1. 문제 링크
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1414
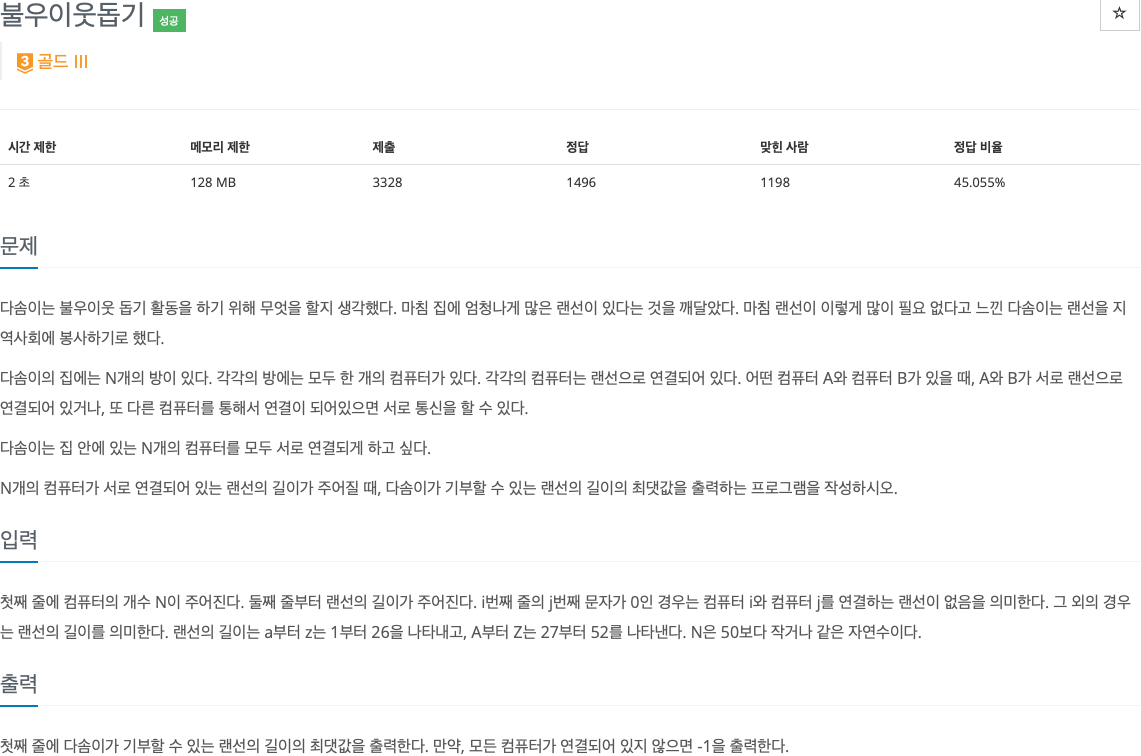
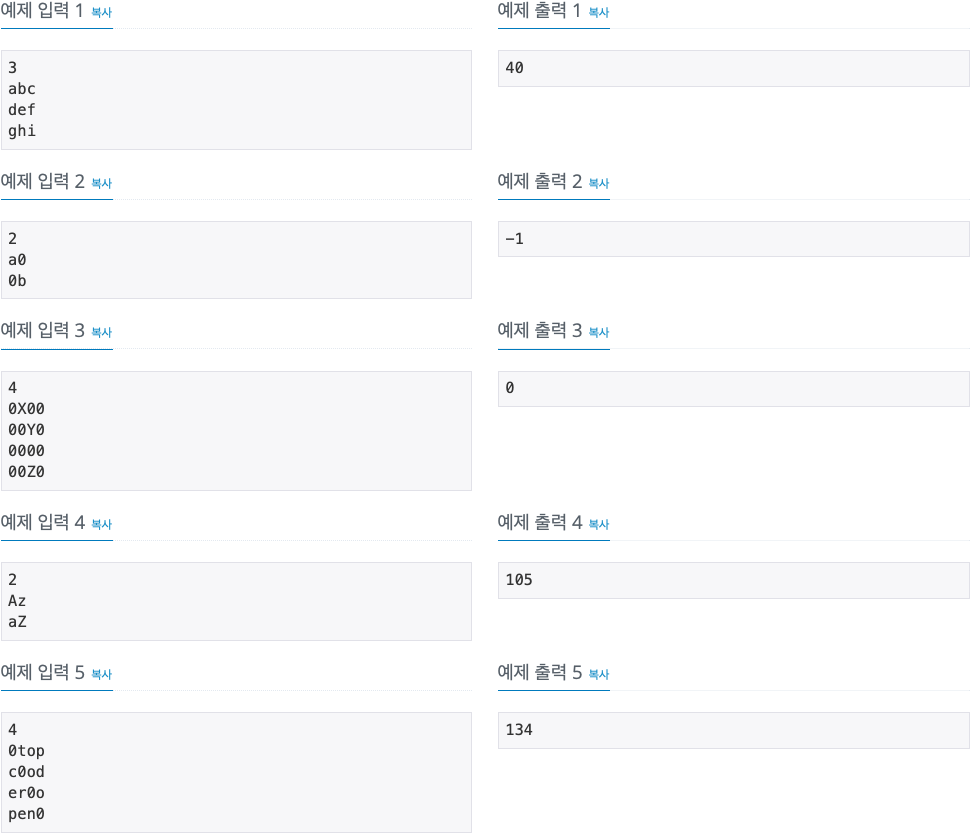
2. 문제
3. 소스코드
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
static final int ALPHABET_COUNT = 26;
static int computerCount;
static int totalLanLength;
static int[] parents;
static Queue<Lan> lans;
static void input() {
Reader scanner = new Reader();
computerCount = scanner.nextInt();
totalLanLength = 0;
parents = new int[computerCount];
lans = new PriorityQueue<>();
for (int startComputer = 0; startComputer < computerCount; startComputer++) {
String info = scanner.nextLine();
parents[startComputer] = startComputer;
for (int endComputer = 0; endComputer < computerCount; endComputer++) {
if (info.charAt(endComputer) == '0') {
continue;
}
int length = computeLanLength(info.charAt(endComputer));
totalLanLength += length;
if (startComputer != endComputer) {
lans.offer(new Lan(startComputer, endComputer, length));
}
}
}
}
static int computeLanLength(char length) {
if (Character.isLowerCase(length)) {
return length - 'a' + 1;
}
return (length - 'A' + 1) + ALPHABET_COUNT;
}
/*
* 최소 스패닝 트리 문제이다
* N개의 컴퓨터가 있을 때, (N - 1)개의 랜선만 이용하면 N개의 컴퓨터를 모두 연결할 수 있다
* 그러므로 주어진 랜선 정보를 길이 기준으로 오름차순으로 정렬한 후 그 중 N - 1개만 선택하여 N개의 컴퓨터를 연결한다
* 선택할 때에는 길이가 최대한 작은 랜선이면서 이미 이어진 컴퓨터를 잇는 랜선이 아닌 랜선들만 N - 1개 선택한다
*/
static void solution() {
int usedLength = mst();
if (usedLength == -1) {
System.out.println(usedLength);
return;
}
System.out.println(totalLanLength - usedLength);
}
static int mst() {
int count = 0;
int totalLength = 0;
while (!lans.isEmpty() && count < computerCount - 1) {
Lan lan = lans.poll();
if (!isSameParents(lan.startComputer, lan.endComputer)) {
union(lan.startComputer, lan.endComputer);
totalLength += lan.length;
count++;
}
}
if (count < computerCount - 1) {
return -1;
}
return totalLength;
}
static int findParent(int computerNumber) {
if (computerNumber == parents[computerNumber]) {
return computerNumber;
}
return parents[computerNumber] = findParent(parents[computerNumber]);
}
static void union(int computer1, int computer2) {
int parent1 = findParent(computer1);
int parent2 = findParent(computer2);
if (parent1 != parent2) {
if (parent1 < parent2) {
parents[parent2] = parent1;
} else {
parents[parent1] = parent2;
}
}
}
static boolean isSameParents(int computer1, int computer2) {
int parent1 = findParent(computer1);
int parent2 = findParent(computer2);
return parent1 == parent2;
}
static class Lan implements Comparable<Lan> {
int startComputer;
int endComputer;
int length;
public Lan(int startComputer, int endComputer, int length) {
this.startComputer = startComputer;
this.endComputer = endComputer;
this.length = length;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Lan o) {
return length - o.length;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
input();
solution();
}
static class Reader {
BufferedReader br;
StringTokenizer st;
public Reader() {
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
}
String next() {
while (st == null || !st.hasMoreElements()) {
try {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return st.nextToken();
}
int nextInt() {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
String nextLine() {
String str = "";
try {
str = br.readLine();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return str;
}
}
}
