1. 문제 링크
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1944
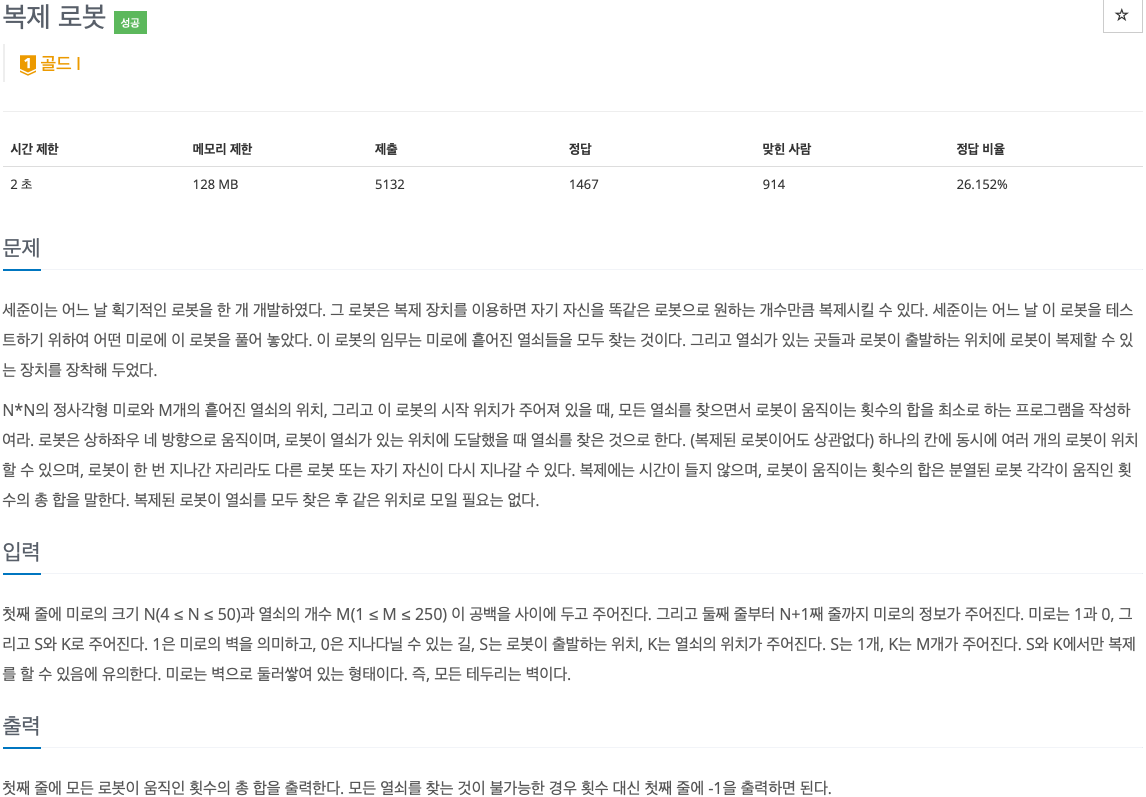
2. 문제

3. 소스코드
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static int N, M;
static char[][] map;
static List<int[]> keys;
static PriorityQueue<Edge> edges;
static int[] parents;
static int[] dx = {-1, 0, 1, 0}, dy = {0, -1, 0, 1};
static void input() {
Reader scanner = new Reader();
N = scanner.nextInt();
M = scanner.nextInt();
map = new char[N][N];
keys = new ArrayList<>(); // 시작 지점 및 키가 있는 위치
edges = new PriorityQueue<>(); // 각 지점 사이의 거리
parents = new int[M + 1];
for(int idx = 0; idx <= M; idx++)
parents[idx] = idx;
for(int row = 0; row < N; row++) {
String info = scanner.nextLine();
for(int col = 0; col < N; col++) {
map[row][col] = info.charAt(col);
if(map[row][col] == 'S' || map[row][col] == 'K')
keys.add(new int[] {row, col});
}
}
}
static void solution() {
// 한 지점으로부터 다른 모든 지점으로부터의 거리를 BFS를 통해 구하고 이를 edges라는 PriorityQueue에 넣는다
for(int idx = 0; idx < keys.size(); idx++) bfs(idx);
// 구한 모든 거리들을 이용해 MST를 만들어 최소 거리를 구한다
int totalDistance = kruskal();
System.out.println(totalDistance);
}
static int kruskal() {
// distance : MST에 포함된 모든 간선들의 총 거리, count : 선택된 간선의 개수
int distance = 0, count = 0;
for(count = 0; count < M && !edges.isEmpty(); count++) {
Edge edge = edges.poll();
// 시작점과 도착점의 부모가 같다면 해당 간선을 이으면 사이클이 발생하므로 해당 간선은 선택하지 않는다
if(isSameParent(edge.startIdx, edge.endIdx)) {
count--;
continue;
}
// 그렇지 않다면 간선을 잇고 총 거리를 증가시킨다
union(edge.startIdx, edge.endIdx);
distance += edge.cost;
}
// 총 M + 1개의 정점이 있으므로 M개의 간선이 선택되지 않았다면 MST를 만들 수 없다는 뜻이므로 -1을 반환한다
if(count < M) return -1;
// 그렇지 않다면 총 거리를 반환한다
return distance;
}
static int findParent(int idx) {
if(idx == parents[idx]) return idx;
return parents[idx] = findParent(parents[idx]);
}
static void union(int idx1, int idx2) {
int parent1 = findParent(idx1), parent2 = findParent(idx2);
if(parent1 != parent2) {
if(parent1 < parent2) parents[parent2] = parent1;
else parents[parent1] = parent2;
}
}
static boolean isSameParent(int idx1, int idx2) {
int parent1 = findParent(idx1), parent2 = findParent(idx2);
return parent1 == parent2;
}
static void bfs(int startIdx) {
Queue<Loc> queue = new LinkedList<>();
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[N][N];
int[] start = keys.get(startIdx);
queue.offer(new Loc(start[0], start[1], 0));
visited[start[0]][start[1]] = true;
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
Loc cur = queue.poll();
for(int dir = 0; dir < dx.length; dir++) {
int cx = cur.x + dx[dir], cy = cur.y + dy[dir];
if(isInMap(cx, cy)) {
if(map[cx][cy] != '1' && !visited[cx][cy]) {
// 한 위치에서 주변 위치들을 살펴보며 아직 방문하지 않았고 그 위치가 시작 지점이나 열쇠가 있는 지점이라면
// 시작 지점과 현재 지점 및 해당 거리를 edges에 저장한다
if(map[cx][cy] == 'S' || map[cx][cy] == 'K') {
for(int idx = 0; idx < keys.size(); idx++) {
if(keys.get(idx)[0] == cx && keys.get(idx)[1] == cy)
edges.offer(new Edge(startIdx, idx, cur.moveNum + 1));
}
}
visited[cx][cy] = true;
queue.offer(new Loc(cx, cy, cur.moveNum + 1));
}
}
}
}
}
static boolean isInMap(int x, int y) {
return x >= 0 && x < N && y >= 0 && y < N;
}
static class Loc {
int x, y, moveNum;
public Loc(int x, int y, int moveNum) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.moveNum = moveNum;
}
}
static class Edge implements Comparable<Edge> {
int startIdx, endIdx, cost;
public Edge(int startIdx, int endIdx, int cost) {
this.startIdx = startIdx;
this.endIdx = endIdx;
this.cost = cost;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Edge o) {
return cost - o.cost;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
input();
solution();
}
static class Reader {
BufferedReader br;
StringTokenizer st;
public Reader() {
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
}
String next() {
while(st == null || !st.hasMoreElements()) {
try {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return st.nextToken();
}
int nextInt() {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
String nextLine() {
String str = "";
try {
str = br.readLine();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return str;
}
}
}

글 잘 봤습니다.