1. 문제 링크
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/2001
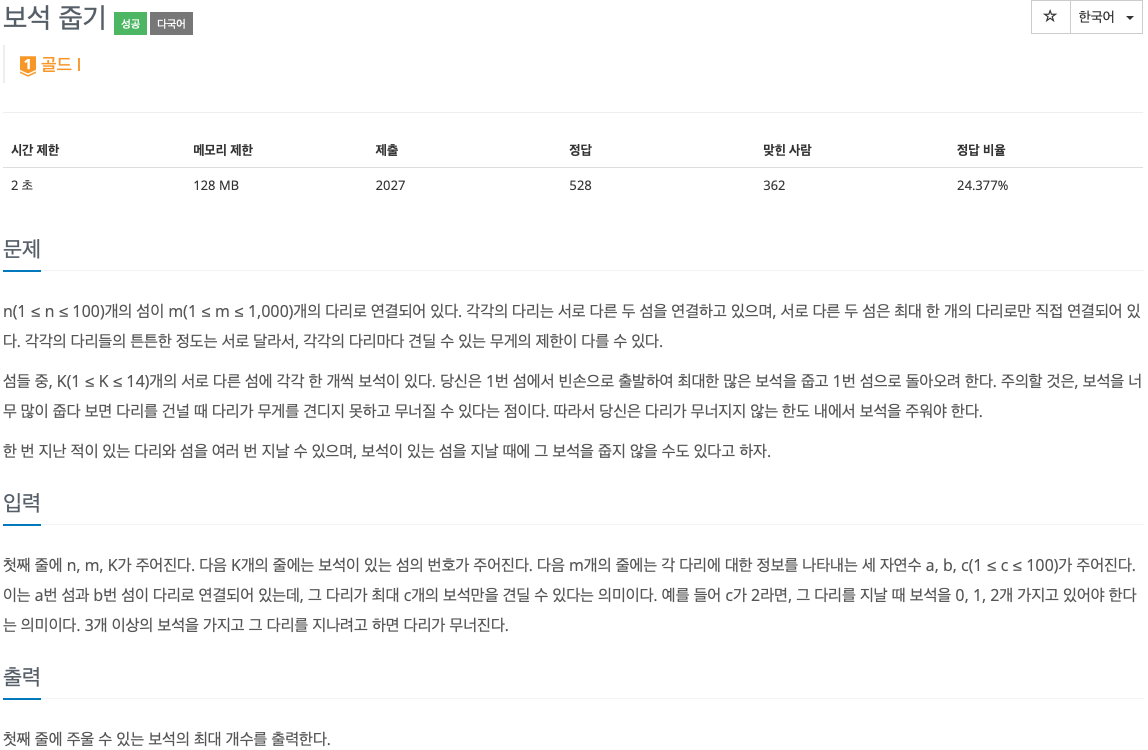
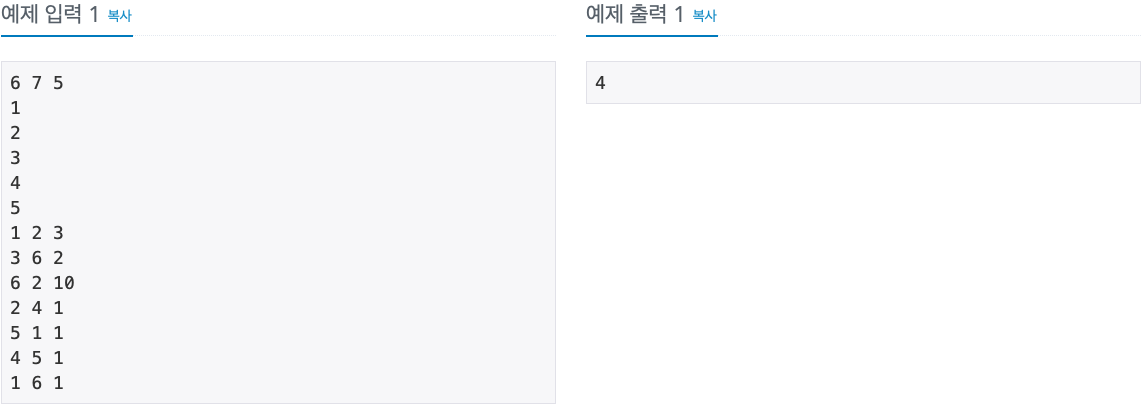
2. 문제
3. 소스코드
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static int islandNum;
static int bridgeNum;
static int jewelryIslandNum;
static int max;
static int[] jewelryIslands; // 보석이 있는 섬들을 나타내는 배열
static Map<Integer, List<Edge>> map; // 각 섬에 연결된 다리 정보
static void input() {
Reader scanner = new Reader();
islandNum = scanner.nextInt();
bridgeNum = scanner.nextInt();
jewelryIslandNum = scanner.nextInt();
jewelryIslands = new int[islandNum + 1];
map = new HashMap<>();
for(int island = 1; island <= islandNum; island++) {
map.put(island, new ArrayList<>());
}
// 보석이 있는 섬들을 낮은 번호의 섬부터 0을 시작으로 하여 번호를 매긴다
// 이 번호들을 jewelryIslands에 저장한다
int[] jewelryIslandsArr = new int[jewelryIslandNum];
for(int idx = 0; idx < jewelryIslandNum; idx++) {
jewelryIslandsArr[idx] = scanner.nextInt();
}
Arrays.sort(jewelryIslandsArr);
Arrays.fill(jewelryIslands, -1);
for(int idx = 0; idx < jewelryIslandNum; idx++) {
jewelryIslands[jewelryIslandsArr[idx]] = idx;
}
for(int bridge = 0; bridge < bridgeNum; bridge++) {
int island1 = scanner.nextInt();
int island2 = scanner.nextInt();
int weight = scanner.nextInt();
map.get(island1).add(new Edge(island2, weight));
map.get(island2).add(new Edge(island1, weight));
}
}
static void solution() {
bfs(1);
System.out.println(max);
}
// 1. 시작점이 보석을 가지고 있는지 확인하여 보석을 가진 경우에는 보석을 주운 경우와 줍지 않은 경우를 Queue에 넣어주고 방문체크를 진행한다
// 보석이 없다면 Queue에 시작점을 넣어주고 방문체크를 진행한다
// 2. Queue에서 다음 갈 수 있는 섬들을 탐색하며 방문되어 있는지, 다리를 건널 수 있는지 체크한다
// 3. 다음 섬에 대해 보석을 줍지 않는 경우를 Queue에 넣어주고 방문체크를 진행한다
// 4. 다음 섬이 보석을 갖고 있는지 확인하고, 있다면 비트 마스킹을 이용해 이미 주운 보석이 아닌지 확인한 후 아니라면 비트 연산을 통해 보석을 주운 것을 체크하고 Queue에 넣어주며 방문체크를 진행한다
// 5. 만약 탐색하고 있는 위치가 시작점이라면 그때까지의 주운 보석 수를 이용하여 최댓값을 갱신한다
static void bfs(int start) {
Queue<Path> queue = new LinkedList<>();
// visited[n][bit] = n번 섬까지 bit에 해당하는 보석들을 주워왔을 때 방문한 적이 있는지 여부
// - ex. visited[6][00111] : 보석이 있는 섬 중 0번째 섬, 1번째 섬, 2번째 섬의 보석을 주워오면서 6번 섬까지 도달한 경우가 있는지 여부를 나타낸다
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[islandNum + 1][1 << jewelryIslandNum];
boolean isFirst = true; // 시작인지 나타내는 변수
queue.offer(new Path(start, 0, 0));
// 시작점을 queue에 넣어 BFS 탐색 시에 이용
// 만약 시작점에 보석이 있다면 해당 보석을 줍지 않고 이동하는 경우를 의미한다
visited[start][0] = true;
if(jewelryIslands[start] != -1) { // 시작점에 보석이 있다면
// 시작점의 보석을 줍고 이동하는 경우를 의미한다
// 그러한 경우를 queue에 넣어 BFS 탐색 시에 이용한다
int bit = 1 << jewelryIslands[start];
visited[start][bit] = true;
queue.offer(new Path(start, 1, bit));
// 보석 하나를 주웠기 때문에 주운 보석 개수의 최댓값을 나타내는 max 변수의 값을 1로 변경한다
max = 1;
}
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
// 현재 queue에 들어있는 원소의 수
// 같은 이동 횟수에 해당하는 원소들에 대해서 탐색하기 위해 미리 원소의 수를 뽑는다
int size = queue.size();
for(int count = 0; count < size; count++) {
Path cur = queue.poll();
// 만약 현재 위치가 시작지점이고 시작하는 경우가 아니며 들고있는 보석의 수가 0이 아니라면
// 즉, 보석들을 주워 다시 시작지점으로 돌아왔다면
if(cur.island == start && cur.jewelryWeight != 0 && !isFirst) {
// 주운 보석 개수의 최댓값을 갱신
max = Math.max(max, cur.jewelryWeight);
continue;
}
// 현재 위치에서 갈 수 있는 다른 섬들을 순회하며 이동한다
for(Edge next : map.get(cur.island)) {
// 만약 다음 위치로 가기 위한 다리가 현재 들고 있는 보석의 수만큼을 견디지 못하거나 이미 방문한 적이 있다면
// 다음 경우를 확인한다
if(next.weight < cur.jewelryWeight || visited[next.island][cur.visited])
continue;
// 다음 위치를 queue에 넣어 다음 탐색 시에 해당 위치를 이용한다
// 만약 다음 위치가 보석이 있는 섬이라면 해당 섬의 보석은 줍지 않고 이동하는 경우를 의미한다
visited[next.island][cur.visited] = true;
queue.offer(new Path(next.island, cur.jewelryWeight, cur.visited));
if(jewelryIslands[next.island] != -1) { // 다음 위치가 보석이 있는 섬이라면
int bit = 1 << jewelryIslands[next.island]; // 다음 위치가 몇 번째 보석이 있는 섬인지 확인하여 이를 비트로 나타낸다
// 만약 다음 위치의 보석을 아직 줍지 않았다면
if((cur.visited & bit) == 0) {
// 다음 위치의 보석을 주운 상태의 비트를 계산한다
int temp = cur.visited | bit;
// 다음 위치의 보석을 주운 경우로 queue에 넣어 다음 탐색 시에 이용한다
visited[next.island][temp] = true;
queue.offer(new Path(next.island, cur.jewelryWeight + 1, temp));
}
}
}
}
// 처음 한 번의 for문을 돌고 나면 이제는 더이상 시작 상태가 아니므로 isFirst 값을 false로 변경한다
isFirst = false;
}
}
static class Path {
int island; // 현재 섬 번호
int jewelryWeight; // 주운 보석 개수
int visited; // 주운 보석에 대한 비트
public Path(int island, int jewelryWeight, int visited) {
this.island = island;
this.jewelryWeight = jewelryWeight;
this.visited = visited;
}
}
static class Edge {
int island;
int weight;
public Edge(int island, int weight) {
this.island = island;
this.weight = weight;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
input();
solution();
}
static class Reader {
BufferedReader br;
StringTokenizer st;
public Reader() {
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
}
String next() {
while(st == null || !st.hasMoreElements()) {
try {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return st.nextToken();
}
int nextInt() {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
}
}
