1. 문제 링크
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/17070
2. 문제

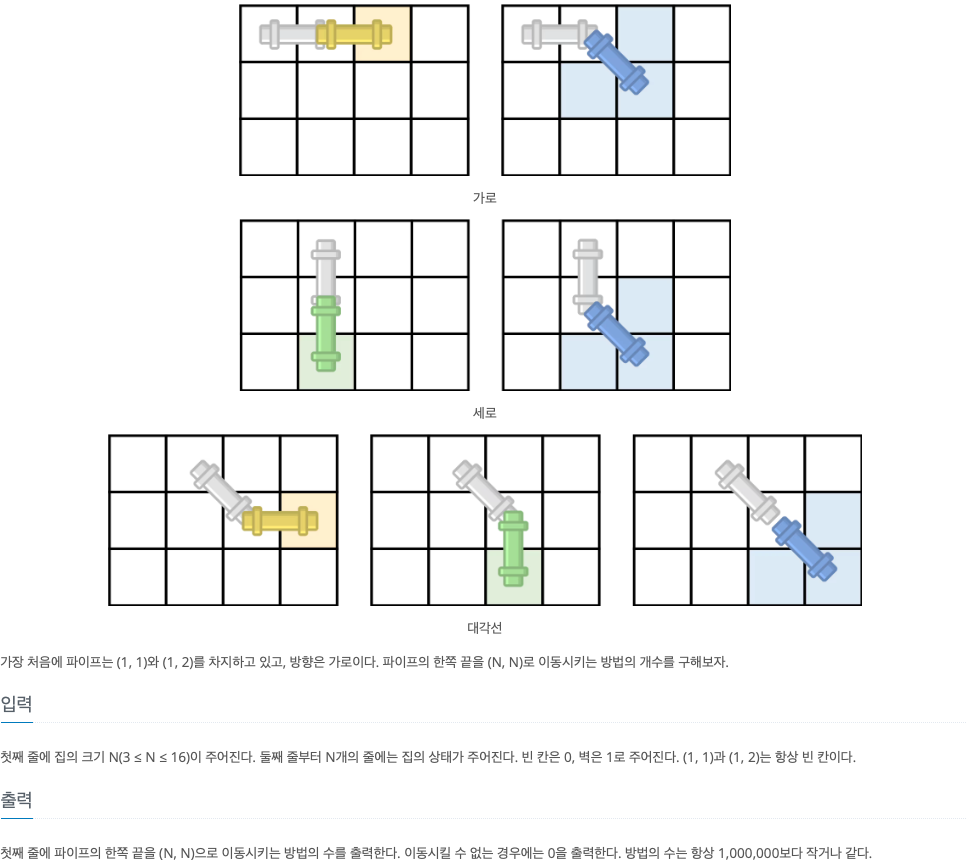
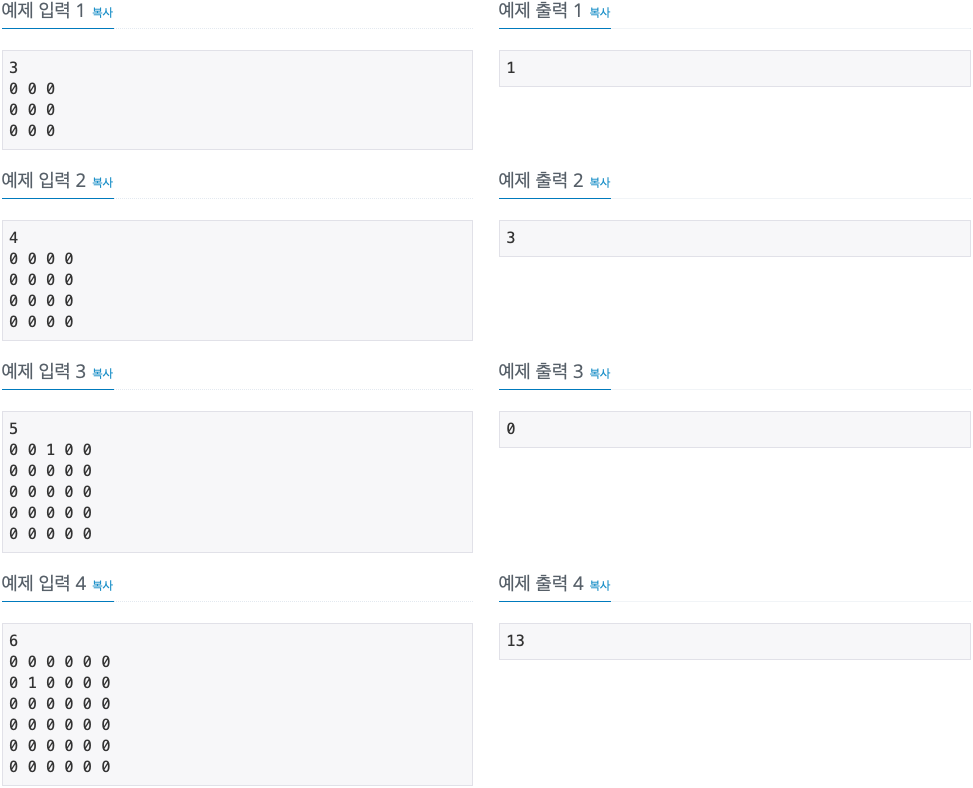
3. 소스코드
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
static int houseSize;
static int answer;
static boolean[][] map;
static void input() {
Reader scanner = new Reader();
houseSize = scanner.nextInt();
answer = 0;
map = new boolean[houseSize][houseSize];
for (int row = 0; row < houseSize; row++) {
for (int col = 0; col < houseSize; col++) {
int info = scanner.nextInt();
map[row][col] = (info == 0);
}
}
}
/*
* 최종적으로 (N, N)까지 파이프를 이동시키는 데에 있어서 파이프가 차지하는 두 칸 중 더 뒤에 있는((N, N)에 가까운) 칸이 영향을 미치므로 해당 칸만 생각한다
* 파이프가 놓여져있는 방향을 기준으로 이동시킬 수 있는 방향 및 칸이 정해져있으므로 각 파이프를 해당 위치들로 이동시켜보며
* (N, N) 위치에 도달했을 때 이동시키는 방법의 개수를 증가시킨다
* 이를 DFS를 통해 각 경우를 이동시켜보며 총 이동시키는 방법의 개수를 구한다
*/
static void solution() {
dfs(0, 1, 0);
System.out.println(answer);
}
static void dfs(int x, int y, int direction) {
if (x == houseSize - 1 && y == houseSize - 1) {
answer++;
return;
}
if (direction == 0 || direction == 1) {
if (y + 1 < houseSize && map[x][y + 1]) {
dfs(x, y + 1, 0);
}
}
if (direction == 1 || direction == 2) {
if (x + 1 < houseSize && map[x + 1][y]) {
dfs(x + 1, y, 2);
}
}
if (x + 1 < houseSize && y + 1 < houseSize && isBlank(x, y)) {
dfs(x + 1, y + 1, 1);
}
}
static boolean isBlank(int x, int y) {
return map[x][y + 1] && map[x + 1][y] && map[x + 1][y + 1];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
input();
solution();
}
static class Reader {
BufferedReader br;
StringTokenizer st;
public Reader() {
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
}
String next() {
while (st == null || !st.hasMoreElements()) {
try {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return st.nextToken();
}
int nextInt() {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
}
}
