예외
- 프로그램 실행 중 예상하지 못한 상황이 발생하는 것을 의미한다.
-> 대표적인 산술 예외 :10 / 0(0으로 나누기) - 의도적으로 예외를 발생시킬 때는
throw키워드를 통해 발생시킨다. - 예외를 처리하지 않으면 프로그램이 중단될 수 있습니다.
- 그래서
예외처리(try-catch)를 통해 프로그램이 안정적으로 실행되게 할 수 있다.
의도하지 않은 예외
- 아래 코드에서
10 / 0연산을 수행하면서ArithmeticException(산술예외)가 발생하고 프로그램이 비정상적으로 종료된다. - 예외를 처리하지 않으면 이후 코드는 실행되지 않는다.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("프로그램 시작");
int result = 10 / 0; // ❌ 예외 발생 (ArithmeticException)
System.out.println("이 문장은 실행되지 않음");
}
}콘솔 메세지
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
at chapter3.exception.Main.main(Main.java:8)
Process finished with exit code 1의도적인 예외 - throw
- 특정 조건에서 의도적으로 예외를 발생시킬 수도 있다.
- 아래 코드에서
age < 18조건을 만족하면IllegalArgumentException을 발생시킨다. throw를 활용하면 특정 상황에서 예외를 명확하게 정의하고 제어할 수 있다.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int age = 10;
if (age < 18) {
// ✅ 의도적으로 예외를 발생시키는 부분
throw new IllegalArgumentException("미성년자는 접근할 수 없습니다!");
}
System.out.println("....");
}
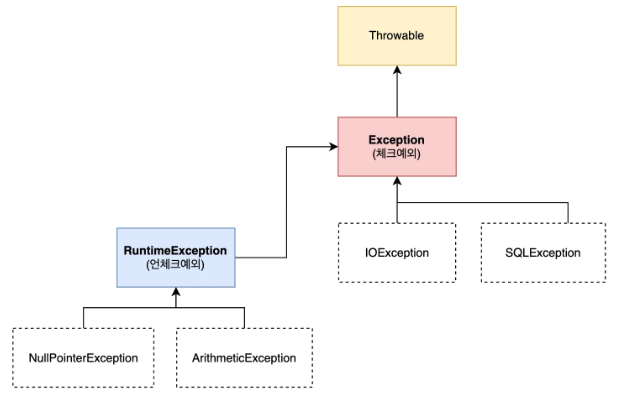
}예외 구조와 종류
- RuntimeException - UncheckedException
RuntimeException을 상속받는 모든 예외를UncheckedException이라고 한다.- 예외처리를 컴파일러가 확인하지 않는다.
- Exception - CheckedException
-Exception클래스를 직접 상속받는 모든 예외를CheckedException이라고한다.RuntimeException과RuntimeException을 상속받은 예외는 제외한다.
- 예외처리를 컴파일러가 확인해 준다.
예외 전파
- 예외 전파는 메서드에서 발생한 예외가 해당 메서드 내에서 처리되지 않았을 때 메서드를 호출한 상위 메서드로 전달되는 과정이다.
- 예외가 프로그램 시작 지점(
main()) 까지 전파되고 끝내 처리되지 않으면 프로그램이 비정상 종료 된다.
RuntimeException - UncheckedException
- 컴파일러가 예외 처리를 강제하지 않는 예외이다.
- 예외 처리를 하지 않아도 컴파일 오류(빨간 줄) 가 발생하지 않는다.
- 처리되지 않은 예외는 계속 프로그램 시작 지점까지 전파된다.
- 끝내 예외가 처리되지 않으면 프로그램이 비정상적으로 종료된다.
RuntimeException을 상속받는 모든 예외를UncheckedException이라고 한다.
✅ try-catch 활용
public class ExceptionPractice {
public void callUncheckedException() {
if (true) {
System.out.println("언체크 예외 발생");
throw new RuntimeException(); // ✅ 예외발생
}
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 예외 실습 객체 인스턴스화
ExceptionPractice exceptionPractice = new ExceptionPractice();
// ✅ 언체크 예외 호출
exceptionPractice.callUncheckedException();
// ❌ 예외처리를 해주지 않았기 때문에 프로그램이 종료됩니다.
System.out.println("이 줄은 실행되지 않습니다.");
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExceptionPractice exceptionPractice = new ExceptionPractice();
// ✅ 상위로 전파된 예외처리
try {
exceptionPractice.callUncheckedException();
} catch (RuntimeException e) { // ✅ 예외처리
System.out.println("언체크 예외 처리");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("체크 예외 처리");
}
System.out.println("프로그램 종료");
}
}Exception - CheckedException
Exception클래스를 직접 상속받는 모든 예외를CheckedException이라고 한다.RuntimeException을 상속받는 예외는 제외
- 컴파일러가 예외 처리를 강제하는 예외이다.
- 예외 처리를 하지 않으면 “컴파일 오류가 발생한다(코드에 빨간줄)”
- 반드시
try-catch로 예외를 처리하거나throws키워드를 사용해야 한다.
→throws로 예외 처리의 책임을 호출자에게 전가할 수 있다.
✅ try-catch 활용
CheckedException을try-catch를 사용하여 직접 처리하는 방식이다.
public class ExceptionPractice {
public void callCheckedException() {
// ✅ try-catch 로 예외 처리
try {
if (true) {
System.out.println("체크예외 발생");
throw new Exception();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("예외 처리");
}
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 예외 실습 객체 인스턴스화
ExceptionPractice exceptionPractice = new ExceptionPractice();
// ✅ 체크예외 호출
exceptionPractice.callCheckedException();
}
}✅ throws 활용
- throws 키워드를 사용하여 예외를 호출한 곳에서 처리하도록 강제하는 방식이다.
→ (책임 전가)
public class ExceptionPractice {
public void callCheckedException() throws Exception { // ✅ throws 예외를 상위로 전파
if (true) {
System.out.println("체크예외 발생");
throw new Exception();
}
}
}
package chapter3.exception;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 예외 실습 객체 인스턴스화
ExceptionPractice exceptionPractice = new ExceptionPractice();
// 체크 예외 사용
// ✅ 반드시 상위 메서드에서 try-catch 를 활용해 주어야합니다.
try {
exceptionPractice.callCheckedException();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("예외처리");
}
}
}