연결리스트(Linked List)
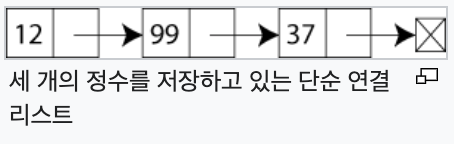
연결 리스트(linked list)는 각 노드가 데이터와 포인터를 가지고 한 줄로 연결되어 있는 방식으로 데이터를 저장하는 자료 구조이다.
Linked List 종류
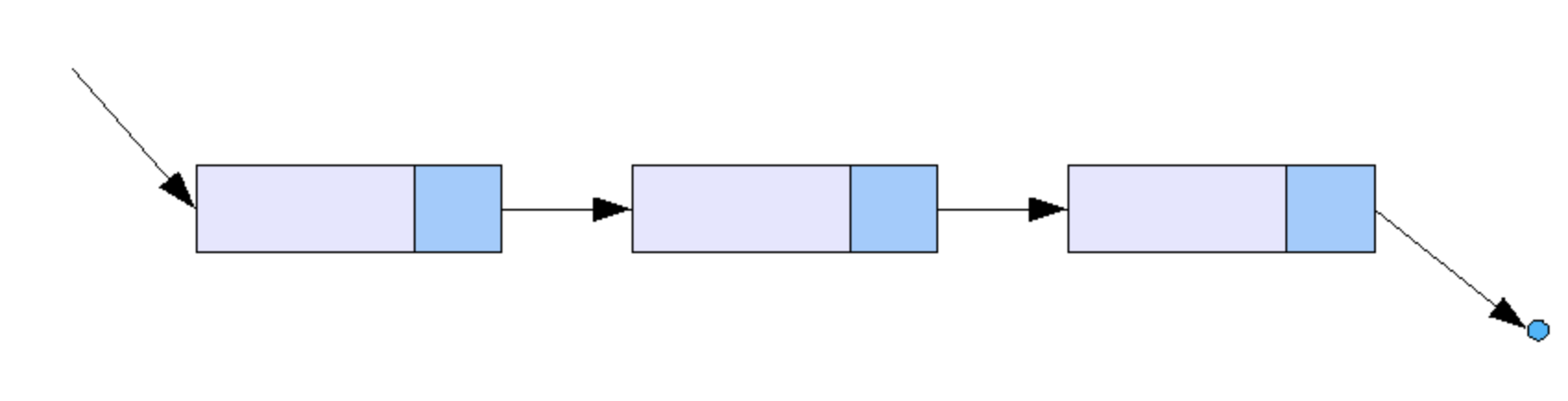
1. 단일 연결 리스트 - Single Linked List
단일 연결 리스트는 각 노드에 자료 공간과 한 개의 포인터 공간이 있고, 각 노드의 포인터는 다음 노드를 가리킨다.
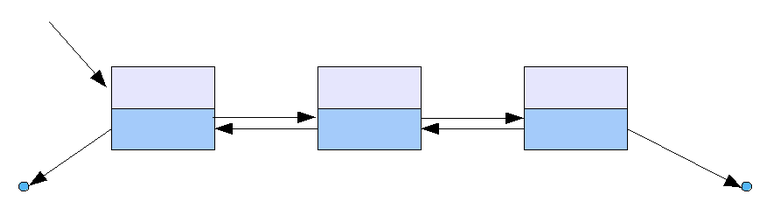
2. 이중 연결 리스트 - Double Linked List
이중 연결 리스트의 구조는 단일 연결 리스트와 비슷하지만, 포인터 공간이 두 개가 있고 각각의 포인터는 앞의 노드와 뒤의 노드를 가리킨다.
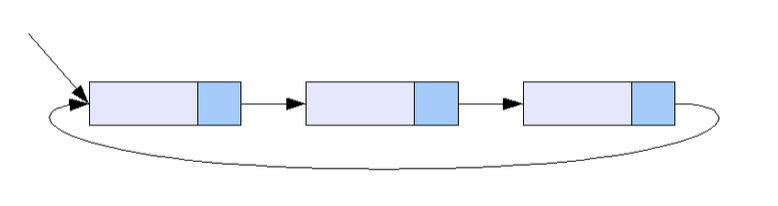
3. 원형 연결 리스트
단순 원형 연결 리스트의 구조
원형 연결 리스트는 일반적인 연결 리스트에 마지막 노드와 처음 노드를 연결시켜 원형으로 만든 구조이다
Linked List의 구성요소
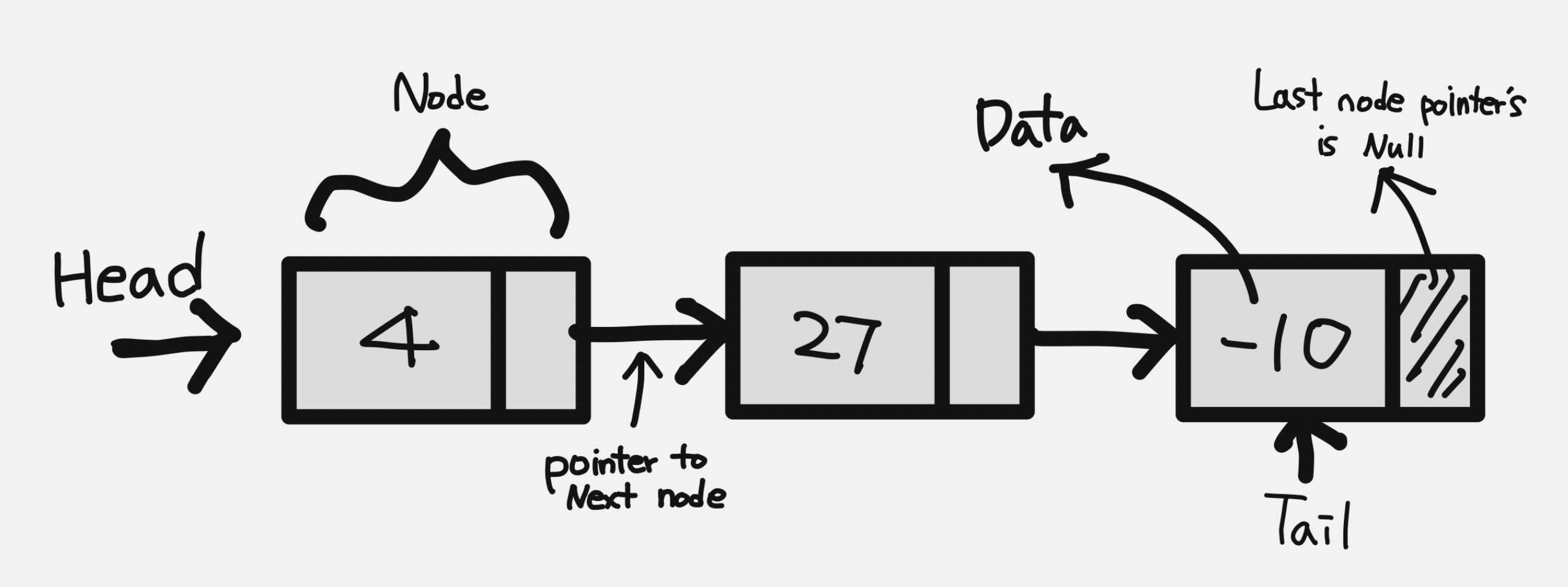
- Node : 리스트에서 데이터를 저장하는 단위
- Pointer : 리스트에서 다음 노드의 주소값
- Head : 리스트의 맨 처음 노드
- Tail : 리스트의 맨 끝 노드
Linked List 와 Array
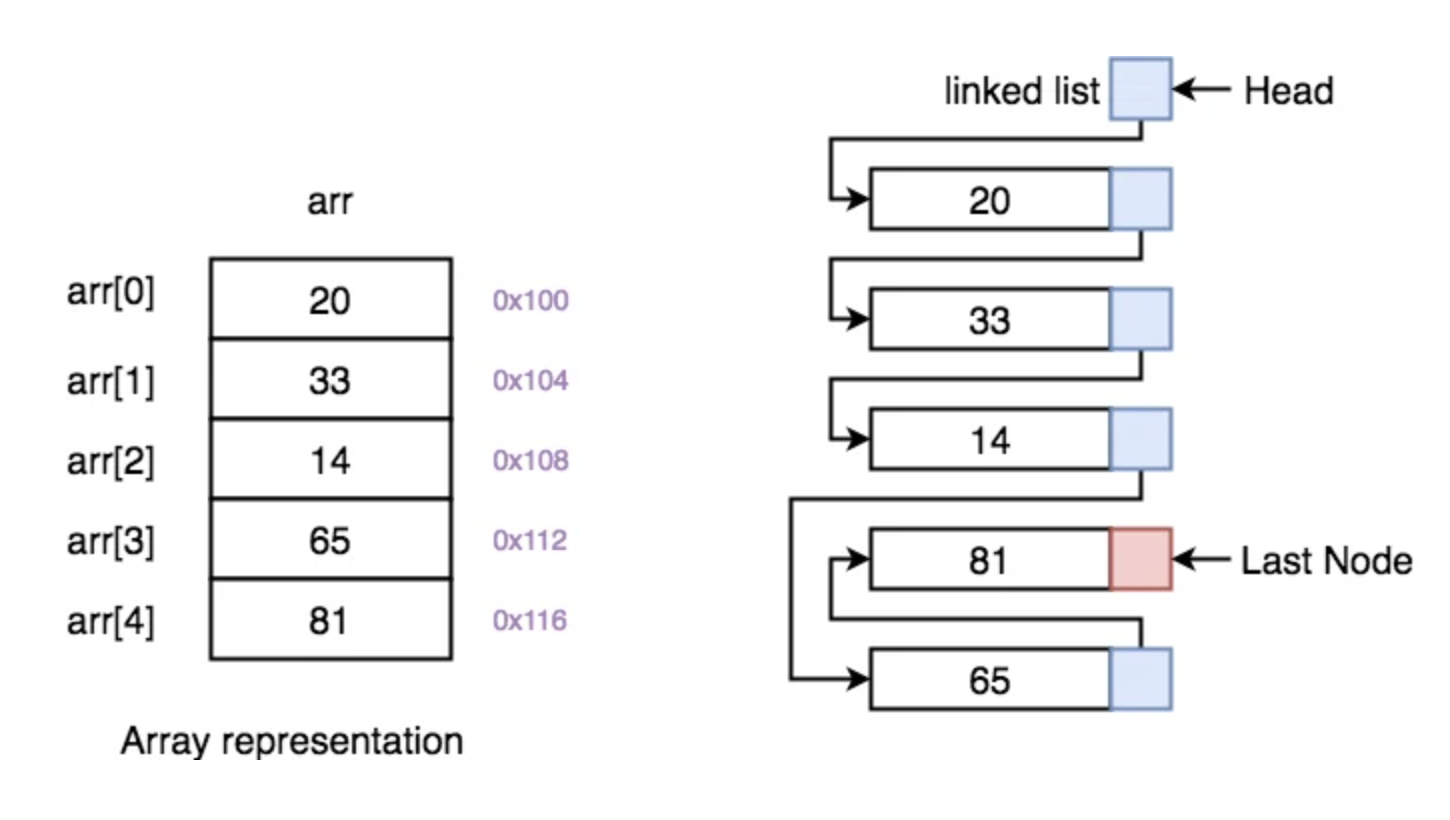
| Array | Linked List |
|---|---|
| 유사한 데이터 유형의 요소 모음 | Linked ㅣ포인터를 사용해 서로 연결된 동일한 유형의 요소 집합 |
| Random Access를 지원(arr[0], arr[6]...), 따라서 요소에 액세스 하는 시간복잡도는 0(1)로 매우 빠르다 | 순차접근을 지원, 순차적으로 탐색해야 한다. 따라서 시간복잡도가 0(n) |
| 요소는 연속적인 메모리 위치에 저장 되거나 메모리 에 연속 적인 방식으로 저장 | 새 요소에 할당된 메모리 위치의 주소는 연결 목록의 이전 노드에 저장되어 두 노드/요소 사이에 연결을 형성 |
| 메모리 위치가 연속적이고 고정되어 삽입 및 삭제 작업에 더 많은 시간이 걸림 | 삽입 및 삭제 작업은 연결 목록에서 빠름 |
| 1차원 , 2차원 또는 다차원 | 선형(단일) 연결 목록 , 이중 연결 목록 또는 원형 연결 목록 |
| 배열은 스택 섹션에 할당된 메모리를 가져옴 | 힙 섹션에 할당된 메모리를 가져 옴 |
삽입 및 삭제 작업에 더 유리한 linked list 반면 독립적이고 요소에 액세스 하기에 유리한 배열
Linked List 직접 구현해보자!
Node 자바스크립트 소스
class Node {
constructor(data, next=null){
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
}
const n1 = new Node(100);
console.log(n1)
// { data:100, next: null}Linked List에 기능을 추가해보자!
첫번째노드에 데이터를 삽입
class LinkedList {
constructor(){
this.head = null;
this.size = 0;
insertFirst(data){
// 데이터를 전달하는 노드 객체를 인스턴스화 한다.
this.head = new Node(data, this.head);
this.size ++;
}마지막노드에 데이터를 삽입
insertList(data){
let node = new Node(data);
let current;
if(!this.head){
// 리스트에 값이 없는 경우 head에 바로 node를 넣는다.
this.head = node;
}else{
current = this.head;
while(current.next){
current = current.next;
}
//마지막 current.next에 요소가 없을때 node추가!
current.next = node;
}
this.size++;
}원하는 index에 데이터를 삽입
insertAt(data, index){
// 🚧 예외처리 인덱스가 범위 밖에 있으면 리턴
if(index > 0 && index > this.size){
return;
}
// index가 0이라면 head에 추가해준다.
if(index === 0){
this.head = new Node(data, this.head);
return;
}
const node = new Node(data);
let current, previous;
// 현재 head의 값은 current로 지정
current = this.head;
let counter = 0;
while(count < index){
//Node before index
previous = current;
count++;
// Node after index
current = current.next;
}
node.next = current;
previous.next = node;
this.size++;
}index의 값 가져오기
getAt(index){
// currnet는 제일 첫번째 값으로 지정
let current = this.head;
let count = 0;
while(count){
if(count == index){
//입력값과 count 가 같을때 data 리턴
console.log(current.data);
}
count++;
current = current.next;
}
return null;
}index의 값 삭제하기
removeAt(index){
// 🚧 예외처리 인덱스가 범위 밖에 있으면 리턴
if(index > 0 && index > this.size){
return;
}
let current = this.head;
let previous;
let count = 0;
// index가 0이라면 첫번째 값인 head에 다음값을 대입해 바로 삭제한다.
if(index === 0){
this.head = current.next;
}else{
while(count < index){
count++;
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
previous.next = current.next;
}
this.size--
}
}리스트 clear 하기
clearList(){
this.head = null;
this.size = 0;
}리스트 프린트
printListData(){
let current = this.head;
while(current){
console.log(current.data);
current = current.next;
}
}
}📚 Test
const ll = new LinkedList();
ll.insertFirst(100);
console.log(ll) // { head:Node { data:100, next: null}, size:0 }
ll.insertFirst(200);
ll.insertFirst(300);
ll.insertList(400);
ll.insertAt(500,2);
ll.getAt(2); //500
ll.removeAt(1);
ll.printListData(); //300 500 100 400
ll.clearList()
ll.printListData(); // reference
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZBdE8DElQQU
https://www.studytonight.com/data-structures/linked-list-vs-array
