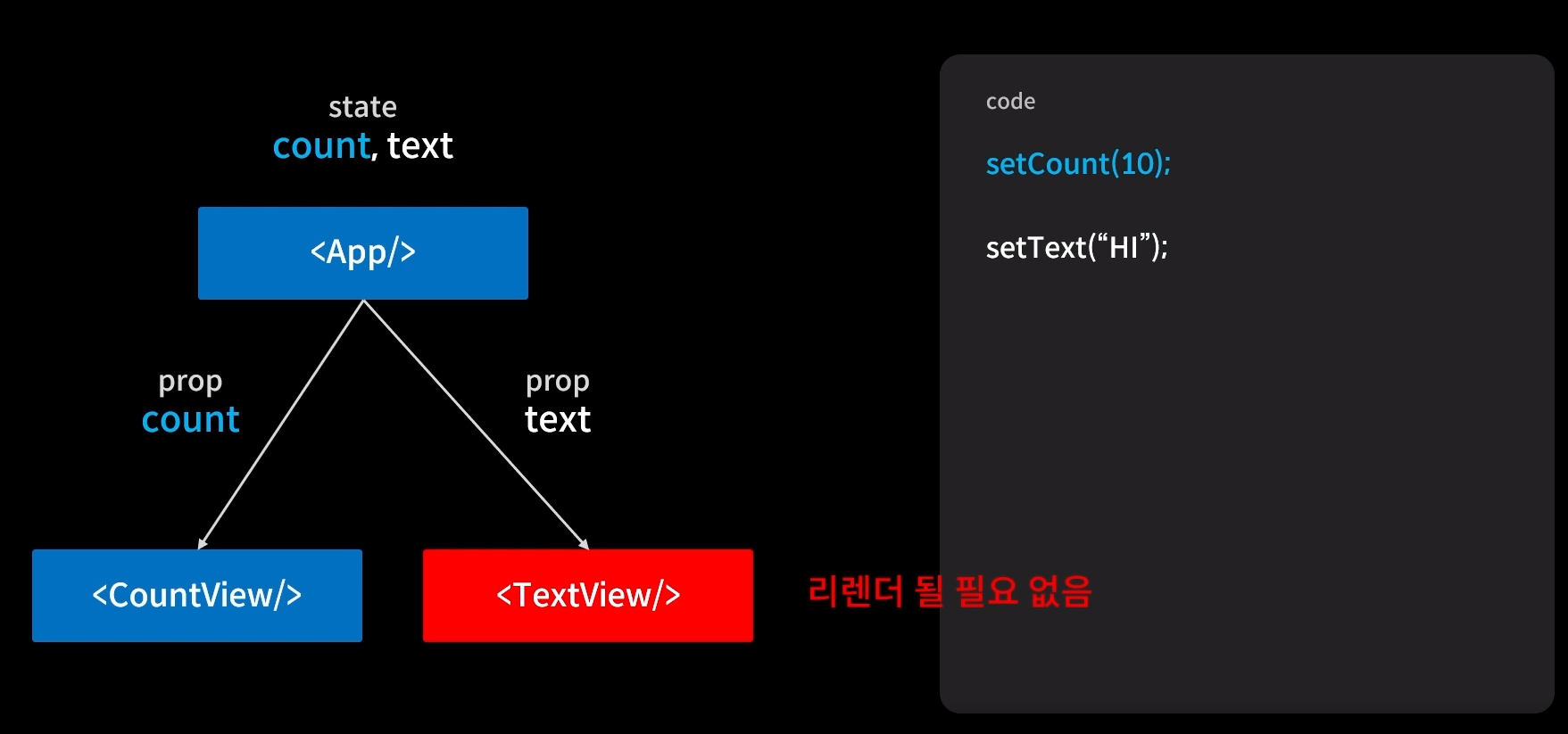
✔ setCount(10)이 실행이 되면서 App컴포넌트의 count의 state가 변화되면서 리렌더링되면서 prop인 두개의 countView컴포넌트와 TextView컴포넌트도 리렌더링 된다.
✔ 부모 컴포넌트가 리렌더링되면 자식 컴포넌트도 저절로 리렌더링 된다.
✔ TextView컴포넌트는 렌더링될 필요가 없는데 강제로 리렌더링되서 연산의 낭비가 된다.
이런 낭비를 막기 위해서는?
🎃 React.memo
함수형 컴포넌트에게 업데이트 조건을 거는 것
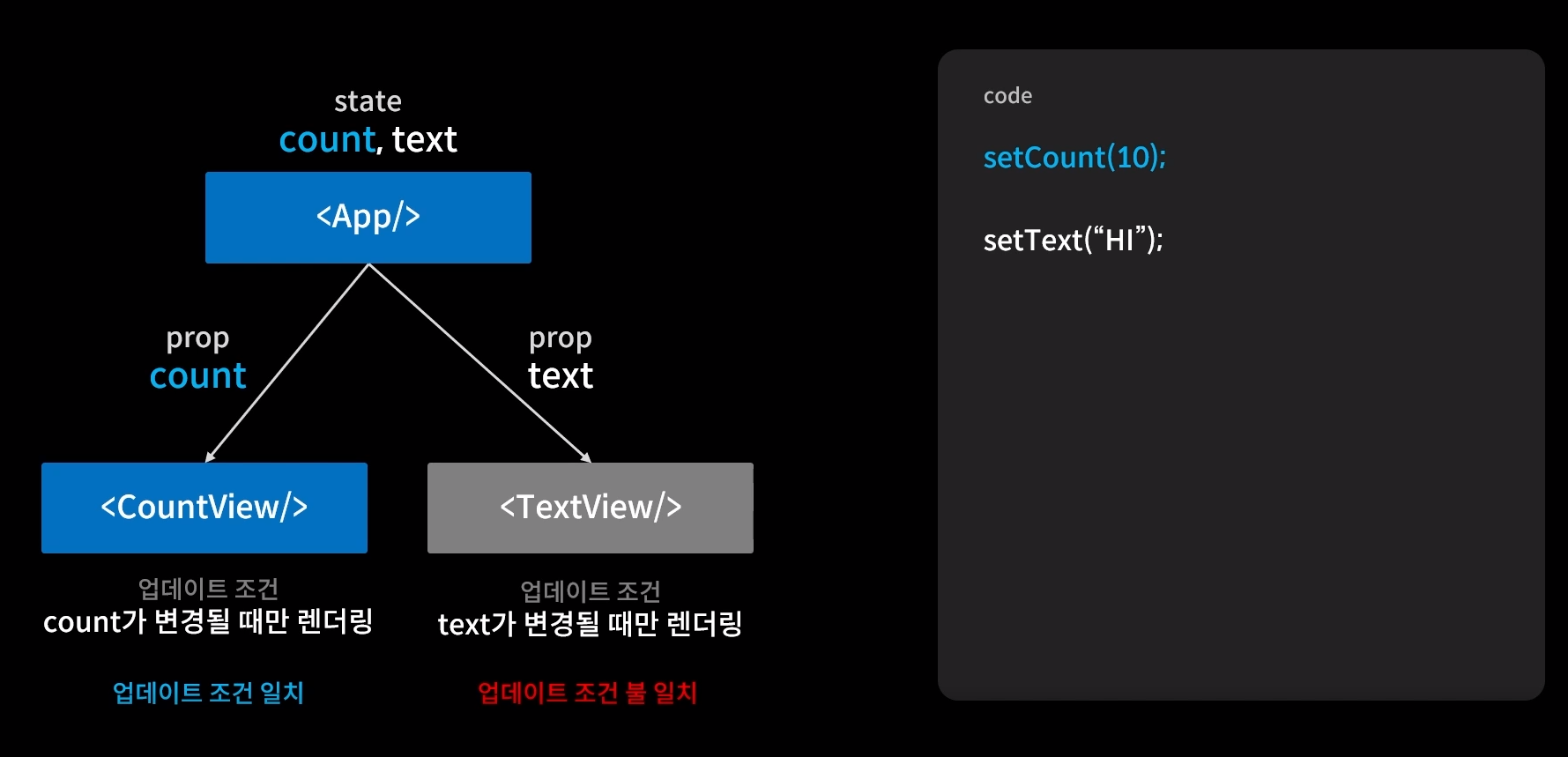
✔ 업데이트 조건이 성립하는 것만 업데이트 되도록 만든다.
❌ React.memo 미사용시
import React, {useEffect, useState} from "react";
const TextView =({text}) => {
useEffect(()=>{
console.log(`Update :: Text : ${text}`)
})
return <div>{text}</div>
}
const CountView = ({count}) => {
useEffect(()=>{
console.log(`Update :: Count : ${count}`)
})
return <div>{count}</div>
}
const OptimizeTest= () => {
const [count, setCount] = useState(1);
const [text, setText] = useState("")
return <div style = {{padding : 50 }}>
<div>
<h2>count</h2>
<CountView count ={count}/>
<button onClick={(e)=>{setCount(count+1)}}>+</button>
</div>
<div>
<h2>text</h2>
<TextView text={text }/>
<input value={text} onChange={(e)=>setText(e.target.value)}/>
</div>
</div>
}
export default OptimizeTest;결과값
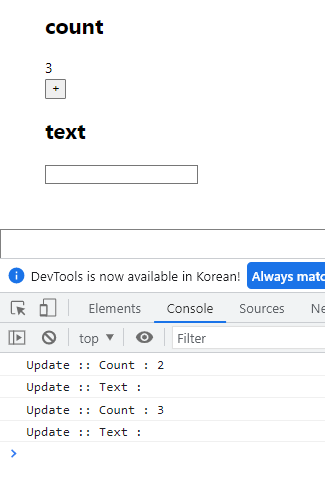
Count부분만 바꿔줬는데 콘솔창에 Text부분도 리렌더링 된 것이 보인다.
⭕ React.memo 사용시
✔ 최적화를 위해 React.memo을 사용하면 된다.
✔ React.memo는 최적화하고 싶은 함수를 감싸준다.
import React, {useEffect, useState} from "react";
//TextView컴포넌트는 prop인 text가 변하지 않으면 렌더링하지 않는다.
const TextView =React.memo(({text}) => {
useEffect(()=>{
console.log(`Update :: Text : ${text}`)
})
return <div>{text}</div>
})
//CountView컴포넌트는 prop인 Count가 변하지 않으면 렌더링하지 않는다.
const CountView =React.memo( ({count}) => {
useEffect(()=>{
console.log(`Update :: Count : ${count}`)
})
return <div>{count}</div>
})
const OptimizeTest= () => {
const [count, setCount] = useState(1);
const [text, setText] = useState("")
return <div style = {{padding : 50 }}>
<div>
<h2>count</h2>
<CountView count ={count}/>
<button onClick={(e)=>{setCount(count+1)}}>+</button>
</div>
<div>
<h2>text</h2>
<TextView text={text }/>
<input value={text} onChange={(e)=>setText(e.target.value)}/>
</div>
</div>
}
export default OptimizeTest;결과값- count만 바꿨을 경우
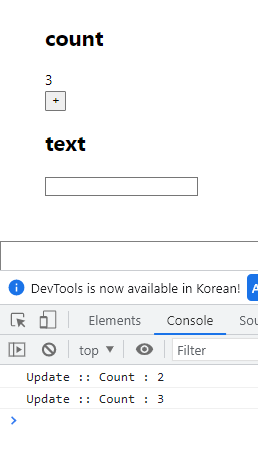
TextView컴포넌트는 렌더링 되지 않는다.
결과값- text만 바꿨을 경우
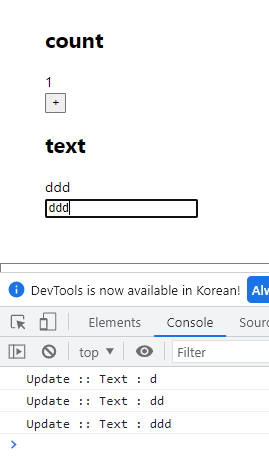
CountView컴포넌트는 렌더링 되지 않는다.
✨ tip.
React.memo을 사용하고 함수를 감싸주려고 하는데 코드가 너무 길떈 아래 코드 처럼 해도 된다.
export default React.memo(OptimizeTest);
😎 얕은 비교(걍 먼솔인지...ㅎ)
import React, {useEffect, useState} from "react";
const CounterA = React.memo(({count})=>{
useEffect(()=> {
console.log(`CounterA Update - count: ${count}`)
})
//아래 jsx코드에서 onClick={()=> setCount(count)}이렇게
//했기에 변하는 것이 없어서 콘솔창에 아무것도 안찍힌다.
return <div>{count}</div>
})
const CounterB = React.memo(({obj})=>{
useEffect(()=> {
console.log(`CounterB Update - count: ${obj.count}`)
})
//아래 jsx코드에서
//onClick ={() => setObj({
// count : obj.count
// {/* 갱신함수 매개변수로 현재 state 값이 count을 넣어줘서
//정작 바꾸는 값이 없다. */}
// })}
//이렇게 줬기때문에 원래라면 콘솔창에 아무것도 안찍혀야 한다.
//하지만 js에서는 객체를 얕은 비교를 하기떄문에 리렌더링 되어 콘솔창에 찍힌다.
return <div>{obj.count}</div>
})
const OptimizeTest= () => {
const [count,setCount] = useState(1);
const [obj,setObj]= useState({
count : 1
//초기값으로 객체를 넣어준다.
})
return <div style = {{padding : 50 }}>
<div>
<h2>Counter A</h2>
<CounterA count={count}/>
<button onClick={()=> setCount(count)}>A button</button>
{/* 갱신함수 매개변수로 현재 state 값이 count을
넣어줘서 정작 바꾸는 값이 없다. */}
</div>
<div>
<h2>Counter B</h2>
<CounterB obj={obj}/>
<button onClick ={() => setObj({
count : obj.count
// {/* 갱신함수 매개변수로 현재 state 값이 count을
//넣어줘서 정작 바꾸는 값이 없다. */}
})}>B button</button>
</div>
</div>
}
export default OptimizeTest;💥 그렇다면 , 객체를 얕은복사가 안되게 해서 렌더링 최적화를 이뤄보자!
const CounterB = ({obj})=>{
useEffect(()=> {
console.log(`CounterB Update - count: ${obj.count}`)
})
return <div>{obj.count}</div>
}
const areEqual = (prevProps, nextProps) => {
return true;
// 이전 props와 현재 props가 같다-> 리렌더링을 일으키지 않는다.
return false;
// 만약 false로 해준다면
//이전 props와 현재 props가 다르다.-> 리렌더링을 일으킨다.리렌더링이 일어나는지 안일어나는지 판단해보자
const CounterB = ({obj})=>{
useEffect(()=> {
console.log(`CounterB Update - count: ${obj.count}`)
})
return <div>{obj.count}</div>
}
const areEqual = (prevProps, nextProps) => {
if(prevProps.obj.count === nextProps.obj.count){
return true;
}
return false
}
const MemoizedCounterB = React.memo(CounterB,areEqual)
//CounterB는 areEqual의 결과에 따라 리렌더링을 할지말지 결정하게 된다.
return <div style = {{padding : 50 }}>
<div>
<h2>Counter A</h2>
<CounterA count={count}/>
<button onClick={()=> setCount(count)}>A button</button>
</div>
<div>
<h2>Counter B</h2>
//**
<MemoizedCounterB obj={obj}/>
<button onClick ={() => setObj({
count : obj.count
})}>B button</button>
</div>
</div>
}
export default OptimizeTest;