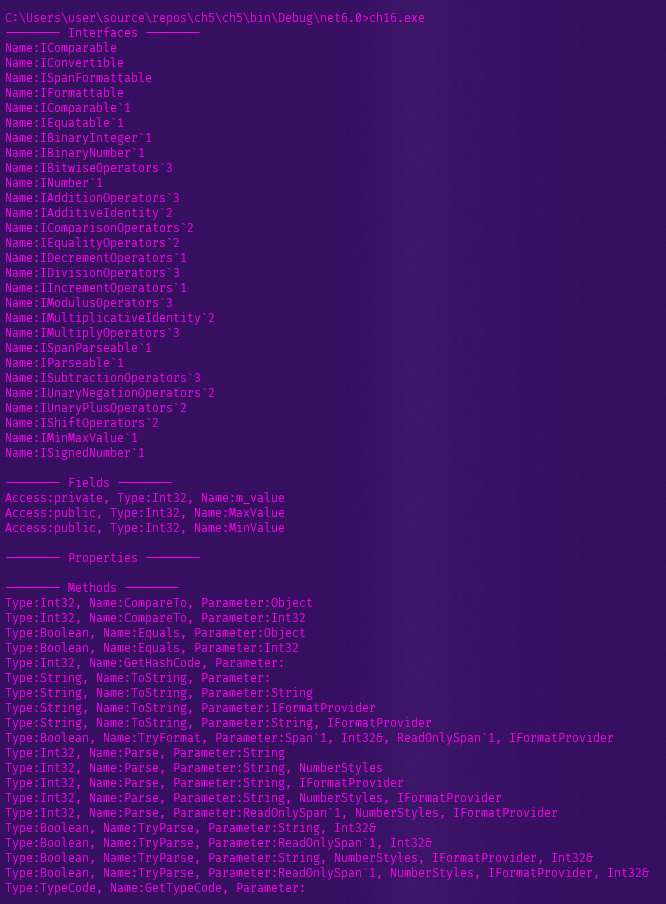
static void PrintInterfaces(Type type)
{
Console.WriteLine("-------- Interfaces -------- ");
Type[] interfaces = type.GetInterfaces(); // Type 메소드
foreach (Type i in interfaces)
Console.WriteLine("Name:{0}", i.Name);
Console.WriteLine();
}
static void PrintFields(Type type)
{
Console.WriteLine("-------- Fields -------- ");
// 메소드 옵션
FieldInfo[] fields = type.GetFields(
BindingFlags.NonPublic |
BindingFlags.Public |
BindingFlags.Static |
BindingFlags.Instance );
foreach (FieldInfo field in fields)
{
String accessLevel = "protected";
// Public 여부에 따라 다르게 설정
if ( field.IsPublic ) accessLevel = "public";
else if ( field.IsPrivate) accessLevel = "private";
Console.WriteLine("Access:{0}, Type:{1}, Name:{2}",
accessLevel, field.FieldType.Name, field.Name);
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
static void PrintMethods(Type type)
{
Console.WriteLine("-------- Methods -------- ");
MethodInfo[] methods = type.GetMethods(); // Type 메소드
foreach (MethodInfo method in methods)
{
Console.Write("Type:{0}, Name:{1}, Parameter:",
method.ReturnType.Name, method.Name);
ParameterInfo[] args = method.GetParameters();
for (int i = 0; i < args.Length; i++)
{
Console.Write("{0}", args[i].ParameterType.Name);
if (i < args.Length - 1)
Console.Write(", ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
static void PrintProperties(Type type)
{
Console.WriteLine("-------- Properties -------- ");
PropertyInfo[] properties = type.GetProperties(); // Type 메소드
foreach (PropertyInfo property in properties)
Console.WriteLine("Type:{0}, Name:{1}",
property.PropertyType.Name, property.Name);
Console.WriteLine();
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a = 0;
Type type = a.GetType(); // Type
// 변수 a의 Type에 대한 정보 출력
PrintInterfaces(type);
PrintFields(type);
PrintProperties(type);
PrintMethods(type);
}
}
}
Object.GetType()외에 형식 정보 얻는 방법
Object.GetType()과 달리 인스턴스 생성이 필요 없다.// typeof 연산자 Type a = typeof(int); // 인수 : 형식의 식별자 자체 Console.WriteLine(a.FullName);// Type.GetType() Type b = Type.GetType("System.Int32"); // 인수 : 형식 네임스페이스를 포함하는 전체 이름 Console.WriteLine(b.FullName);
객체 생성 및 이용
| 동작 | 클래스 | 메소드 |
|---|---|---|
| 인스턴스 생성 | System.Activator | CreateInstance(System.Type 객체) |
| 값 할당 및 읽기 | PropertyInfo | - SetValue(객체, 설정값, 인덱서의 인덱스)- GetValue(객체, 설정값, 인덱서의 인덱스) |
| 메소드 호출 | MethodInfo | Invoke(객체, 메소드 인수) |
예제
using System;
using System.Reflection;
namespace DynamicInstance
{
class Profile
{
private string name;
private string phone;
public Profile()
{
name = ""; phone = "";
}
public Profile(string name, string phone)
{
this.name = name;
this.phone = phone;
}
public void Print()
{
Console.WriteLine($"{name}, {phone}");
}
public string Name
{
get { return name; }
set { name = value; }
}
public string Phone
{
get { return phone; }
set { phone = value; }
}
}
class MainApp
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Type type = Type.GetType("DynamicInstance.Profile"); // DynamicInstance.Profile의 Type 객체
MethodInfo methodInfo = type.GetMethod("Print"); // Print의 MethodInfo 객체
PropertyInfo nameProperty = type.GetProperty("Name"); // Name의 PropertyInfo 객체
PropertyInfo phoneProperty = type.GetProperty("Phone"); // Phone의 PropertyInfo 객체
// 1. System.Activator.CreateInstance | 인스턴스 생성 및 초기화
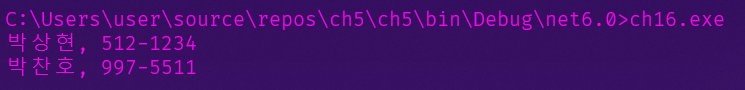
object profile = Activator.CreateInstance(type, "박상현", "512-1234");
// 2. Invoke | Print 메소드 호출
methodInfo.Invoke(profile, null); // Invoke (생성한 형식 인스턴스, 해당 메소드에 필요한 매개변수)
// 3. System.Activator.CreateInstance | 인스턴스 생성
profile = Activator.CreateInstance(type);
// 4. SetValue | 값 기록
nameProperty.SetValue(profile, "박찬호", null); // SetValue(생성한 형식 인스턴스, 설정값, 인덱서의 인덱스)
phoneProperty.SetValue(profile, "997-5511", null);
Console.WriteLine("{0}, {1}",
// GetValue | 값 읽기
nameProperty.GetValue(profile, null), // GetValue(생성한 형식 인스턴스, 설정값, 인덱서의 인덱스)
phoneProperty.GetValue(profile, null));
}
}
}
새로운 형식 생성
-
System.Reflection.Emit클래스로 생성Emit: 프로그램이 실행 중 만들어낸 새 형식을 CLR의 메모리에 "내보낸다"는 의미- 클래스 목록
- 클래스 요소를 만든다는 의미에서
~Builder꼴의 이름을 가짐

- 클래스 요소를 만든다는 의미에서
-
형식 생성 과정
.NET 프로그램 계층 구조
[어셈블리] → [모듈] → [클래스] → [메소드] 또는 [프로퍼티]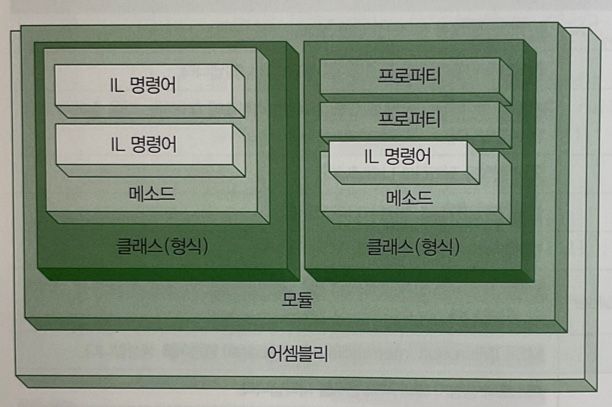
- 어셈블리 생성 →
AssemblyBuilder - 생성한 어셈블리 안에 모듈 만들어 넣기 →
ModuleBuilder - 생성한 모듈 안에 클래스(형식) 만들어 넣기 →
TypeBuilder - 생성한 클래스 안에 메소드나 프로퍼티 만들어 넣기
→MethodBuilder/PropertyBuilder - 메소드를 생성했다면 메소드 안에 IL 명령dj(메소드가 실행할 코드) 넣기
→ILGenerator
- 어셈블리 생성 →
예제
using System;
using System.Reflection;
using System.Reflection.Emit;
namespace EmitTest
{
public class MainApp
{
public static void Main()
{
// 1. 어셈블리
AssemblyBuilder newAssembly =
AssemblyBuilder.DefineDynamicAssembly(
new AssemblyName("CalculatorAssembly"), // 어셈블리 이름
AssemblyBuilderAccess.Run
);
// 2. 모듈
ModuleBuilder newModule = newAssembly.DefineDynamicModule("Calculator"); // 어셈블리 위 생성, 모듈 이름
// 3. 클래스
TypeBuilder newType = newModule.DefineType("Sum1To100"); // 모듈 위 생성, 클래스 이름
//4. 메소드
MethodBuilder newMethod = newType.DefineMethod( // 클래스 위 생성
"Calculate", // 메소드 이름
MethodAttributes.Public,
typeof(int), // 반환 형식
new Type[0] // 매개 변수
);
// 5. IL명령어 (메소드가 실행할 코드)
ILGenerator generator = newMethod.GetILGenerator(); // 메소드 위 생성
generator.Emit(OpCodes.Ldc_I4, 1); // stack에 4bit, 32byte 정수(1) Push
for (int i = 2; i <= 100; i++) // for문으로 1~100 더하는 코드
{
generator.Emit(OpCodes.Ldc_I4, i); // stack에 4bit, 32byte 정수(i) Push
generator.Emit(OpCodes.Add); // stack의 최종 두 값을 꺼내 더한 뒤 그 결과를 Push
}
generator.Emit(OpCodes.Ret); // 계산 stack에 담겨있는 값 반환
newType.CreateType(); // IL명령어를 모두 채워넣었으니 Sum1To100 클래스 CLR에 제출
// ↑ 여기까지 새로운 형식 만드는 과정 ↑ //
// ↓ 형식의 인스턴스를 동적으로 생성해 이용하는 과정 ↓ //
object sum1To100 = Activator.CreateInstance(newType); // 객체 생성
MethodInfo Calculate = sum1To100.GetType().GetMethod("Calculate"); // Calculate 메소드 가져오기
Console.WriteLine(Calculate.Invoke(sum1To100, null)); // 메소드 호출하여 결과 반환
}
}
}
16.2 애트리뷰트 (Attribute)
- 메타 데이터(코드에 대한 정보)를 담는 코드 요소
- 컴파일을 거치면 실행파일(어셈블리) 안에 저장되며, 컴퓨터가 런타임에 읽을 수 있음
- 선언 형식
[ 애트리뷰트_이름( 애트리뷰트_매개변수) ]
public void MyMethod()
{
//...
}예제
using System;
namespace BasicAttribute
{
class MyClass
{
// Obsolete 애트리뷰트 : 컴파일 경고
[Obsolete("OldMethod는 폐기되었습니다. NewMethod()를 이용하세요.")]
public void OldMethod()
{
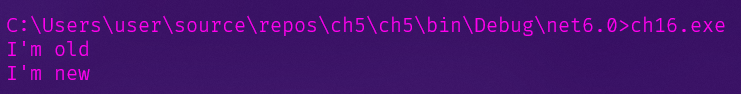
Console.WriteLine("I'm old");
}
public void NewMethod()
{
Console.WriteLine("I'm new");
}
}
class MainApp
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
MyClass obj = new MyClass();
obj.OldMethod();
obj.NewMethod();
}
}
}
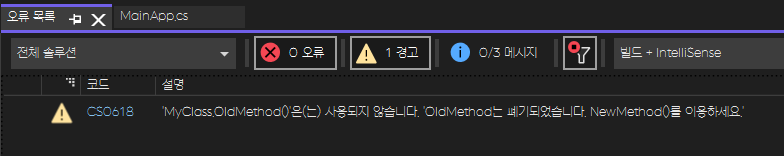
OldMethod()와 NewMethod()를 정상적으로 실행하지만,
컴파일 할 때 비주얼 스튜디오의 오류 목록창을 확인하면 경고 메시지가 뜬다.
호출자 정보 애트리뷰트
- 메소드의 매개 변수에 사용
- 메소드의 호출자 이름
- 호출자 메소드가 정의되어 있는 소스 파일 경로
- 소스 파일 내의 행 번호 파악
- 3가지 호출자 정보 애트리뷰트

예제
using System;
using System.Runtime.CompilerServices;
namespace CallerInfo
{
public static class Trace
{
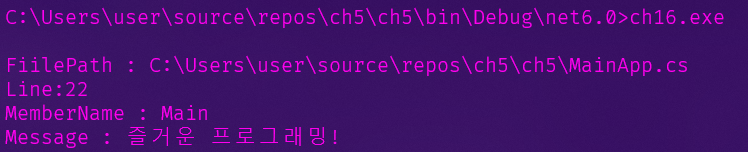
public static void WriteLine(string message,
[CallerFilePath] string file = "", // 메소드가 호출된 소스 파일 정보
[CallerLineNumber] int line = 0, // 호출된 소스 파일 내의 행(Line) 번호
[CallerMemberName] string member = "") // 호출한 메소드 또는 프로퍼티의 이름
{
Console.WriteLine(
$"\nFiilePath : {file}\nLine:{line}\nMemberName : {member}\nMessage : {message}");
}
}
class MainApp
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Trace.WriteLine("즐거운 프로그래밍!");
}
}
}
사용자 정의 애트리뷰트
System.Attribute를 상속해 프로그래머가 직접 정의하는 애트리뷰트
class History : System.Attribute // 상속
{
private string programmer;
public double Version
{
get;
set;
}
public string Changes
{
get;
set;
}
// 생성자
public History(string programmer)
{
this.programmer = programmer;
Version = 1.0;
Changes = "First release";
}
public string Programmer
{
get { return programmer; }
}
}
// History 클래스 사용
[History("Sean", Version=0.1, Changes="2017-11-01 Created class stub")]
class MyClass
{
public void Func()
{
Console.WriteLine("Func()");
}
}-
System.AttributeUsage(p1, p2)-
애트리뷰트를 추가하고 싶을 경우 사용
-
애트리뷰트의 애트리뷰트
-
매개변수
-
p1: 애트리뷰트가 설명하는 대상 (Attribute Target)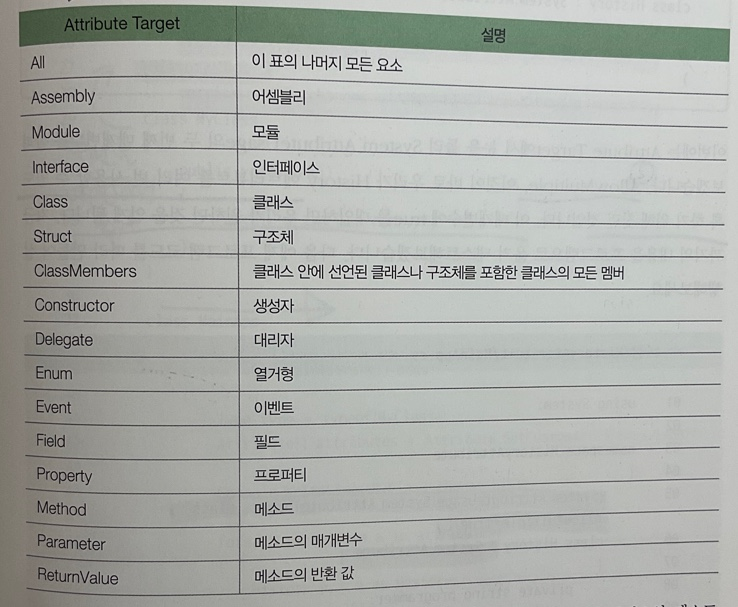
*논리합 연산자를 이용해 결합할 수도 있다.
ex)AttributeTargets.Class | AttributeTargets.Method -
p2: 애트리뷰트의 중복 사용 여부 (AllowMultiple)
-
-
[System.AttributeUsage(
System.AttributeTargets.Class | System.AttributeTargets.Method, // Attribute Target
AllowMultiple=True)] // AllowMultiple
class History : System.Attribute
{
//...
}예제
using System;
namespace HistoryAttribute
{
[System.AttributeUsage(System.AttributeTargets.Class, AllowMultiple = true)] // 중복 사용
class History : System.Attribute
{
private string programmer;
public double Version
{
get;
set;
}
public string Changes
{
get;
set;
}
// 생성자
public History(string programmer)
{
this.programmer = programmer;
Version = 1.0;
Changes = "First release";
}
public string Programmer
{
get { return programmer; }
}
}
// 애트리뷰트 + 설명할 클래스
[History("Sean",
Version = 0.1, Changes = "2017-11-01 Created class stub")]
[History("Bob",
Version = 0.2, Changes = "2020-12-03 Added Func() Method")]
class MyClass
{
public void Func()
{
Console.WriteLine("Func()");
}
}
class MainApp
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Type type = typeof(MyClass);
Attribute[] attributes = Attribute.GetCustomAttributes(type);
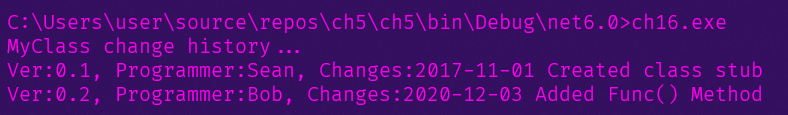
Console.WriteLine("MyClass change history...");
foreach (Attribute a in attributes)
{
History h = a as History;
if (h != null)
Console.WriteLine("Ver:{0}, Programmer:{1}, Changes:{2}",
h.Version, h.Programmer, h.Changes);
}
}
}
}
연습문제
- 다음 코드 중에서 올바로 동작하지 않는 것을 고르시오 => 2, 3번
using System;
using static System.Console;
namespace Ex_16
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
object myObject = '1';
Type t1 = myObject.GetType(); // 1번
//Type t2 = typeof("int"); // 2번
//Type t3 = Type.GetType(int); // 3번
Type t4 = Type.GetType("System.Int32"); // 4번
WriteLine(t1);
//WriteLine(t2);
//WriteLine(t3);
WriteLine(t4);
}
}
}- 1번 : 선언된 변수나 클래스가 있다면 동작
- 2번 :
typeof는 형식의 식별자 자체를 매개변수로 받으므로int라고 작성해야 동작 - 3번, 4번 :
Type.GetType()은 네임스페이스를 포함한 형식이름을 매개변수로 받으므로 동작하려면 4번처럼 바꾸어야 함
- 애트리뷰트와 주석의 차이는 무엇입니까?
- 애트리뷰트
- 사람이 쓰면 컴파일을 거쳐 실행파일(어셈블리) 안에 저장되어 컴퓨터가 런타임에 읽을 수 있다.
- 주석
- 사람이 읽고 쓰는 정보로, 컴파일을 거치면 실행파일에서는 제거되어 컴퓨터가 읽지는 못한다.