추상화
- 불필요한 정보를 제거하고 본질적인 특징만 남기는 것을 의미한다.
- 객체지향 프로그래밍에서는 추상화의 계층적 특징을 활용해서 유지보수성이 좋은 프로그램을 만들 수 있다.
- ex) 고양이 -> 동물 -> 생명체
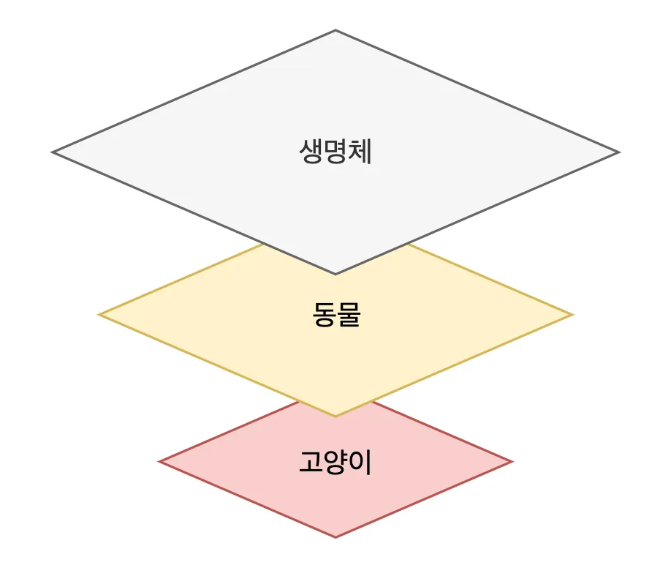
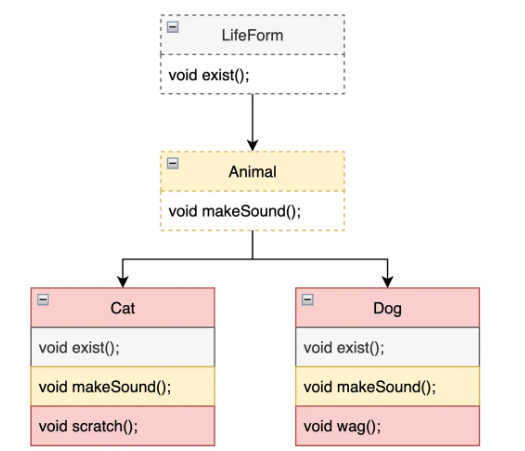
인터페이스 상속을 활용한 추상 계층 표현
public interface LifeForm {
void exist(); // ✅ 공통: 모든 생명체는 존재한다.
}public interface Animal extends LifeForm {
void makeSound(); //✅ 공통: 모든 동물은 소리를 냅니다.
}public class Cat implements Animal {
@Override
public void exist() {
System.out.println("고양이가 존재합니다.");
}
@Override
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("야옹");
}
public void scratch() {
System.out.println("스크래치");
}
}public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cat cat = new Cat();
cat.exist();
cat.makeSound();
cat.scratch();
}
}클래스 상속을 활용한 추상 계층 표현
public class LifeForm {
public void exist() {
System.out.println("존재합니다2"); // ✅ 공통: 모든 객체는 존재한다.
}
}public class Animal extends LifeForm {
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("소리를 냅니다2"); // ✅ 공통: 모든 생명체는 성장한다.
}
}public class Cat extends Animal {
@Override
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("야옹2");
}
public void scratch() {
System.out.println("스크래치!");
}
}public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cat cat = new Cat();
cat.exist();
cat.makeSound();
cat.scratch();
}
}다형성
- 하나의 타입으로 여러 객체를 다룰 수 있는 것이다.
- 추상 계층이라는 특징을 활용해서 다형성을 구현할 수 있다.
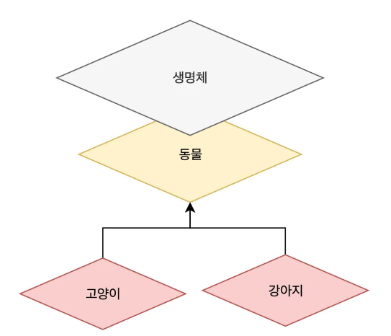
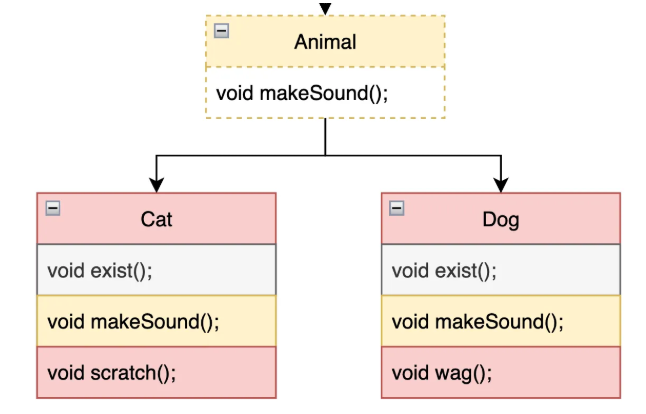
인터페이스를 활용한 다형성
public interface LifeForm {
void exist();
}
public interface Animal extends LifeForm {
void makeSound();
}
public class Cat implements Animal {
@Override
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("야옹");
}
@Override
public void exist() {
System.out.println("고양이가 존재합니다.");
}
public void scratch() {
System.out.println("스크래치!");
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 다형성 활용
Animal animal = new Cat();
animal.exist(); // ✅
animal.makeSound(); // ✅
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 다형성 활용
Animal animal = new Cat();
animal.exist(); // ✅
animal.makeSound(); // ✅
}
}ㅤ
형변환(Casting)
- 부모타입으로 자식타입을 다룰 수 있는 이유는 자동으로 형변환이 발생했기 때문이다.
- 자식타입 -> 부모타입 : 업캐스팅(UpCasting)
- 부모타입 -> 자식타입 : 다운캐스팅(DownCasting)
업캐스팅 (자식 -> 부모)
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 다형성 활용
Animal animal = new Cat(); // ✅ 자동 형 변환
animal.exist(); // ✅
animal.makeSound(); // ✅
}
}⚠️ 업캐스팅 주의사항
업캐스팅은 부모의 타입으로 데이터를 다룰 수 있지만 자식 클래스의 고유기능을 활용할 수는 없다.
- 자식클래스의 고유 기능을 사요하려면 다운캐스팅이 필요하다.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 다형성 활용
Animal animal = new Cat(); // ✅ 자동 형 변환
animal.exist();
animal.makeSound();
animal.scratch(); // ❌ 사용 불가
}
}
ㅤ
다운캐스팅 (부모 -> 자식)
- 다운캐스팅으로 자식 클래스의 고유 메서드를 사용할 수 있다.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 다형성 활용
Animal animal = new Cat();
animal.exist();
animal.makeSound();
Cat cat = (Cat) animal; // ✅ 다운캐스팅(부모Animal -> 자식Cat)
cat.scratch(); // ✅ 자식 클래스의 기능 활용 가능
}
}⚠️ 다운캐스팅 주의사항
잘못된 다운캐스팅은 컴파일단계에서 감지할 수 없다.
- 컴파일러는 다운캐스팅이 문법적으로 올바른지 여부만 검사해주기 때문에 런타임시에 실제 어떤 객체가 변수에 할당되는지 검사해주지 않는다.
- 컴파일 시점에는 오류 없이 통과되지만 런타임시점에
ClassCastException이 발생할 가능성이 있다.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 다운 캐스팅
Animal dog = new Dog();
// 문법적으로 잘못된건 아니라서 에러가 발생하지 않습니다.
Cat cat1 = (Cat) dog; // ⚠️
cat1.scratch(); // ❌ 해당 라인이 실행할때만 에러 여부를 확인할 수 있습니다.
}
}ㅤ
✅ 다운캐스팅을 사용할 때 항상
instanceof를 활용해야 한다.
instanceof는 객체가 특정 클래스나 인터페이스의 인스턴스인지 확인해 주는 역할을 한다.- 주로 다운캐스팅 하기 전 타입을 검사해서
ClassCastException을 예방하는데 활용된다.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal animal2 = new Dog();
// ✅ 안전한 다운캐스팅(animal2 가 Cat 의 인스턴스 유형인지 확인합니다.)
if (animal2 instanceof Cat) {
Cat cat = (Cat) animal2;
cat.scratch();
} else {
System.out.println("객체가 고양이가 아닙니다.");
}
}
}