AlexNet 이란
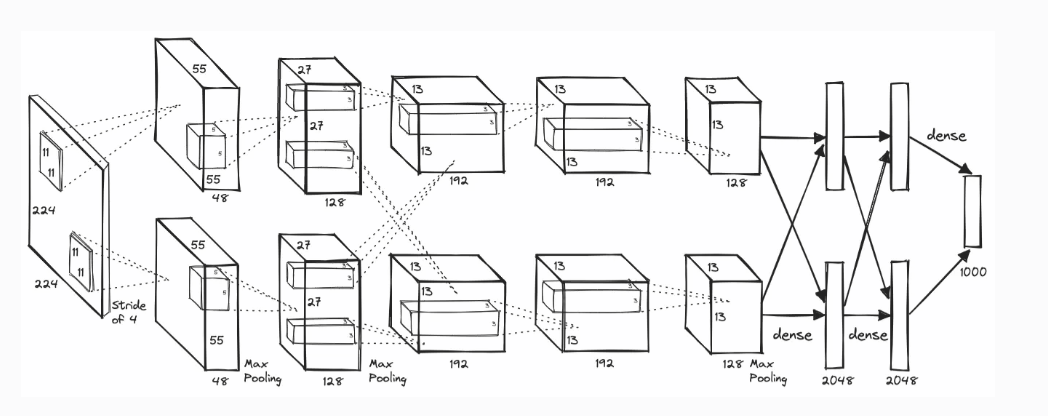
2012년 ILSVRC에서 우승을 차지하여 Deep Learning 붐을 일으킨 CNN 모델
5개의 Conv Layer와 3개의 Linear Layer로 구성되었으며 입력으로 ImageNet 데이터 셋을 받는다.
CiFAR 10 이란

32x32 크기의 작은 이미지들로 구성된 10개의 class를 가진 dataset이다.
50000장의 학습데이터와 10000장의 테스트데이터를 제공한다.
PyTorch 라이브러리에서 호출하여 사용 가능하다.
To do
CiFAR 10 이미지를 입력으로 받는 AlexNet을 구현하고 의도적으로 Overfittig을 시켜
Regularization과 Data Augmentation에 대한 분석을 시도한다.
모델 설계
# MyNeuralNetwork.py
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class MyNeuralNetwork(nn.Module):
# Parameter, which name is dropout_rate, is for testing Overfitting
def __init__(self, dropout_rate=0):
super().__init__()
# define Feature Extractor
# Implement with Input Size 32x32
self.feature_extractor = nn.Sequential(
# 1st Layer
nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
# 2nd Layer
nn.Conv2d(64, 192, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
# 3rd Layer
nn.Conv2d(192, 384, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
# 4th Layer
nn.Conv2d(384, 256, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
# 5th Layer
nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
)
# define Classifier
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Dropout(p=dropout_rate),
nn.Linear(256*4*4, 4096),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Dropout(p=dropout_rate),
nn.Linear(4096, 4096),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Linear(4096, 10),
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.feature_extractor(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
x = self.classifier(x)
return xConvolution Layer
| Layer | Input Size | Kernel | Flow | Output Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | 3 x 32 x 32 | 3x3, s=1, p=1 | Conv -> ReLU -> MaxPool | 64 x 16 x 16 |
| 2nd | 64 x 16 x 16 | 3x3, s=1, p=1 | Conv -> ReLU -> MaxPool | 192 x 8 x 8 |
| 3rd | 192 x 8 x 8 | 3x3, s=1, p=1 | Conv -> ReLU | 384 x 8 x 8 |
| 4th | 384 x 8 x 8 | 3x3, s=1, p=1 | Conv -> ReLU | 256 x 8 x 8 |
| 5th | 256 x 8 x 8 | 3x3, s=1, p=1 | Conv -> ReLU -> MaxPool | 256 x 4 x 4 |
Fully Connected Layer
| Layer | Input Size | Flow | Output Size | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flatten | 256 x 4 x 4 | Flatten (1D Vector) | 4,096 | - |
| FC 1 | 4,096 | Drop -> Linear -> ReLU | 4,096 | p=0.5 (Train) |
| FC 2 | 4,096 | Drop -> Linear -> ReLU | 4,096 | p=0.5 (Train) |
| Output | 4,096 | Linear | 10 | Class Scores |
Dropout 확률은 실행 모드에 따라 0 or 0.5
Dataset 준비
# dataset.py
import torch
from torchvision import datasets, transforms
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, Subset, random_split
import numpy as np
def get_dataloaders(batch_size=128, overfit=False, num_overfit_samples=1000, num_overfit_valid=500):
# Preprocess unit
base_preprocess = [
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.4914, 0.4822, 0.4465), (0.2023, 0.1994, 0.2010))
]
# Loading dataset
test_dataset = datasets.CIFAR10(root='./data', train=False, download=True, transform=transforms.Compose(base_preprocess))
if overfit:
preprocess = transforms.Compose(base_preprocess)
full_train_dataset = datasets.CIFAR10(root='./data', train=True, download=True, transform=preprocess)
else:
preprocess = transforms.Compose([
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
transforms.RandomCrop(32, padding=4),
] + base_preprocess)
full_train_dataset = datasets.CIFAR10(root='./data', train=True, download=True, transform=preprocess)
# split dataset train/val
if overfit:
# overfit mode, Use 1000:500
train_indices = range(num_overfit_samples)
val_indices = range(num_overfit_samples, num_overfit_samples + num_overfit_valid)
train_dataset = Subset(full_train_dataset, train_indices)
val_dataset = Subset(full_train_dataset, val_indices)
else:
# none overfit mode, Use 9:1 randomly
train_size = int(0.9 * len(full_train_dataset))
val_size = len(full_train_dataset) - train_size
train_dataset, val_dataset = random_split(full_train_dataset, [train_size, val_size])
# 4. Data Loader
train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
val_loader = DataLoader(val_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False)
test_loader = DataLoader(test_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False)
return train_loader, val_loader, test_loaderOverfit 모드
- 학습데이터 1000장, 검증데이터 500장으로 준비
Regularized 모드
- 학습 데이터 50000장을 9:1로 split, 테스트 데이터 10000장 로드
- Random flip, Random crop -> Data Augmentation 적용
학습 단계
# train.py
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
import argparse
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from MyNeuralNetwork import MyNeuralNetwork
from dataset import get_dataloaders
# Weight Initialization
def init_weights(m):
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d) or isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
# He Init, Mean 0, random Std
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
# bias init to 0
if m.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
def main(args):
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
print(f"Training config: Overfit={args.overfit}, Epochs={args.epochs}, Batch={args.batch}, LR={args.lr}")
# from dataset.py
train_loader, val_loader, test_loader = get_dataloaders(
batch_size=args.batch,
overfit=args.overfit
)
# Set model mode
if args.overfit:
dropout_p = 0.0
wd = 0.0
else:
# None Overfit mode, apply 2 methods of Regularization
dropout_p = 0.5 # Dropout
wd = 1e-4 # Weight Decay
model = MyNeuralNetwork(dropout_rate=dropout_p).to(device)
model.apply(init_weights)
# Use Cross Entrophy Loss Function and Adam Optimizer
loss_func = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=args.lr, weight_decay=wd)
history = {
'train_loss': [], 'train_acc': [],
'val_loss': [], 'val_acc': []
}
print(f"Starting Train (Device: {device}, Mode: {args.overfit})")
# default epoch is 40
for epoch in range(args.epochs):
# Training
model.train()
train_loss, train_correct, train_total = 0, 0, 0
for images, labels in train_loader:
images, labels = images.to(device), labels.to(device)
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = model(images)
loss = loss_func(outputs, labels)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
train_loss += loss.item() * images.size(0)
_, predicted = outputs.max(1)
train_total += labels.size(0)
train_correct += predicted.eq(labels).sum().item()
epoch_train_loss = train_loss / train_total
epoch_train_acc = 100. * train_correct / train_total
# Validation
model.eval()
val_loss, val_correct, val_total = 0, 0, 0
with torch.no_grad():
for images, labels in val_loader:
images, labels = images.to(device), labels.to(device)
outputs = model(images)
loss = loss_func(outputs, labels)
val_loss += loss.item() * images.size(0)
_, predicted = outputs.max(1)
val_total += labels.size(0)
val_correct += predicted.eq(labels).sum().item()
epoch_val_loss = val_loss / val_total
epoch_val_acc = 100. * val_correct / val_total
history['train_loss'].append(epoch_train_loss)
history['train_acc'].append(epoch_train_acc)
history['val_loss'].append(epoch_val_loss)
history['val_acc'].append(epoch_val_acc)
if (epoch + 1) % 5 == 0 or epoch == 0:
print(f"Epoch [{epoch+1}/{args.epochs}] "
f"Train Loss: {epoch_train_loss:.4f} | Train Acc: {epoch_train_acc:.2f}% | "
f"Val Acc: {epoch_val_acc:.2f}%")
if not args.overfit:
print(f"=========================================")
print(f"Final Test is starting")
model.eval()
test_correct = 0
test_total = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for images, labels in test_loader:
images, labels = images.to(device), labels.to(device)
outputs = model(images)
_, predicted = outputs.max(1)
test_total += labels.size(0)
test_correct += predicted.eq(labels).sum().item()
final_acc = 100. * test_correct / test_total
print(f"Final Test Accuracy: {final_acc:.2f}%")
print(f"=========================================")
# Visualization for Report
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 5))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(history['train_loss'], label='Train Loss')
plt.plot(history['val_loss'], label='Val Loss')
plt.title('Loss Change')
plt.legend()
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(history['train_acc'], label='Train Acc')
plt.plot(history['val_acc'], label='Val Acc')
plt.title('Accuracy Change')
plt.legend()
# Save result plot and model parameters by model for analysis report
mode_name = "overfit" if args.overfit else "regularized"
plt.savefig(f'result_{mode_name}.png')
print(f"Training finished. Saved result plot as result_{mode_name}.png")
torch.save(model.state_dict(), f'model_{mode_name}.pth')
print(f"Saved model parameters to model_{mode_name}.pth")
if __name__ == "__main__":
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--overfit', action='store_true', help='Run in overfit mode')
parser.add_argument('--batch', type=int, default=128)
parser.add_argument('--lr', type=float, default=1e-4)
parser.add_argument('--epochs', type=int, default=40)
args = parser.parse_args()
main(args)실행 방법은 Github README.md 참고
CrossEntropy Loss, Adam Optimizer 사용
Regularized 모드는 Dropout=0.5, Weight Decay=1e-4 적용
Discussion
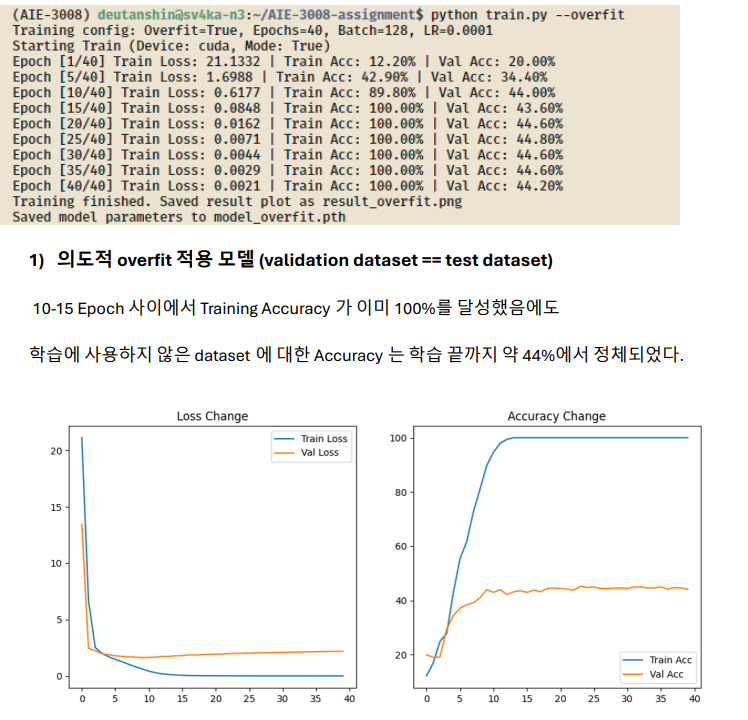
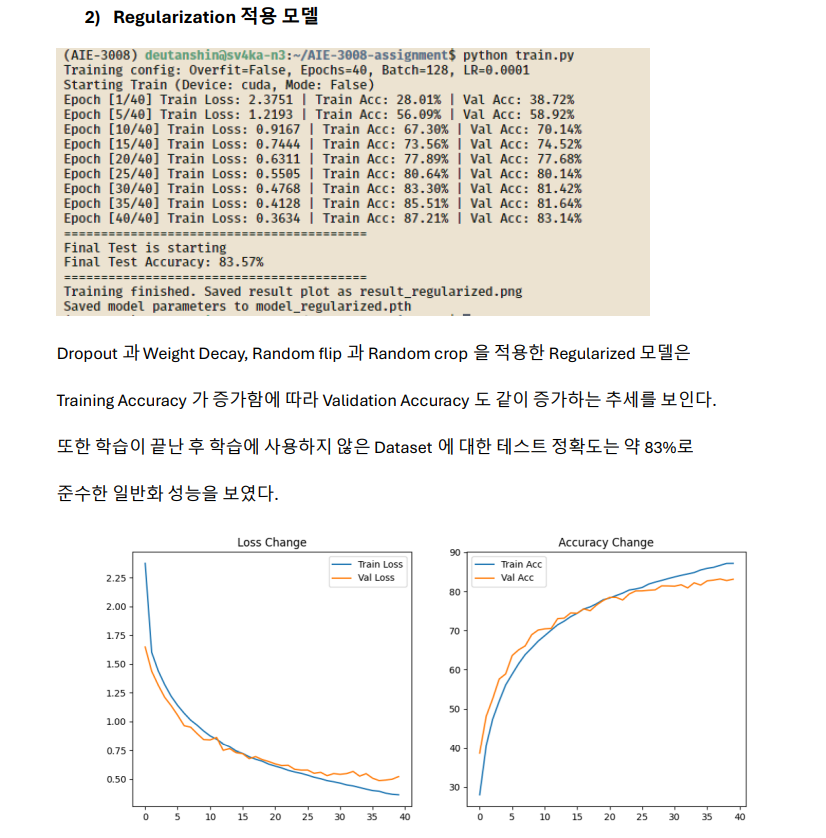
최종 Test Accuracy는 정규화와 데이터 증강을 적용한 모델의 일반화 성능이
의도적 overfitting 모델보다 약 2배 높은 것을 확인할 수 있다.
