1. 문제 링크
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/12896
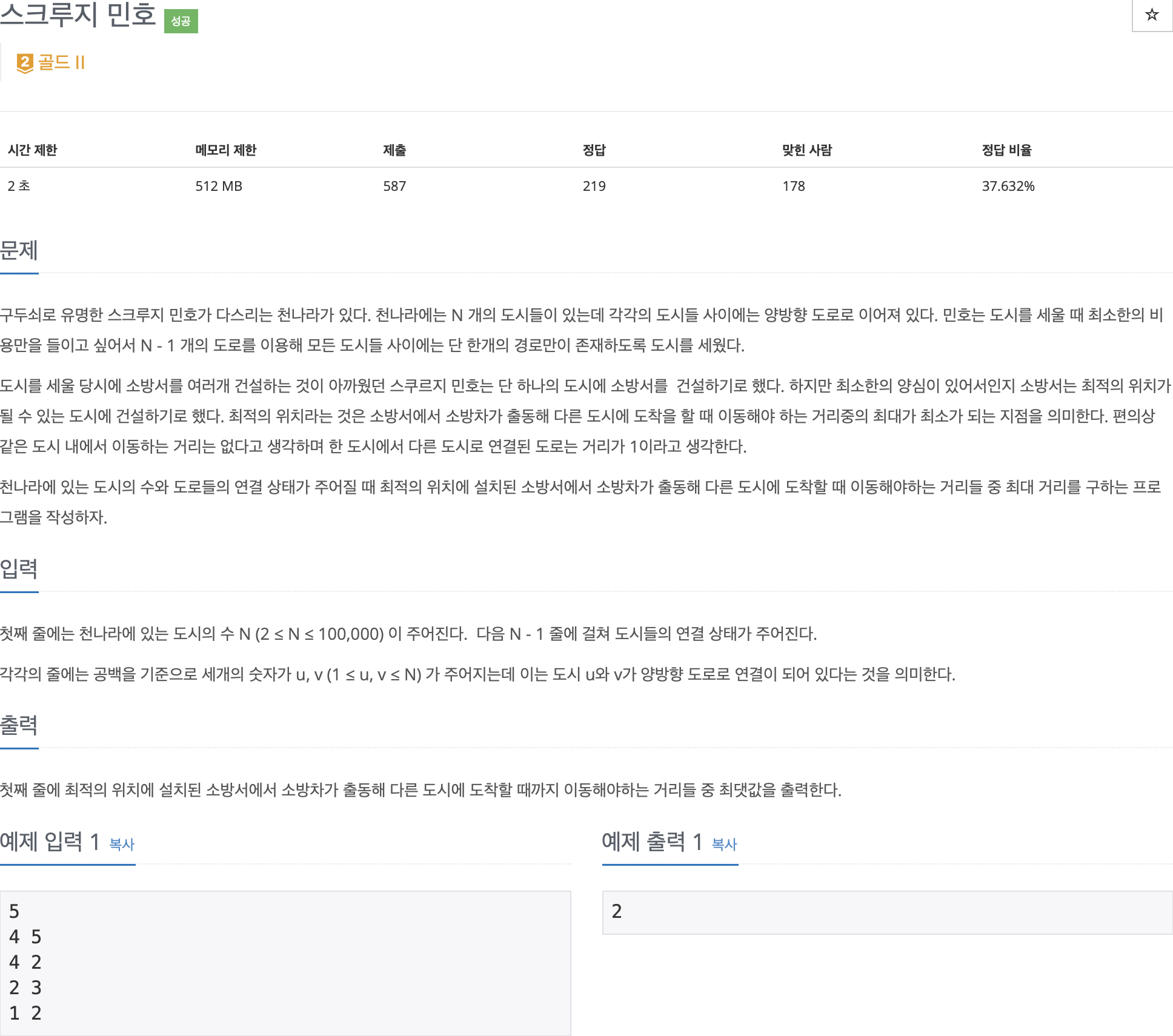
2. 문제
3. 소스코드
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
static int cityCount;
static int longestCity;
static int longestDistance;
static Map<Integer, List<Integer>> roads;
static void input() {
Reader scanner = new Reader();
cityCount = scanner.nextInt();
roads = new HashMap<>();
for (int city = 1; city <= cityCount; city++) {
roads.put(city, new ArrayList<>());
}
for (int road = 0; road < cityCount - 1; road++) {
int city1 = scanner.nextInt();
int city2 = scanner.nextInt();
roads.get(city1).add(city2);
roads.get(city2).add(city1);
}
}
/*
* 구하고자 하는 것은 최적의 위치에 소방서를 건설했을 때, 소방서부터 다른 도시들까지의 거리 중 최대 거리이다
* 최적의 위치는 소방서로부터 다른 모든 도시들까지의 거리 중 최대 거리가 최소가 되는 지점을 의미한다
* 그런데 각 도시 사이에 연결된 도로는 모두 길이가 1로 동일한 상황이므로
* 이는 주어진 트리에서 중앙에 있는 노드를 찾으라는 문제와 같다!
* - 트리에는 가장 먼 두 개의 정점이 있을 것이다
* - 여기서 말하는 가장 먼 두 개의 정점이란 트리를 일직선으로 핀다고 생각했을 때,
* 양쪽 끝에 있는 노드를 의미한다
* - 가장 먼 두 개의 정점 사이에 있는 노드들 중 중앙에 위치한 노드는 두 개의 정점까지의 거리가 같거나 비슷할 것이기 때문에
* 최대 거리가 최소가 될 수 있다.
* - 다른 노드들은 한쪽에 거리가 더 가중될 수 밖에 없기 때문에 최대값을 기준으로 봤을 때 최소가 될 수 없다
*
* 가장 먼 두 개의 정점 찾기
* 1. 임의의 한 도시부터 가장 먼 도시를 찾은 후에
* 2. 그 도시부터 가장 먼 도시를 찾는다
* - 이때 2번 작업에서 발생하는 한 도시부터 다른 가장 먼 도시까지의 거리가 이 트리의 최대 길이가 된다
* - 우리는 중앙에 위치한 도시를 찾는 것이기 때문에 이 거리를 반으로 나누면 최적의 위치에서 다른 도시까지의 최대 거리를 구할 수 있다
* - 이때, 홀수라면 한 쪽이 1 더 길기 때문에 트리의 최대 길이에 1을 더한 후에 2로 나눠 최적의 위치에서 다른 도시까지의 최대 거리를 구한다
*/
static void solution() {
int firstLongestCity = getLongestCity(1);
int secondLongestCity = getLongestCity(firstLongestCity);
System.out.println((1 + longestDistance) / 2);
}
static int getLongestCity(int city) {
longestCity = longestDistance = 0;
dfs(city, 0, new boolean[cityCount + 1]);
return longestCity;
}
static void dfs(int city, int distance, boolean[] visited) {
if (distance > longestDistance) {
longestDistance = distance;
longestCity = city;
}
visited[city] = true;
for (int nextCity : roads.get(city)) {
if (!visited[nextCity]) {
dfs(nextCity, distance + 1, visited);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
input();
solution();
}
static class Reader {
BufferedReader br;
StringTokenizer st;
public Reader() {
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
}
String next() {
while (st == null || !st.hasMoreElements()) {
try {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return st.nextToken();
}
int nextInt() {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
}
}
