형 변환
package chap_01;
public class _07_TypeCasting {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 형변환 TypeCasting
// 정수형에서 실수형으로
// 실수형에서 정수형으로
// int to float, double
int score = 93;
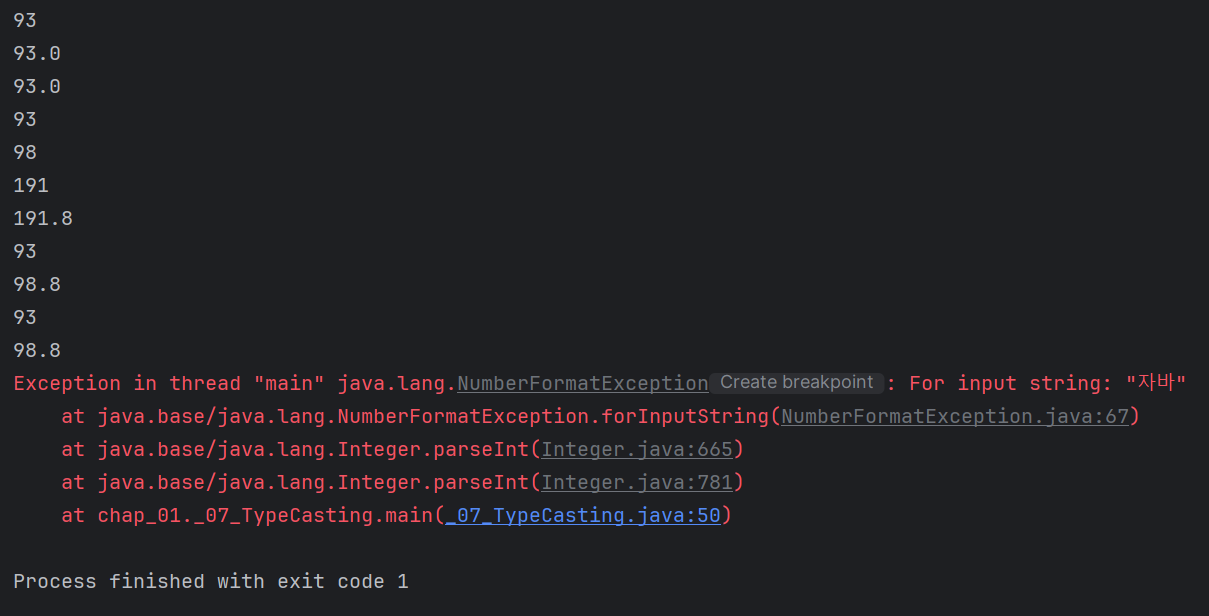
System.out.println(score); // 93
System.out.println((float) score); // 93.0
System.out.println((double) score); // 93.0
// float, double to int
float score_f = 93.3F;
double score_d = 98.8;
System.out.println((int) score_f); // 93
System.out.println((int) score_d); // 98
// 정수 + 실수 연산
score = 93 + (int) 98.8; // 93 + 98
System.out.println(score); // 191
score_d = (double) 93 + 98.8; // 93.0 + 98.8
System.out.println(score_d); // 191.8
// 변수에 형변환된 데이터 집어넣기
double convertedScoreDouble = score; // 191 -> 191.0
// int -> long -> float -> double (자동 형변환)
int convertedScoreInt = (int) score_d; // 191.8 -> 191
// double -> float -> long -> int (수동 형변환)
// 숫자를 문자열로
String s1 = String.valueOf(93);
s1 = Integer.toString(93);
System.out.println(s1); // 93
String s2 = String.valueOf(98.8);
s2 = Double.toString(98.8);
System.out.println(s2); // 98.8
// 문자열을 숫자로
int i = Integer.parseInt("93");
System.out.println(i); // 93
double d = Double.parseDouble("98.8");
System.out.println(d); // 98.8
int error = Integer.parseInt("자바");
}
}
Quiz
Q. 버스 도착 정보를 출력하는 프로그램 작성
각 정보는 적절한 자료형의 변수에 정의
정보
- 버스 번호는 "1234", "상암08"과 같은 형태
- 남은 시간은 분 단위(예: 3분, 5분)
- 남은 거리는 km 단위(예: 1.5km, 0.8km)