Spread
: 변수를 확장시키는 것.
ex) const friends = [1, 2, 3, 4]; console.log(friends); console.log(...friends); // "..."가 friends array 안의 1,2,3,4 라는 값을 확장시킴.
- 위 예시 코드 출력값 비교.
1. 2개의 array 안의 값을 하나의 array로 묶기.
ex) const friends = [1, 2, 3, 4]; const family = [“a”, “b”, “c”]; console.log([friends, family]); // 2개의 array가 하나로 묶이지만, //하나로 묶인 array 안에 friends와 family가 array 형태로 존재한다. // 이때, 2개의 array 값들을 하나의 array로 묶기위해 spread operator를 사용한다.
- 1번의 예시 코드에 spread operator 사용하기.
ex) const friends = [1, 2, 3, 4]; const family = [“a”, “b”, “c”]; console.log([...friends, ...family]);
- 1번 예시 코드와 2번 예시 코드 출력값 비교.
2. 2개의 object 안의 data를 하나의 object로 묶기.
ex) const sexy = { name: "nico", age: 24 }; const hello = { sexy: true, hello: "hello" }; console.log({...sexy, ...hello})
- 출력값
3. spread operator를 활용한 예제.
1. 기존 array에 내용 추가하여 새로운 array 만들기.
(= 기존 데이터를 복사해서 새로운 데이터를 만들고 싶을 때, 사용.)
(object에도 사용가능)
1.ex) const friends = [“nico”, “lynn”]; const newFriends = […friends, “dal”]; // 이때, 새로운 데이터를 앞쪽에 넣고 싶다면, // const newFriends = [“dal”, …friends]; console.log(newFriends);
- 1번 출력값
- 또다른 활용 예시 코드.
ex) const first = [“mon”, “tue”, “wed”]; const weekend = [“sat”, “sun”]; const fullWeek = […first, “thu”, “fri”, …weekend];
- 2번 출력값
2. object에 property를 조건부로 추가하기.
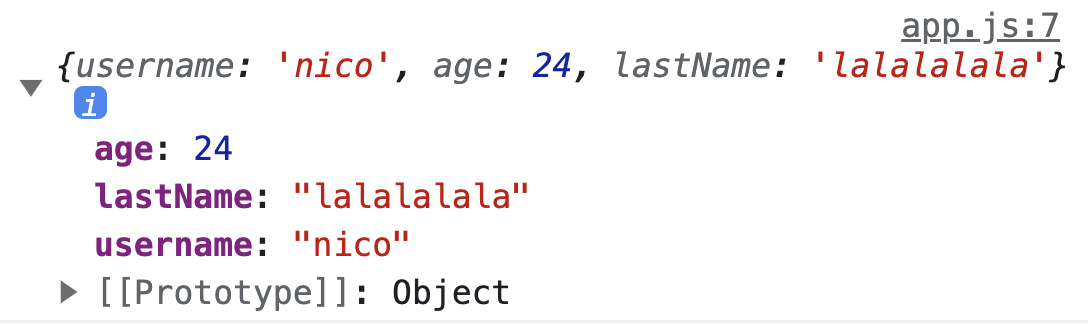
ex) const lastName = prompt("Last name"); const user = { username: "nico", age: 24, lastName: lastNAme !== "" ? lastName: undefined // lastName !== "" 이면, lastName 값을 넣어주고, // lastName이 빈 문자열이면, undefined를 넣어준다. }; console.log(user);
- lastName !== "" 일때, 출력값
- lastName이 빈 문자열 일때, 출력값
- 1번 예시 코드에서 lastName이 빈 문자열 일때, key값 제거하기.
ex) const lastName = prompt("Last name"); const user = { username: "nico", age: 24, ...(lastName !== "" && {lastName}) }; console.log(user);
- lastName이 빈 문자열 일때, 출력값
Rest parameter
: 모든 값을 하나의 변수로 축소(constract) 시킨다.
- spread는 변수를 확장시키고, rest는 변수를 축소시킨다.
(rest는 array를 만든다.)- 구문 : ...rest
(이때, rest 대신 다른 이름을 넣어도 된다.)
ex) const infiniteArgs = (...kimchi) => console.log(kimchi); // spread operator를 작성하고 아무 이름이나 적으면, // 적은 argument가 array 형태로 출력된다. infiniteArgs(“1”, 2, true, “lalala”, [1, 2, 3, 4]);
- 1번 출력값
ex) const bestFriendMaker = (firstOne, ...rest) => { console.log(`My best friend is ${firstOne}`); console.log(rest); }; bestFriendMaker(“nico”, “lynn”, “dall”, “japan guy”);
- 2번 출력값
Spread, Rest, Destructuring을 활용한 예시.
1. object에서 특정 data 제거하기.
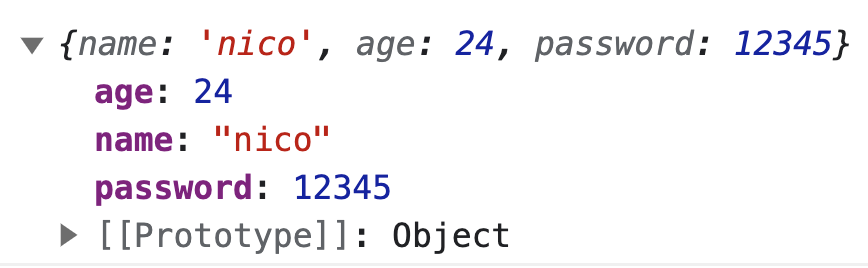
ex) const user = { name: "nico", age: 24, password: 12345 }; const killPassword = ({password, ...rest}) => rest; // destructuring으로 제거하고자 하는 data는 password, 나머지 data는 ...rest로 구분한다음, // rest만 반환해준다. const cleanUser = killPassword(user); console.log(cleanUser);
- 1번 출력값
2. 기본값 설정하기.
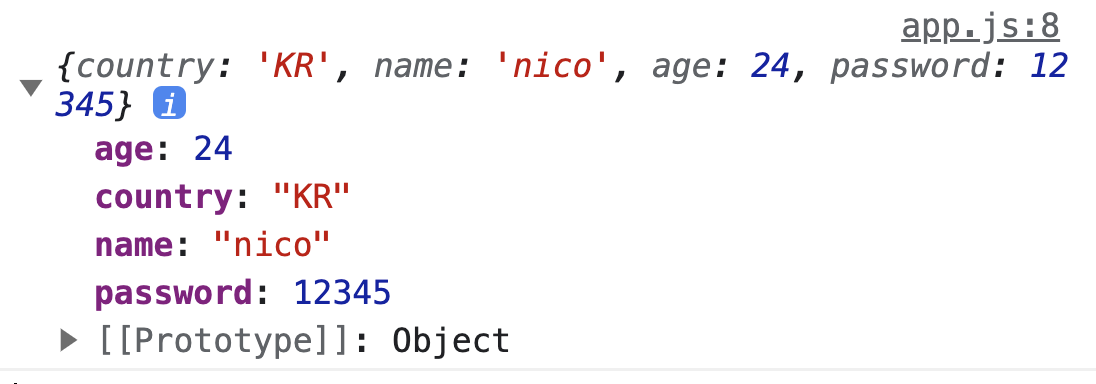
ex) const user = { name: "nico", age: 24, password: 12345 }; const setCountry = ({country = "KR" , ...rest}) => ({country, ...rest}); console.log(setCountry);
- 1번 출력값
3. 속성명 바꾸기.
ex) const user = { NAME: "nico", age: 24, password: 12345 }; const rename = ({NAME: name, ...rest}) => ({name, ...rest}); console.log(rename(user));
- 1번 출력값