🧭 최단 경로 문제
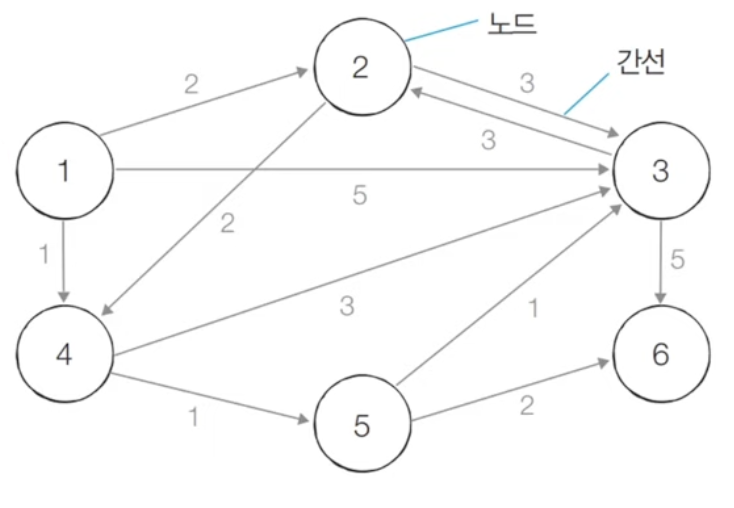
최단 경로 알고리즘은 가장 짧은 경로를 찾는 알고리즘을 의미한다.
다양한 문제 상황
- 한 지점에서 다른 한 지점까지의 최단 경로
- 한 지점에서 다른 모든 지점까지의 최단 경로
- 모든 지점에서 다른 모든 지점까지의 최단 경로
📌 다익스트라 알고리즘
특정한 노드에서 출발하여 다른 모든 노드로 가는 최단 경로를 계산합니다.
단일 시작점 최단 경로 문제에 적합합니다.
- 다익스트라 최단 경로 알고리즘은
음의 간선이 없을 때정상적으로 동작한다.
현실 세계의 도로(간선)은 음의 간선으로 표현되지 않는다. - 다익스트라 최단 경로 알고리즘은
그리디 알고리즘으로 분류된다.
매 상황에서 아직 방문하지 않은 가장 비용이 적은 노드를 선택해 임의의 과정을 반복한다. - 알고리즘 동작 과정에서 최단 거리 테이블은 각 노드에 대한 현재까지의 최단 거리 정보를 가지고 있다.
- 처리 과정에서 더 짧은 경로를 찾으면 "이제부터는 이 경로가 제일 짧은 경로야" 라고 갱신한다.
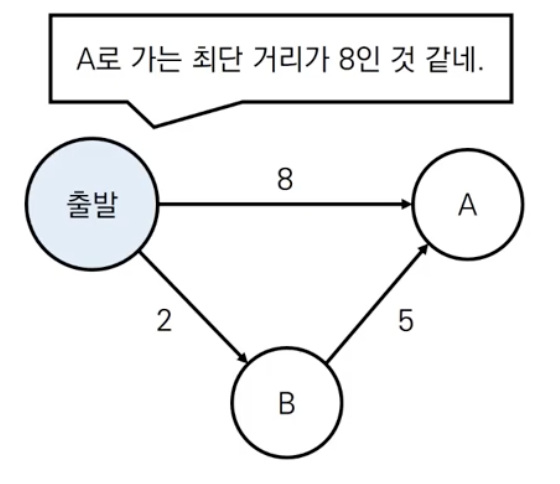
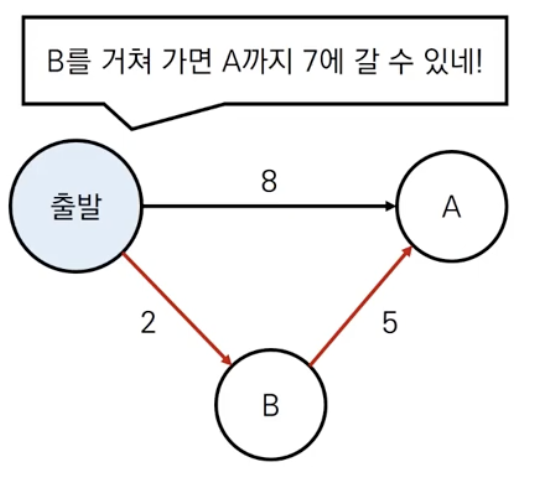
플로이드 워샬 알고리즘은 뭘까?
알고리즘 동작 과정
-
출발 노드를 설정한다.
-
최단 거리 테이블을 초기화한다.
-
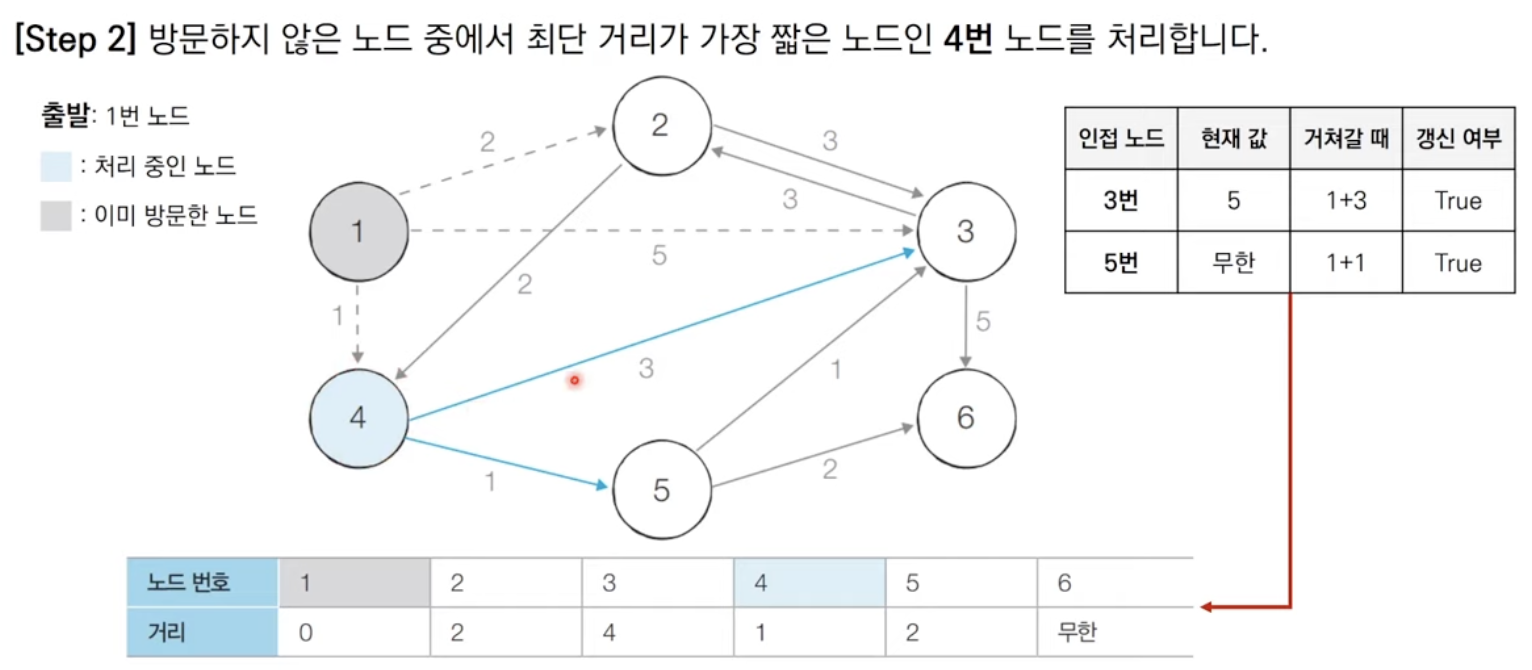
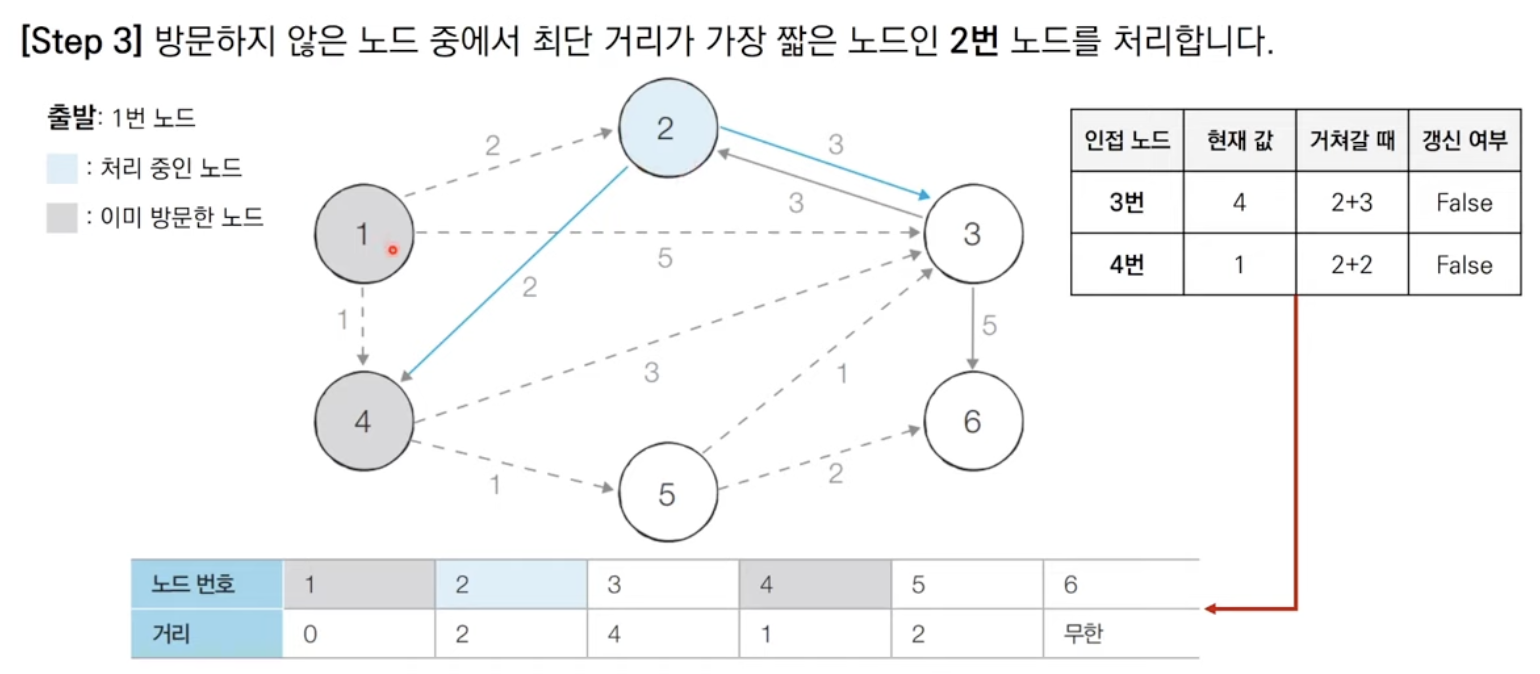
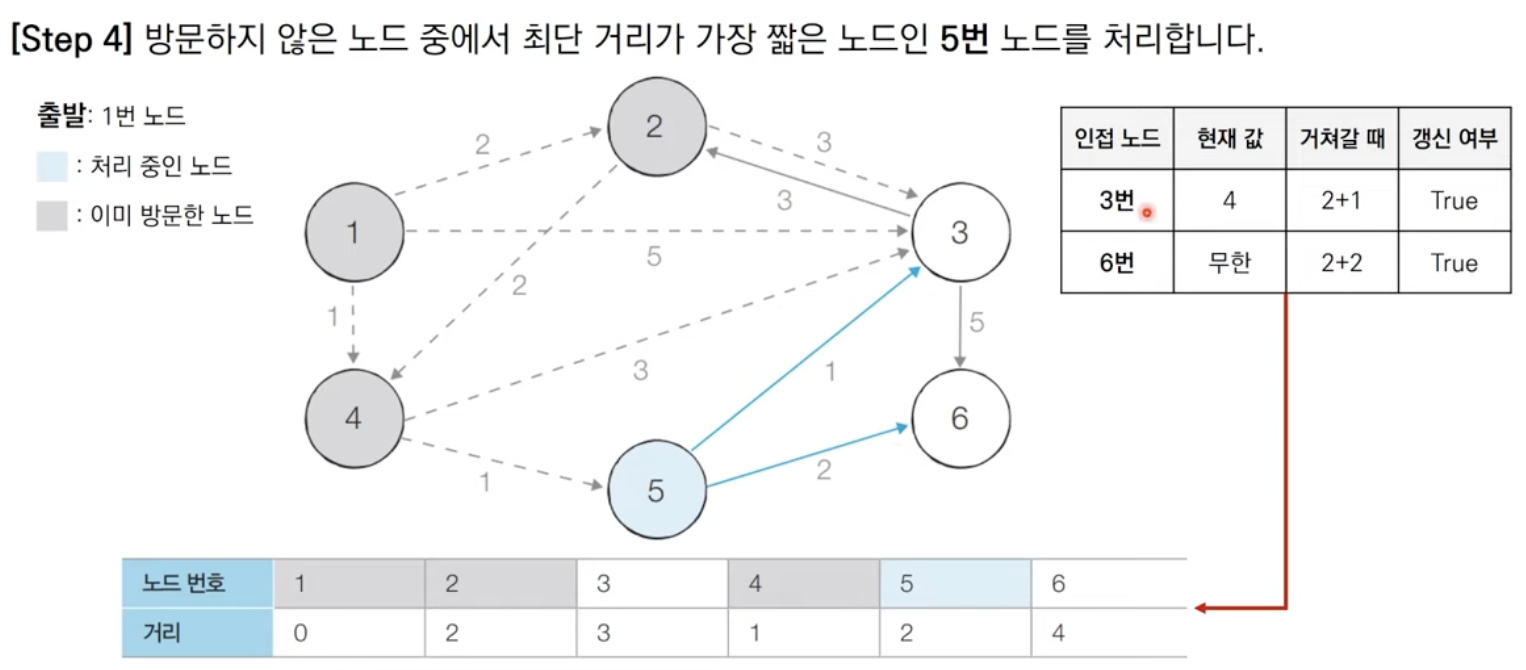
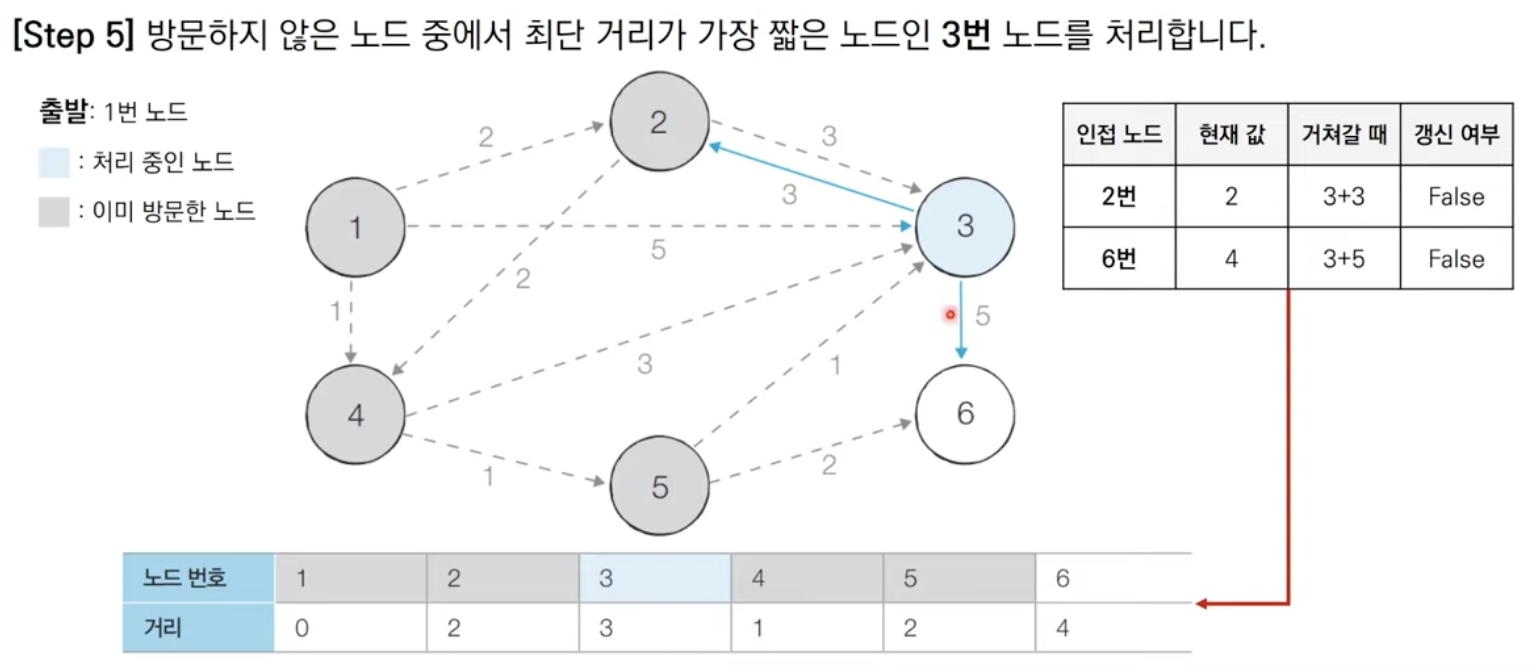
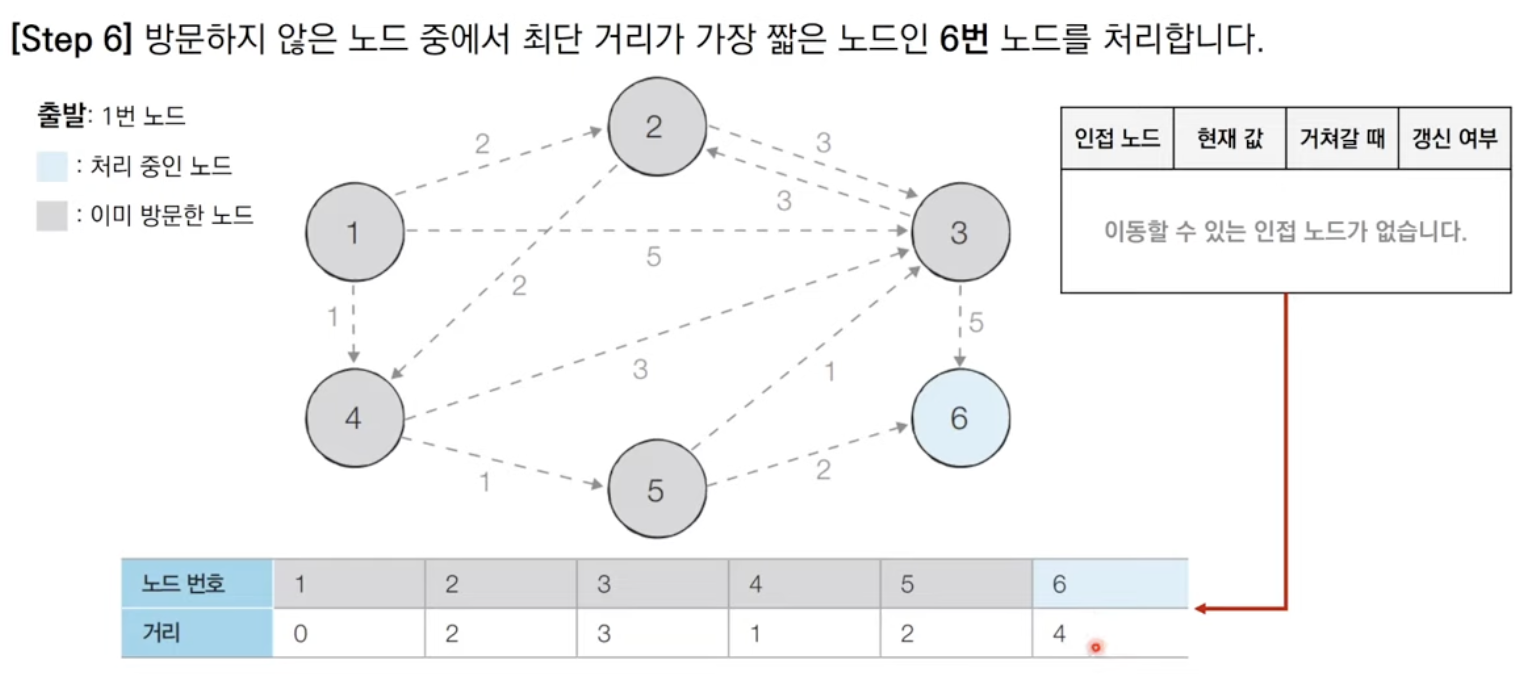
방문하지 않은 노드 중에서 최단 거리가 가장 짧은 노드를 선택한다.
-
해당 노드를 거쳐 다른 노드로 가는 비용을 계산하여 최단 거리 테이블을 갱신한다.
-
위 과정에서 3번과 4번을 반복한다.

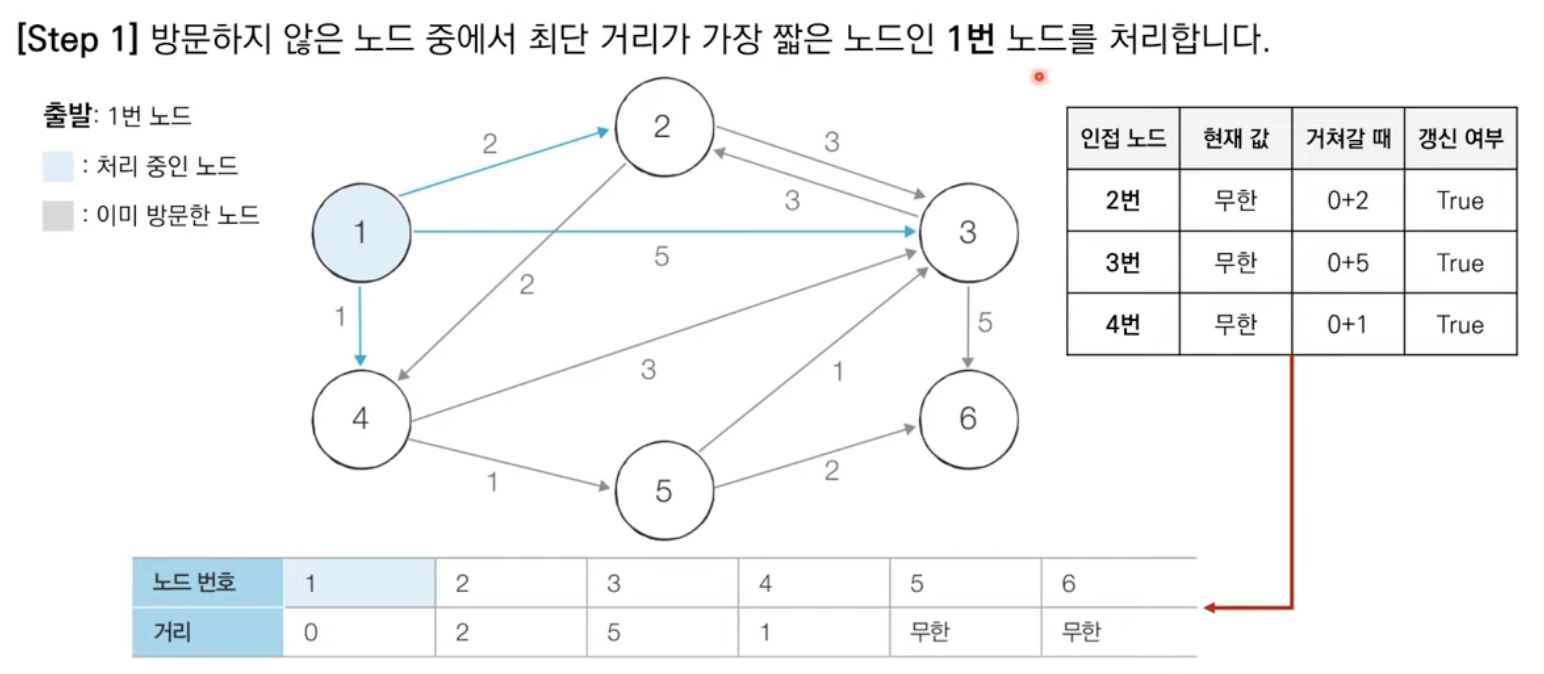
알고리즘의 특징
-
그리디 알고리즘
매 상황에서 방문하지 않은 가장 비용이 적은 노드를 선택해 임의의 과정을 반복한다. -
단계를 거치며 한번 처리된 노드의 최단 거리는 고정되어 더 이상 바뀌지 않는다.
한 단계당 하나의 노드에 대한 최단 거리를 확실히 찾는 것으로 이해할 수 있다.
- 다익스트라 알고리즘을 수행한 뒤에 테이블에 각 노드까지의 최단 거리 정보가 저장된다.
완벽한 형태의 최단 경로를 구하려면 소스코드에 추가적인 기능을 더 넣어야 한다.
👩🏻💻 간단한 다익스트라 코드
import java.util.*;
class Node {
private int index;
private int distance;
public Node(int index, int distance) {
this.index = index;
this.distance = distance;
}
public int getIndex() {
return this.index;
}
public int getDistance() {
return this.distance;
}
}
public class Main {
public static final int INF = (int) 1e9;
public static int n, m, start;
public static ArrayList<ArrayList<Node>> graph = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Node>>();
public static boolean[] visited = new boolean[100001];
public static int[] d = new int[100001];
public static int getSmallestNode() {
int min_value = INF;
int index = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (d[i] < min_value && !visited[i]) {
min_value = d[i];
index = i;
}
}
return index;
}
public static void dijkstra(int start) {
d[start] = 0;
visited[start] = true;
for (int j = 0; j < graph.get(start).size(); j++) {
d[graph.get(start).get(j).getIndex()] = graph.get(start).get(j).getDistance();
}
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
int now = getSmallestNode();
visited[now] = true;
for (int j = 0; j < graph.get(now).size(); j++) {
int cost = d[now] + graph.get(now).get(j).getDistance();
if (cost < d[graph.get(now).get(j).getIndex()]) {
d[graph.get(now).get(j).getIndex()] = cost;
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
m = sc.nextInt();
start = sc.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
graph.add(new ArrayList<Node>());
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int a = sc.nextInt();
int b = sc.nextInt();
int c = sc.nextInt();
graph.get(a).add(new Node(b, c));
}
Arrays.fill(d, INF);
dijkstra(start);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (d[i] == INF) {
System.out.println("INFINITY");
}
else {
System.out.println(d[i]);
}
}
}
}총 O(V)번에 걸쳐서 최단 거리가 가장 짧은 노드를 매번 선형 탐색해야 한다.
따라서 전체 시간 복잡도는 0(V^2)이다.
일반적으로 코딩 테스트의 최단 경로 문제에서
전체 노드의 개수가 5,000개 이하라면이 코드로 문제를 해결할 수 있다.
하지만 노드의 개수가 10,000개를 넘어가는 문제라면 어떻게 해야 할까?
우선순위 큐를 사용하면 된다.
최단 거리가 가장 짧은 노드를 구할 때, 우선순위 큐를 사용하는 것이다.
👩🏻💻 개선된 다익스트라 코드
import java.util.*;
class Node implements Comparable<Node> {
private int index;
private int distance;
public Node(int index, int distance) {
this.index = index;
this.distance = distance;
}
public int getIndex() {
return this.index;
}
public int getDistance() {
return this.distance;
}
// 거리(비용)가 짧은 것이 높은 우선순위를 가지도록 설정
@Override
public int compareTo(Node other) {
if (this.distance < other.distance) {
return -1;
}
return 1;
}
}
public class Main {
public static final int INF = (int) 1e9;
public static int n, m, start;
public static ArrayList<ArrayList<Node>> graph = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Node>>();
public static int[] d = new int[100001];
public static void dijkstra(int start) {
PriorityQueue<Node> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
pq.offer(new Node(start, 0));
d[start] = 0;
while(!pq.isEmpty()) {
Node node = pq.poll();
int dist = node.getDistance(); // 현재 노드까지의 비용
int now = node.getIndex(); // 현재 노드
if (d[now] < dist) continue;
for (int i = 0; i < graph.get(now).size(); i++) {
int cost = d[now] + graph.get(now).get(i).getDistance();
if (cost < d[graph.get(now).get(i).getIndex()]) {
d[graph.get(now).get(i).getIndex()] = cost;
pq.offer(new Node(graph.get(now).get(i).getIndex(), cost));
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
m = sc.nextInt();
start = sc.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
graph.add(new ArrayList<Node>());
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int a = sc.nextInt();
int b = sc.nextInt();
int c = sc.nextInt();
// a번 노드에서 b번 노드로 가는 비용이 c라는 의미
graph.get(a).add(new Node(b, c));
}
Arrays.fill(d, INF);
dijkstra(start);
// 모든 노드로 가기 위한 최단 거리를 출력
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (d[i] == INF) {
System.out.println("INFINITY");
}
else {
System.out.println(d[i]);
}
}
}
}힙 자료구조를 이용하는 다익스트라 알고리즘의 시간 복잡도는 0(ElogV)이다.
- 노드를 하나씩 꺼내 검사하는 반복문(while문)은 노드의 개수 V 이상의 횟수로는 처리되지 않는다.
결과적으로 현재 우선순위 큐에서 꺼낸 노드와 연결된 다른 노드들을 확인하는 총횟수는 최대 간선의 개수(E)만큼 연산이 수행될 수 있다. - 직관적으로 전체 과정은 E개의 원소를 우선순위 큐에 넣었다가 모두 빼내는 연산과 매우 유사하다.

