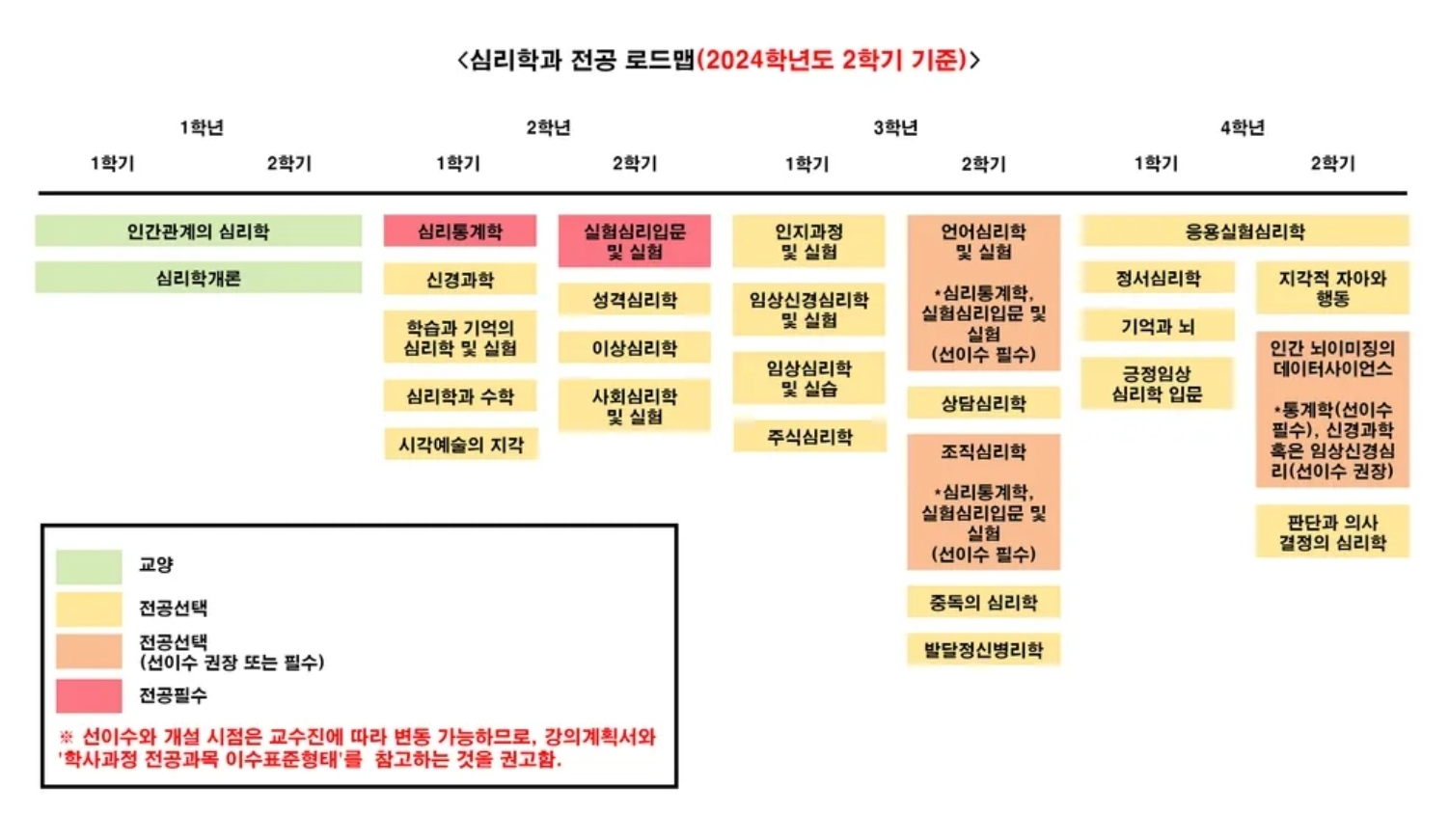
수강신청을 할 때는 선이수 과목을 모두 이수했는지 확인하는 것이 중요해요!
위상 정렬에서도 선행 조건을 지키며 작업의 순서를 결정하게 됩니다.
위상 정렬
- 순서가 있는 작업을 순서에 맞춰 정렬하는 알고리즘
- 즉, 방향성 그래프에서 순서를 지키며 모든 노드를 순서대로 나열하는 것
- 단, 그래프에는 사이클이 없어야 함
- 특정 노드를 방문하기 위해선, 해당 노드를 가리키는 이전의 모든 노드를 먼저 방문해야 함
진입차수, 진출차수

- 진입차수 (indegree): 특정 노드로 들어오는 간선의 개수
- 진출차수 (outdegree): 특정 노드에서 나가는 간선의 개수
- 특정 노드를 방문하기 위해선, 해당 노드를 가리키는 이전의 모든 노드를 먼저 방문해야 함
- 즉, 진입차수가 0이 되어야 함
큐를 이용한 위상 정렬
- (1) 진입차수가 0인 모든 노드를 큐에 삽입

- (2) 큐가 빌 때까지 다음 과정을 반복
- 큐에서 원소를 꺼내, 해당 노드에서 나가는 간선을 그래프에서 제거
- 새롭게 진입차수가 0이 된 모든 노드를 큐에 삽입
- 일반적으론 번호가 낮은 노드부터 삽입
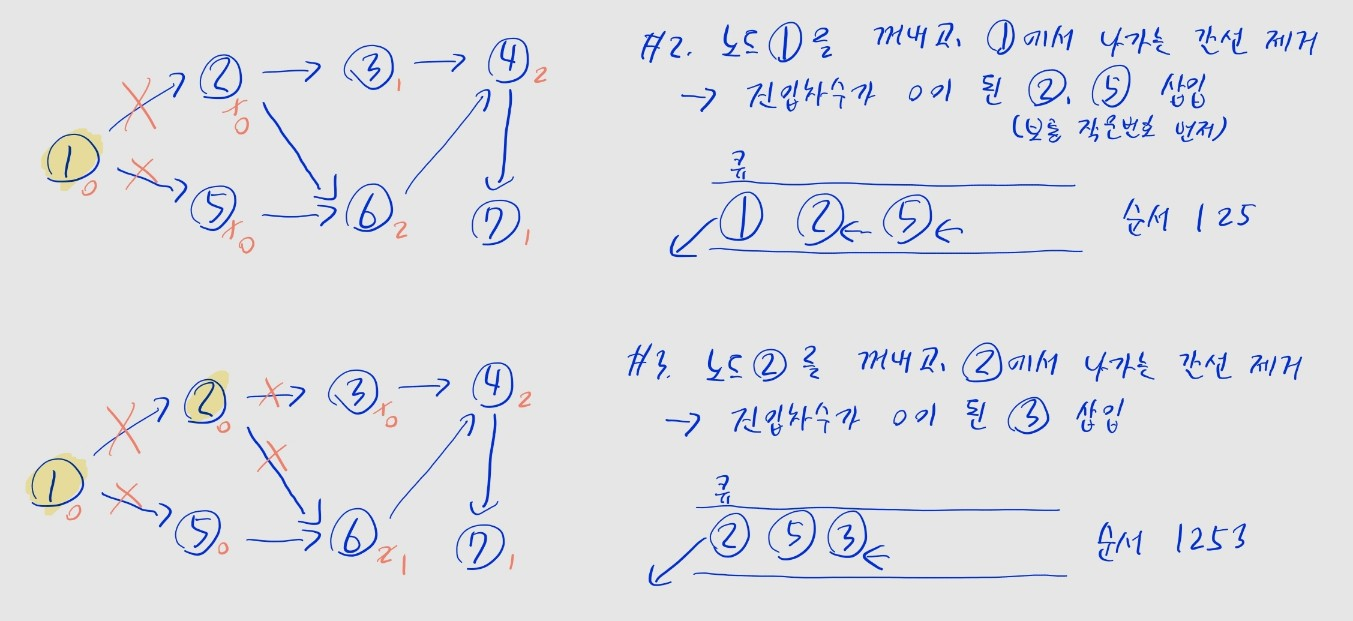
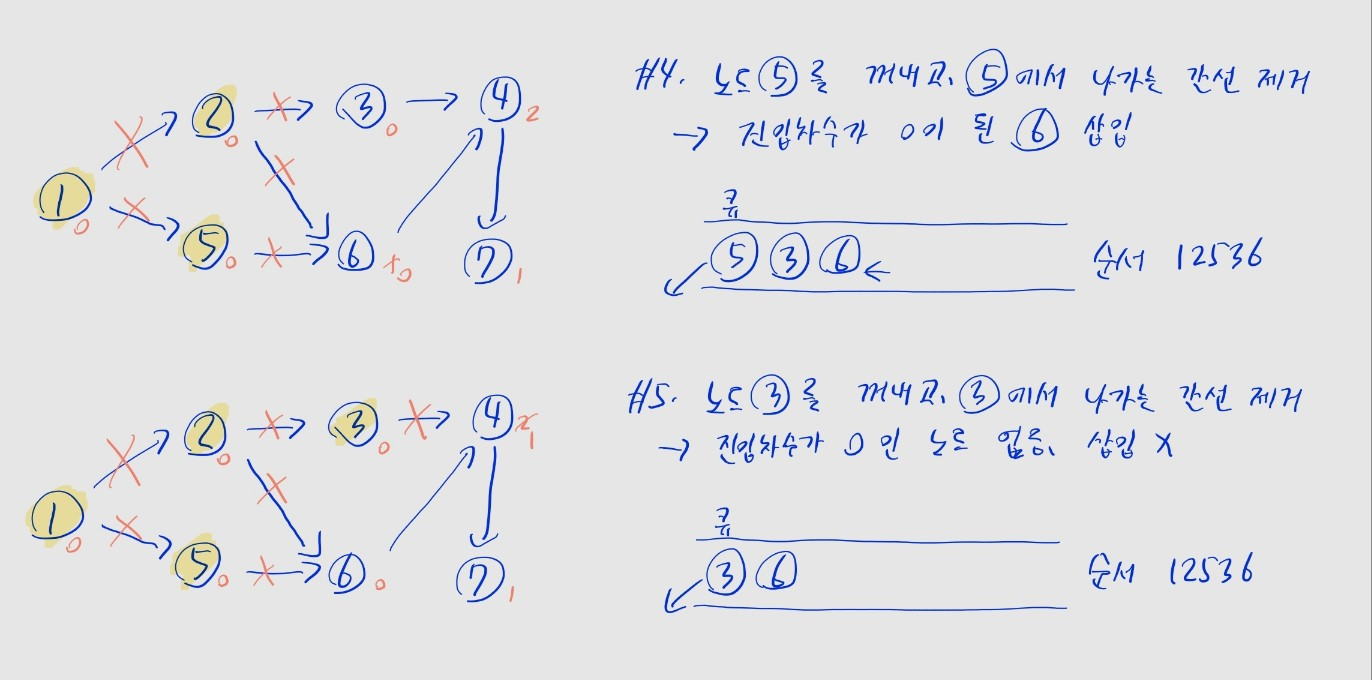
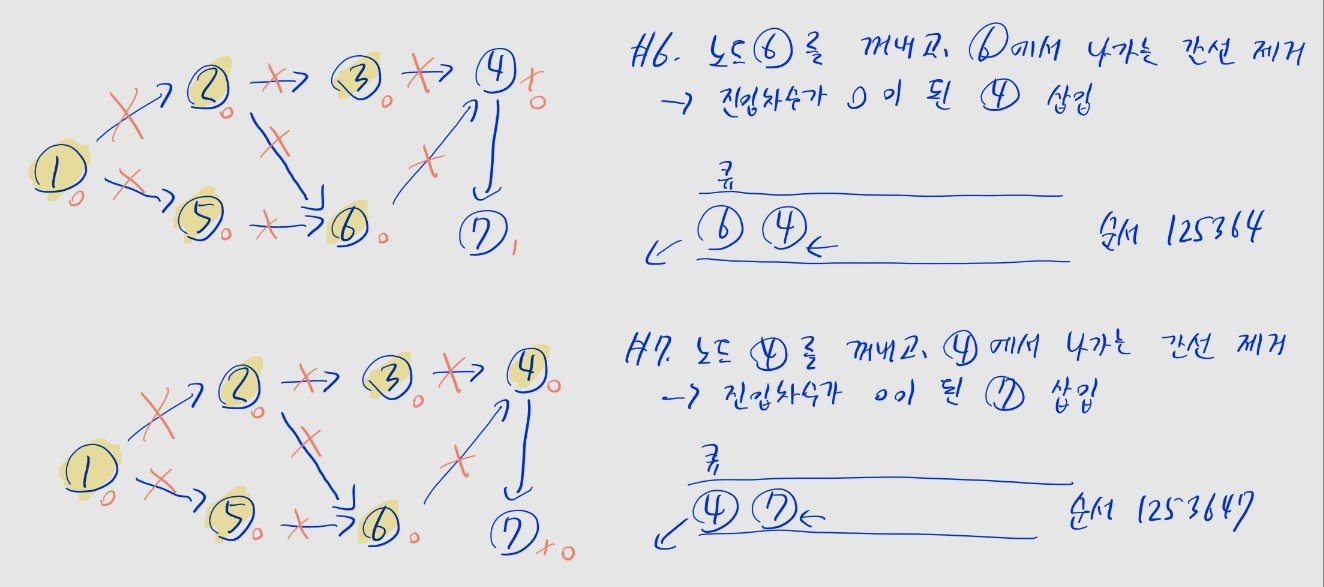
- (3) 각 노드가 큐에 삽입된 순서가, 위상 정렬의 결과
- 위 예제에선
1 -> 2 -> 5 -> 3 -> 6 -> 4 -> 7
- 위 예제에선
- cf. 모든 원소를 방문하기 전에 큐가 빈다면, 사이클이 존재한다고 판단할 수 있음
- 사이클에 포함된 모든 원소는 큐에 들어갈 수 없기 때문

구현
from collections import deque
N = 7 # 노드의 수
# 연결 리스트: 각 노드에 연결된 간선 정보
graph = [
[],
[2, 5],
[3, 6],
[4],
[7],
[6],
[4],
[]
]
# 각 노드의 진입 차수 계산
indegree = [0] * (N + 1)
for i in range(1, N + 1):
for j in graph[i]:
indegree[j] += 1- 각 노드의 진입 차수를
indegree리스트로 관리
# 위상 정렬
def top_sort():
result = [] # 정렬 결과
queue = deque()
# 진입차수가 0인 노드 삽입
for i in range(1, N + 1):
if indegree[i] == 0:
queue.append(i)
# 큐가 빌 때까지
while queue:
# 노드를 꺼내고
curr = queue.popleft()
result.append(curr)
# 노드에서 꺼내는 간선을 제거
for i in graph[curr]:
indegree[i] -= 1
# 진입차수가 0이 된 경우 삽입
if indegree[i] == 0:
queue.append(i)
# 결과 출력
for i in result:
print(i, end=" ")
top_sort() # 1 2 5 3 6 4 7- 큐에서 노드를 꺼내고, 노드에서 나가는 간선을 제거하는 작업 반복
- 인접 리스트에서 간선을 직접 제거할 필요는 없고,
indegree리스트의 값만 1 감소시켜주면 됨
시간 복잡돔
- 차례대로 모든 노드를 확인하며, 모든 간선을 제거
- 노드가 개 간선이 개일 때
문제풀이
2252. 줄 세우기
- 각 학생을 그래프의 노드로 표현하면,
- 학생 A가 학생 B의 앞에 서야 한다: 노드 A -> B 방향의 간선이 존재한다
- 위와 같은 형태의 그래프에서 위상 정렬을 하면 쉽게 풀리는 문제

- cf. 오른쪽처럼 그래프의 모든 노드가 연결되어 있지 않다고 해도, 위상 정렬은 가능함에 유의
from collections import deque
import sys
input = sys.stdin.readline
N, M = map(int, input().split())
graph = [[] for _ in range(N + 1)]
indegree = [0] * (N + 1)
for _ in range(M):
# 학생 A가 학생 B 앞에 서야 됨
# 즉, 노드 A -> 노드 B 방향의 간선이 존재함
a, b = map(int, input().split())
graph[a].append(b)
indegree[b] += 1
def topsort():
queue = deque()
for i in range(1, N + 1):
if indegree[i] == 0:
queue.append(i)
while queue:
curr = queue.popleft()
print(curr, end=" ")
for i in graph[curr]:
indegree[i] -= 1
if indegree[i] == 0:
queue.append(i)
topsort()
전 아직 시작도 못 했는데 덕분에 보고 갑니다~