[Pytorch Geometric Tutorial] 1. Introduction to Pytorch geometric
Pytorch Geometric Tutorial👶
목록 보기
1/2

<References>
Problems of dealing graph in deep learning
- Different sizes
- 노드 크기에 따라 adjacency matrix의 크기가 달라짐
- NOT invariant to node ordering
- 그래프가 위상적으로 동일하더라도 adjacency matrix는 다를 수 있음
Notation
Computation Graph
: The neighbour of a node define its computation graph
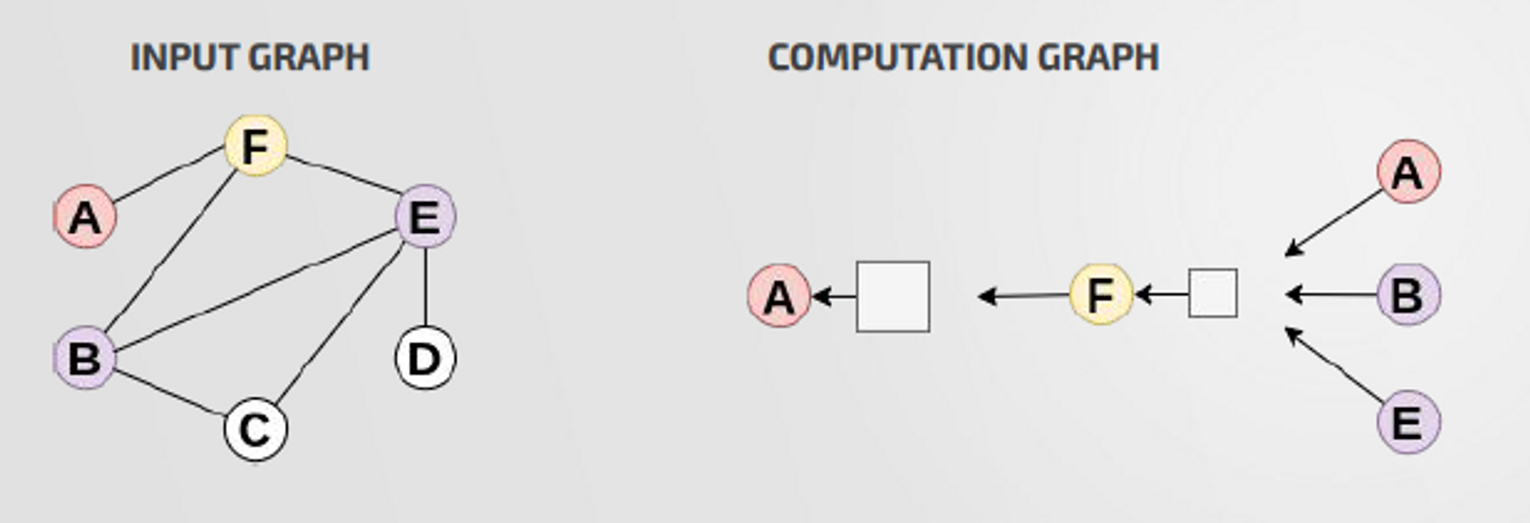
- Neighbor node들의 정보를 aggreagte하여 박스를 거쳐 target node의 representation을 만들어 냄
- 박스 : Neural Network
- Ordering invariant Aggregation : sum, average같이 노드 순서에 상관없는 노드 정보 aggregation
- redundancy : 각 노드들에 대해 2hop의 computational graph를 만들면 중복되는 부분이 발생하게됨
Math
- 0번째 layer에서 node v의 representation은 node feature이다
- : layer0에서 노드 v의 representation
- : node 의 feature
- 노드 representation update
- : layer k+1에서 노드 v의 representation
- : layer k에서 노드 v의 representation
- : 노드 v의 neighbor 에 대해 임베딩을 평균한 것
- : Weights(박스), shared for all computation graph
- : Activation function(relu)
- k번째 layer에서 node v의 representation
GraphSAGE
Inductive Representation Learning on Large Graphs
위의 Math에서 간단한 수정으로 구현할 수 있음
- average ⇒ general aggregation function
- 주변 노드 정보를 합친 정보와 이전 layer의 자기 자신에 대한 정보를 더하는 대신, concatenate(,)
- Pool : Element-wise min/max
- LSTM : note not order invariant
Implementations
https://github.com/sujinyun999/PytorchGeometricTutorial/blob/main/Tutorial1/Tutorial1.ipynb
