Static
static키워드는 모든 객체가 함께 사용하는 변수나 메서드를 만들 때 사용된다.- 객체를 만들지 않아도 클래스 이름만으로 바로 사용할 수 있다.
- static 변수와 메서드는 한 번만 생성되고 메서드영역에 저장된다.
Static 활용
- static 키워드는 변수, 메서드에 붙일 수 있다.
- static 키워드로 선언된 변수와 메서드는 MethodArea에 저장된다.
- 각 객체는 클래스영역에 저장된 데이터를 활용할 수 있다.
class Person {
// ✅ static 변수
static int population = 0;
// ✅ static 메서드
static void printPopulation() {
System.out.println("현재 인구 수: " + population);
}
}System.out.println("static 변수: " + Person.population);
System.out.println("static 메서드: " + Person.printPopulation);인스턴스 멤버
- 객체를 만들 때 마다 생성되는 변수와 메서드이다.
- 객체를 생성한 후에만 사용할 수 있다.
- 각 객체가 개별적으로 값을 가진다.
- 인스턴스는
Heap영역에 위치한다.
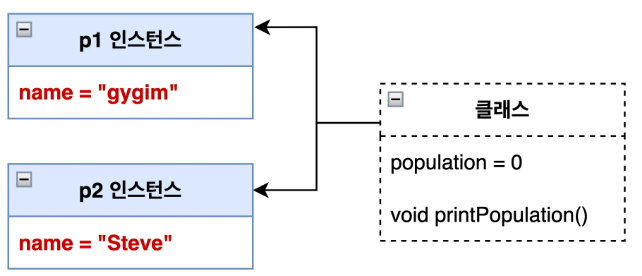
인스턴스 변수
- 객체가 생성될 때마다 따로 만들어지는 변수이다.
- 객체를 생성한 후 접근할 수 있다.
- 아래에
name변수는 각 객체마다 별도로 저장된다.
class Person {
String name; // ✅ 인스턴스 변수
}public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p1 = new Person(); // p1 객체 생성
p1.name = "gygim"; // ✅ p1 객체의 데이터에 접근
Person p2 = new Person(); // p2 객체 생성
p2.name = "Steve"; // ✅ p2 객체의 데이터에 접근
}
}
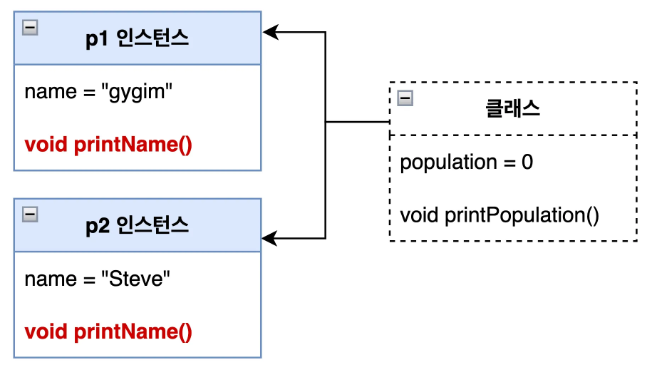
인스턴스 메서드
- 객체의 속성을 활용하는 메서드이다.
- 객체가 생성된 후에만 사용할 수 있다.
class Person {
String name;
void printName() { // ✅ 인스턴스 메서드
System.out.println("나의 이름은 " + this.name + "입니다.");
}
}public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p1 = new Person();
p1.name = "gygim";
p1.printName(); // ✅ p1 객체의 메서드 실행
Person p2 = new Person();
p2.name = "Steve";
p2.printName(); // ✅ p2 객체의 메서드 실행
}
}
클래스 멤버
- 클래스 자체에 속하는 변수와 메서드를 의미한다.
static키워드를 사용해서 선언한다.- 해당 클래스로 만들어진 객체가 공유해서 사용할 수 있다.
- 클래스가 로드될때
Method Area에 적재된다. - 객체 생성 없이 사용 가능하다.
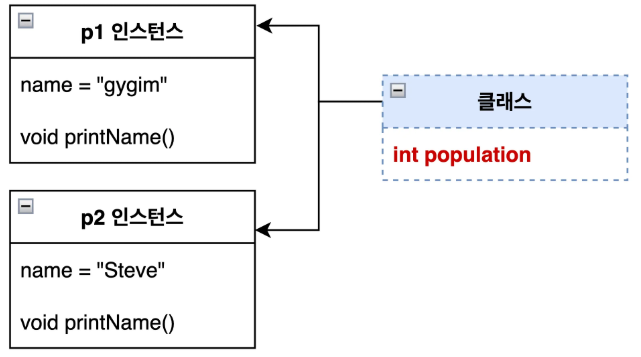
클래스 변수
- 클래스가 로드될 때 한번만 생성되며 모든 객체가 공유하는 변수이다.
Heap이 아니라Method Area에 저장된다.- 객체를 만들지 않아도
클래스명.변수명으로 접근이 가능하다.
class Person {
static int population = 0; // ✅ 클래스 변수
}public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// ✅ 객체 생성 전에도 클래스 레벨에서 직접 접근가능
System.out.println("현재 인구 수: " + Person.population);
Person p1 = new Person();
Person p2 = new Person();
// ✅ 모든 객체가 하나의 값을 공유
System.out.println("현재 인구 수: " + Person.population);
}
}
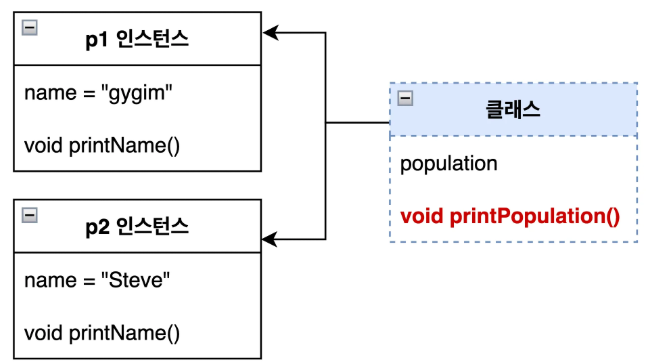
클래스 메서드
- 객체 없이 사용할 수 있다.
- 클래스 변수만 사용할 수 있고 인스턴스 변수는 사용할 수 없다.
class Person {
static int population = 0;
public Person(String name) {
this.name = name;
population++; // 생성자 호출시 populataion 1 증가
}
static void printPopulation() {
System.out.println("현재 인구 수: " + population); // ✅ 클래스 메서드
}
}public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// ✅ 객체생성 여부에 상관없이 사용 가능
Person.printPopulation(); // 현재 인구 수: 0
Person p1 = new Person("gygim"); // 생성시마다 population 1 증가
Person p2 = new Person("Steve"); // 생성시마다 population 1 증가
Person.printPopulation(); // 현재 인구 수: 2
}
}
ㅤ
⚠️
Static사용시 주의사항
static은 공유가 필요한 곳에서만 사용해야한다.
public class Student {
static String name; // ⚠️ 모든 객체가 동일한 name을 공유 (위험)
public Student(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void printName() {
System.out.println("이름: " + name);
}
}public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1 = new Student("gygim");
Student s2 = new Student("Steve");
s1.printName(); // ⚠️ "이름: Steve"
s2.printName(); // ⚠️ "이름: Steve"
}
}ㅤ
⚠️
Static 메서드에서는 인스턴스변수에 접근할 수 없다.
- 인스턴스 멤버를 사용하기 위해서는 먼저 객체가 생성되어야 한다.
public class Person {
String name;
public static void staticMethod() {
System.out.println(this.name); // ⚠️ 오류 발생
}
}public class Example {
int instanceVar = 10;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Example ex = new Example();
System.out.println(ex.instanceVar); // ✅ 정상 출력
}
}
ㅤ
⚠️
static변수와 메모리는 프로그램이 종료될 때까지 메모리에 유지된다.
-> 너무 많은static을 남용하면 메모리 낭비로 이어진다.
final
final의 용도
1. 변수는 변경이 불가능하게 만든다.
- 변수에
final을 붙이면 변수를 한 번만 설정할 수 있다.
final int a = 100;
a = 200; // ❌ 오류 발생!2. 클래스는 상속할 수 없게 만든다.
final로 선언된 클래스는 상속할 수 없다.
final class Animal {
void sound() {
System.out.println("Animal sound!");
}
}
// class Dog extends Animal {} // ❌ 오류! final 클래스는 상속할 수 없음3. 메서드는 수정할 수 없게 만든다.
final로 선언된 메서드는 오버라이딩 할 수 없다.
class Parent {
final void show() {
System.out.println("Hello from Parent");
}
}
class Child extends Parent {
@Override
void show() { // ❌ 오류! final 메서드를 재정의할 수 없음
System.out.println("Hello from Child");
}
}상수(constant)
- 변하지 않고 항상 일정한 값을 갖는 수이다.
- Java에서 상수는 대문자로 표현하는 것이 관례이다.
- 프로그램 실행 중에 절대로 변경되어서는 안되기 때문에
static final키워드를 사용해 선언한다.
불변 객체(Immutable Object)
- 내부 상태를 변경할 수 없는 객체이다.
final을 속성에 활용한다.- 변경이 필요할 경우 새로운 객체를 만들어야 한다.
🚫 잘못된 불변 객체 사용
final은 참조 변경을 막지만 내부상태 변경은 막지 않는다.
public class Circle {
final static double PI = 3.14159; // ✅ 직접 만든 원주율 상수
double radius; // ⚠️ final 로 선언되어 있지 않기 때문에 외부에서 변경 가능
Circle(double radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
}final Circle c1 = new Circle(2);
c1 = new Circle(3); // ❌ final은 변수 c1이 한 번 참조한 객체는 다른 객체로 변경될 수 없음을 의미함 (참조 불변)
// 하지만 객체 내부의 속성 값은 변경 가능 (불변 객체가 아님)
c1.radius = 3; // ⚠️ 내부 상태 변경 가능 (객체 자체가 불변이 아님)✅ 올바른 불변 객체 활용
- 속성을
final로 선언한다.
public final class Circle {
final static double PI = 3.14159;
final double radius; // ✅ final 로 선언해서 값이 변경되지 않도록 합니다.
Circle(double radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
}⚠️ 불변 객체의 값을 변경해야 하는 경우
- 불변성을 유지하면서 값을 변경하는 효과를 얻을 때 활용한다.
- 기존 객체의 상태를 직접 변경할 수 없기 때문에 새로운 객체를 생성한다.
- 생성자를 새로 호출하거나 아래의 기능을 활용할 수 있다.
public final class Circle {
public static final double PI = 3.14159;
private final double radius;
public Circle(double radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
// ✅ 반지름이 다른 새로운 Circle 생성 (불변 객체 유지)
public Circle changeRadius(double newRadius) {
return new Circle(newRadius); // 생성자 호출: 기존 객체 변경 X, 새 객체 생성
}
}