비동기적(Asynchronous) 처리 방식이란?
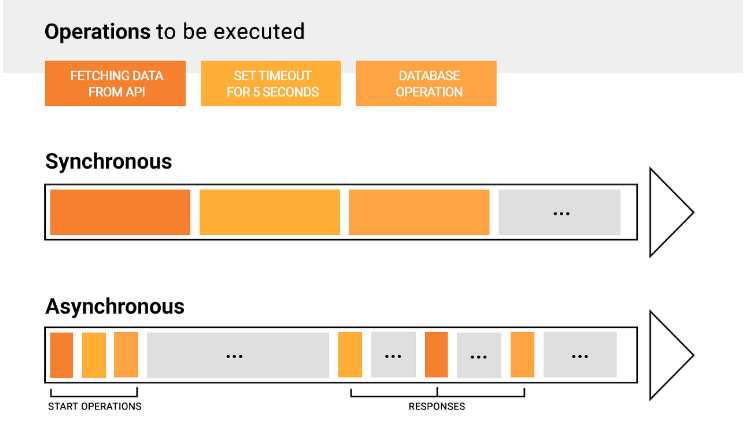
일반적인 프로그램의 코드는 특정 작업이 끝나면 다음 작업을 진행하는 순차처리 방식으로 실행된다. 이를 동기적(Synchronous) 처리 방식이라고 한다.
반대로 비동기적(Asynchronous) 처리 방식이란 특정 작업의 종료 일시와 상관 없이 다음 작업을 진행할 수 있다. 즉 A작업이 시작하면 동시에 B작업이 실행되고, A, B 작업은 결과값이 나오는대로 출력된다
When to use
동기처리와 비동기처리 방식의 차이점을 잘 보여주는 그림이 있어 첨부해봤다.
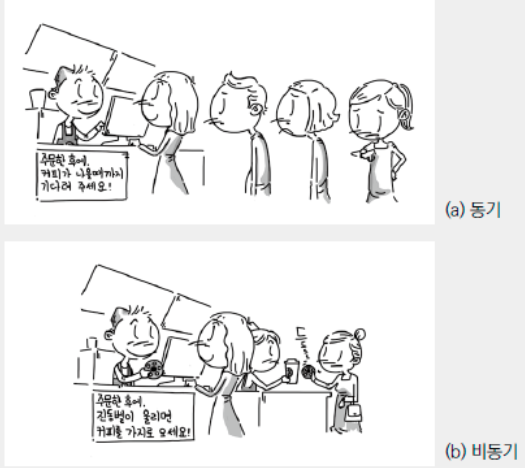
위 설명만 보면 비동기적 처리 방식이 동기적 처리방식보다 더 효율적으로 보이지만 때에 따라서 다르다. 상황에 따라 비동기적 프로그래밍 방식이 더 비효율적일 수도 있다. 아래의 링크는 어느 경우에 비동기적, 동기적 처리 방식을 사용해야 할 지에 대한 개발자들의 의견을 모아놓은 링크다.
When to Use(and Not to Use) Asynchronous Programming : 20 Pros Reveal the Best Use Cases
요약하자면,
비동기식 처리 방식이 효율적일 경우
- 앱이 맨처음 시작되기 전 데이터에 대한 preloading이 필요한 때
- 각각의 요청이 서로 독립적인 경우 (많은 양의 요청일수록 더욱 효율적임)
- Response가 유독 느린 웹사이트의 자원을 가져와야 할 때
비동기식 처리 방식이 비효율적일 경우
- 간단한 작업을 처리한다거나
- 로직의 효율성보다는 간결함이 필요할 때
- DB 커넥션 풀을 세팅하지 않고, 하나의 데이터베이스 서버를 돌리고 있는 상태일 때
예시
파이썬으로 간단한 asynchrounous programming 예시를 만들어보자. 우선 asyncio 모듈을 설치해준다
asyncio란?
asyncio(Asynchronous I/O)는 CPU 작업과 I/O의 병렬처리를 지원하는 파이썬 모듈이다.
pip install asyncio먼저 asyncio를 사용하려면 코루틴을 생성해야 한다. 코루틴이란 멀티태스킹이 가능한 함수를 의미한다. 코드의 특정 위치에서 실행을 일시 중단하고 다른 코드를 실행할 수 있다. 일반 함수를 사용하면 코드를 한 번만 실행할 수 있지만, 코루틴을 코드를 여러 지점에서 여러번 실행할 수 있다. 이는 자바스크립트의 promise 객체와 비슷하다고 할 수 있다.
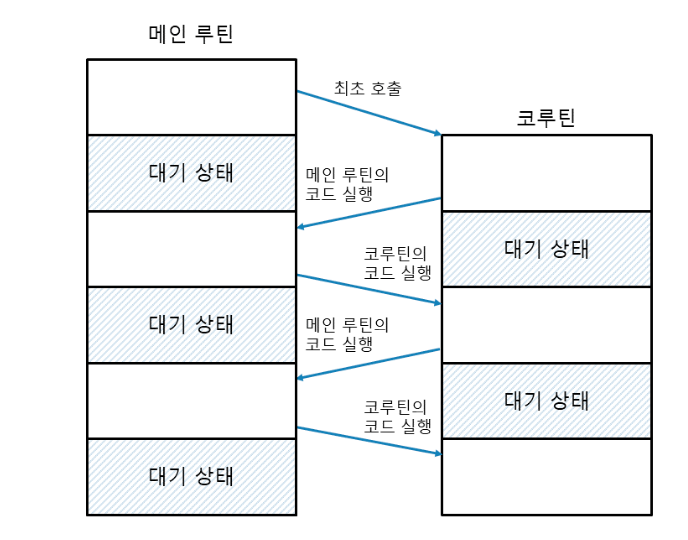
코루틴을 생성하기 위해서는 async def 키워드를 사용한다.
async def say_hi():
print("Hello World")위에서 정의한 say_hi() 함수를 호출하면 coroutine 객체가 리턴된다
if __name__ == "__main__":
a = hello()
print(a)실행결과
<coroutine object hello at 0x7fa82d6f2560>
sys:1: RuntimeWarning: coroutine 'say_hi' was never awaited실제로 정의한 coroutine 객체를 실행해보자
import asyncio
async def say_hi():
print("Hello World")
if __name__ == "__main__":
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop() # 이벤트 루프를 얻음
loop.run_until_complete(say_hi()) #say_hi 코루틴이 끝날 때 까지 기다림시간 비교해보기
웹 페이지의 크기를 출력하는 코드를 비동기식, 동기방식으로 처리해 실행시간을 비교해보자
동기식
from time import time
from urllib.request import Request, urlopen
urls = [
"https://www.google.co.kr/search?q=" + i
for i in ["apple", "pear", "grape", "pineapple", "orange", "strawberry"]
]
begin = time()
result = []
for url in urls:
request = Request(url, headers={"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0"})
response = urlopen(request)
page = response.read()
result.append(len(page))
print(result)
end = time()
print(f"실행 시간 : {end-begin}")결과
[437806, 84419, 76639, 97318, 418479, 70884]
실행 시간 : 15.668166875839233비동기식
import asyncio
from time import time
from urllib.request import Request, urlopen
urls = [
"https://www.google.co.kr/search?q=" + i
for i in ["apple", "pear", "grape", "pineapple", "orange", "strawberry"]
]
async def fetch(url):
request = Request(url, headers={"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0"})
response = await loop.run_in_executor(None, urlopen, request)
page = await loop.run_in_executor(None, response.read)
return len(page)
async def main():
#Task를 ensure_future() 메소드를 사용해 리스트로 만들어준다
fetches = [asyncio.ensure_future(fetch(url)) for url in urls]
result = await asyncio.gather(*fetches)
begin = time()
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
loop.run_until_complete(main())
loop.close()
end = time()
print(f"실행 시간 : {end-begin}")결과
[97318, 418459, 77614, 70884, 77901, 437806]
실행 시간 : 4.584640026092529동기식은 15초, 비동기식은 4초가 걸렸다. 또한 비동기식으로 프로그램을 짤 경우 페이지의 크기 측정이 끝난 순서대로 크기가 출력되는것을 확인할 수 있다.