1. 문제 링크
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1486
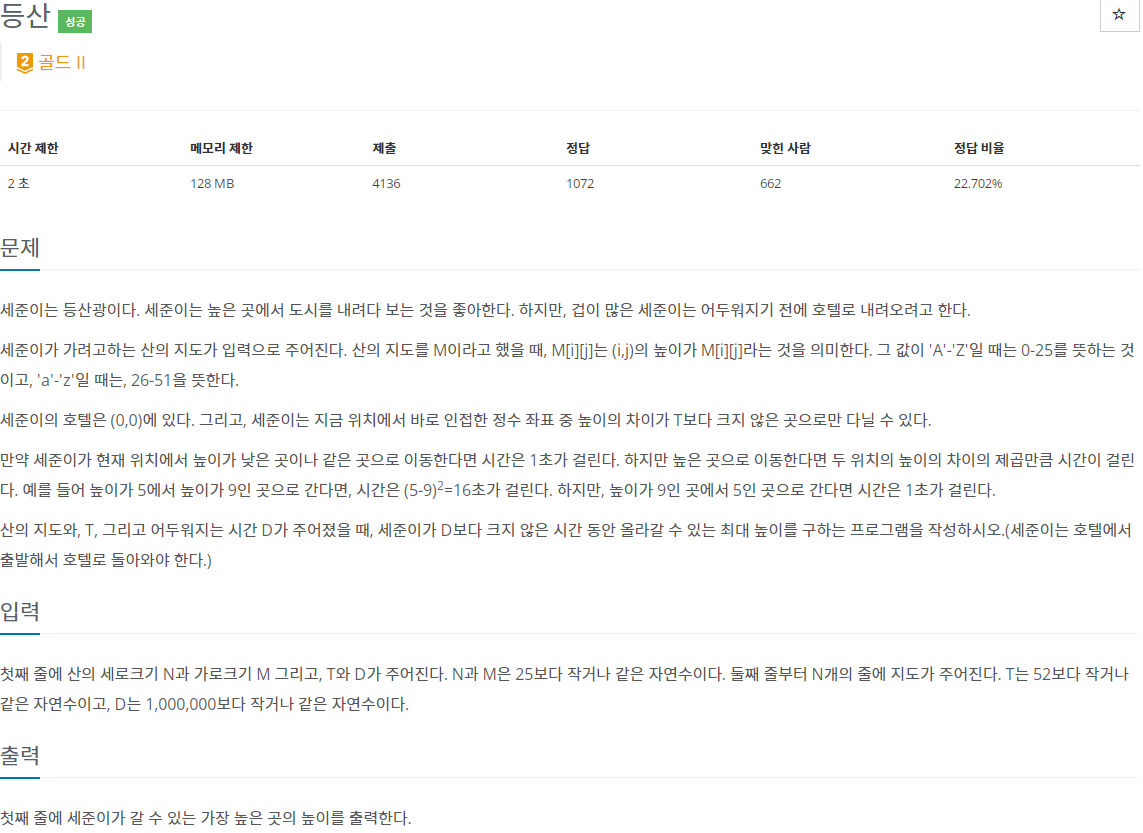
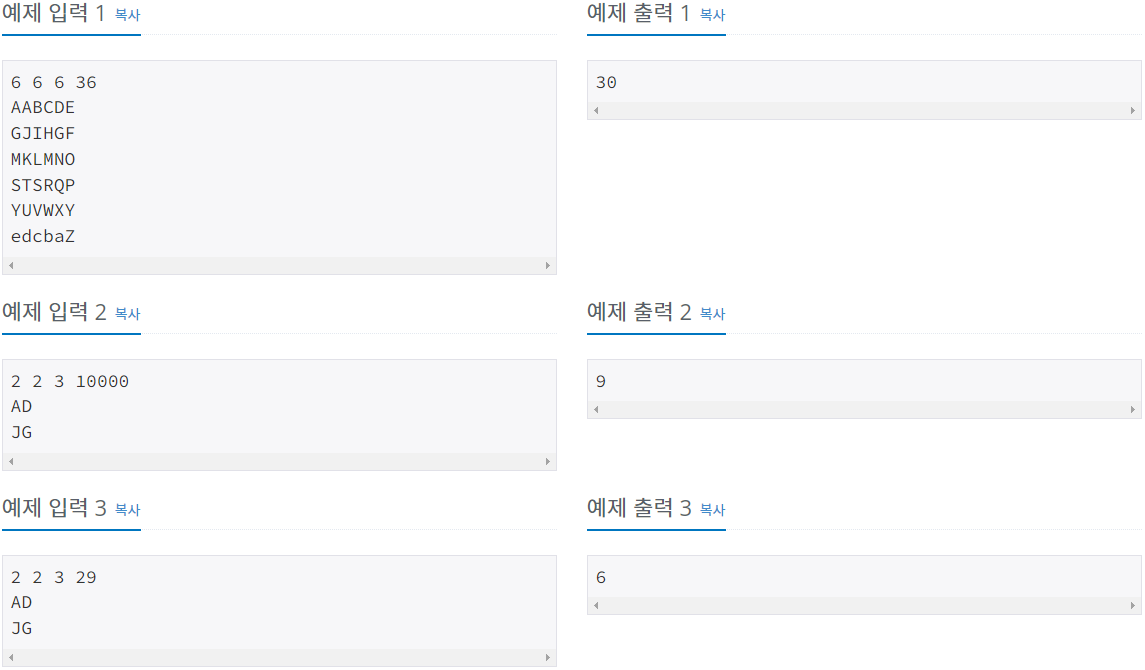
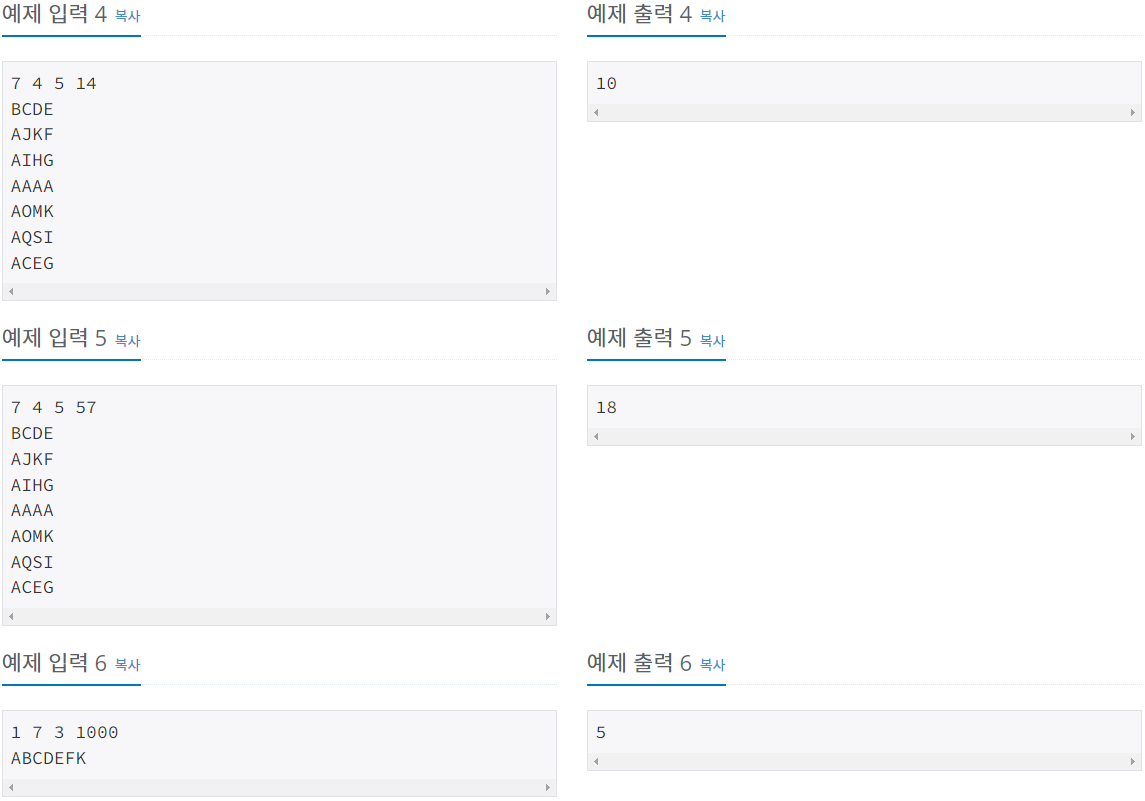
2. 문제
3. 소스코드
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
static int N, M, T, D;
static int[][] map; // 산의 지도
static int[][][][] distance; // 한 위치에서 다른 모든 위치들까지의 최단 시간
static int[] dx = {-1, 0, 1, 0}, dy = {0, -1, 0, 1};
static void input() {
Reader scanner = new Reader();
N = scanner.nextInt();
M = scanner.nextInt();
T = scanner.nextInt();
D = scanner.nextInt();
map = new int[N][M];
distance = new int[N][M][N][M];
for(int idx = 0; idx < N; idx++) {
for(int idx2 = 0; idx2 < M; idx2++) {
for(int idx3 = 0; idx3 < N; idx3++)
Arrays.fill(distance[idx][idx2][idx3], Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
}
for(int row = 0; row < N; row++) {
String info = scanner.nextLine();
for(int col = 0; col < M; col++) {
char curAlphabet = info.charAt(col);
if(curAlphabet >= 'A' && curAlphabet <= 'Z')
map[row][col] = curAlphabet - 'A';
else if(curAlphabet >= 'a' && curAlphabet <= 'z')
map[row][col] = (curAlphabet - 'a') + 26;
}
}
}
static void solution() {
// 각 위치에서 모든 위치까지의 최단 시간을 다익스트라 알고리즘을 통해 구한다
for(int row = 0; row < N; row++) {
for(int col = 0; col < M; col++)
dijkstra(row, col);
}
// 시작점부터 출발하여 다시 시작점으로 돌아올 수 있는 경로 중 가장 높은 곳의 높이를 가져와 출력한다
System.out.println(findMax());
}
static int findMax() {
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
// 시작점부터 시작해서 각 산의 위치까지 시작점부터 갔다가 돌아올 수 있는 위치를 찾고
// 그 위치들 중에서 가장 높은 곳의 높이를 구한다
for(int row = 0; row < N; row++) {
for(int col = 0; col < M; col++) {
if(distance[row][col][0][0] == Integer.MAX_VALUE ||
distance[0][0][row][col] == Integer.MAX_VALUE)
continue;
if(distance[row][col][0][0] + distance[0][0][row][col] <= D)
max = Math.max(max, map[row][col]);
}
}
return max;
}
static void dijkstra(int x, int y) {
PriorityQueue<Loc> queue = new PriorityQueue<>();
distance[x][y][x][y] = 0; // 시작점의 시간은 0
queue.offer(new Loc(x, y, 0)); // 시작점을 PriorityQueue에 넣고 다익스트라 알고리즘 시작
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
Loc cur = queue.poll();
// 만약 이미 이전에 구한 최소 시간이 현재 그 위치까지 온 시간보다 작다면
// 이미 이 경우는 최소 시간이 될 수 없다는 뜻이므로 다음 경우로 넘어간다
if(distance[cur.x][cur.y][x][y] < cur.time) continue;
// 인접한 위치들 중 T 이하로 높이 차이가 나는 곳들 중에서
// 그 위치까지 가는 시간이 D 이하이고 그 위치까지 가는 시간이 이전에 구한 최소 시간보다 작다면
// 최소 시간을 갱신하고 다음 탐색을 위해 Queue에 넣는다
for(int dir = 0; dir < 4; dir++) {
int cx = cur.x + dx[dir], cy = cur.y + dy[dir], nextTime = 0;
if(isInMap(cx, cy) && Math.abs(map[cur.x][cur.y] - map[cx][cy]) <= T) {
if(map[cx][cy] <= map[cur.x][cur.y]) nextTime = cur.time + 1;
else nextTime = (int)Math.pow((map[cx][cy] - map[cur.x][cur.y]), 2) + cur.time;
if(distance[cx][cy][x][y] > nextTime && nextTime <= D) {
distance[cx][cy][x][y] = nextTime;
queue.offer(new Loc(cx, cy, nextTime));
}
}
}
}
}
static boolean isInMap(int x, int y) {
return x >= 0 && x < N && y >= 0 && y < M;
}
static class Loc implements Comparable<Loc> {
int x, y, time;
public Loc(int x, int y, int time) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.time = time;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Loc o) {
return time - o.time;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
input();
solution();
}
static class Reader {
BufferedReader br;
StringTokenizer st;
public Reader() {
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
}
String next() {
while(st == null || !st.hasMoreElements()) {
try {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return st.nextToken();
}
int nextInt() {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
String nextLine() {
String str = "";
try {
str = br.readLine();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return str;
}
}
}