1. 문제 링크
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/2021
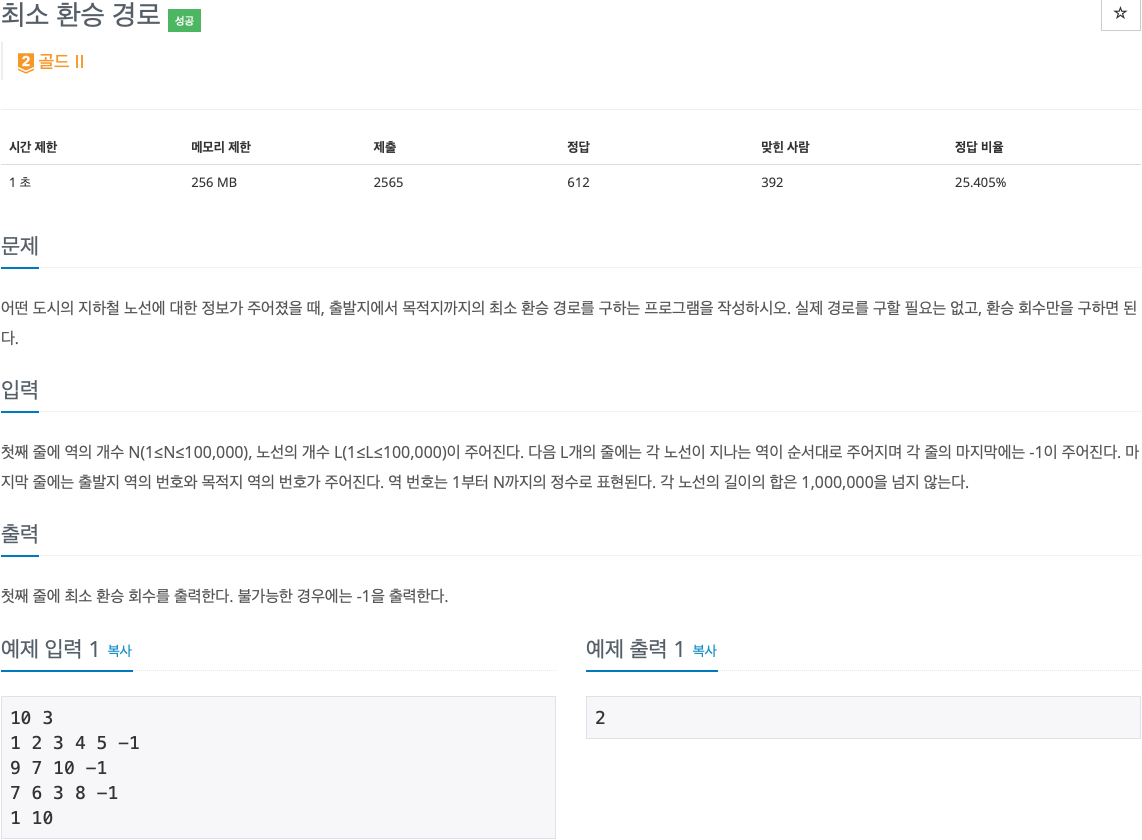
2. 문제
3. 소스코드
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
static int stationCount;
static int lineCount;
static int startStationNumber;
static int endStationNumber;
static Map<Integer, Set<Integer>> lines;
static Map<Integer, Set<Integer>> stations;
static void input() {
Reader scanner = new Reader();
stationCount = scanner.nextInt();
lineCount = scanner.nextInt();
lines = new HashMap<>();
stations = new HashMap<>();
for (int line = 1; line <= lineCount; line++) {
lines.put(line, new HashSet<>());
inputEachLine(line, scanner);
}
startStationNumber = scanner.nextInt();
endStationNumber = scanner.nextInt();
}
static void inputEachLine(int lineNumber, Reader scanner) {
while (true) {
int stationNumber = scanner.nextInt();
if (stationNumber == -1) {
return;
}
lines.get(lineNumber).add(stationNumber);
stations.computeIfAbsent(stationNumber, key -> new HashSet<>());
stations.get(stationNumber).add(lineNumber);
}
}
static void solution() {
System.out.println(bfs(startStationNumber, endStationNumber));
}
/*
* 노선이 지나는 역이 lineCount개 줄에 걸쳐 나타나는데, 위에서부터 각 노선에 번호를 1번부터 lineCount번까지 매긴다
* 각 노선을 지나는 역을 lines라는 Map에, 각 역이 포함되어 있는 노선 번호를 stations라는 Map에 저장한다
* BFS를 통해 최소 환승 횟수를 구한다
* - 방문체크를 해야 할 것이 2개가 존재 - 노선, 역
* - 그러므로 방문한 노선을 체크할 배열 하나와 방문한 역을 체크할 배열 하나를 생성
* - 방문시에 필요한 정보가 역 번호, 노선 번호, 환승 횟수이기 때문에 이를 나타내는 Station 클래스 생성
* - 처음에 어떤 노선을 탈지 아직 정해지지 않았기 때문에 우선 노선 번호를 0으로 하여 출발지 역에 대한 정보를 Queue에 추가
* - 최소 환승 횟수를 구하는 것이기 때문에 PriorityQueue로 생성하고, 환승 횟수 오름차순으로 정렬
* - 현재 역이 포함되어 있는 노선들을 돌며 아직 방문하지 않은 노선들에 대해 각 노선에서 방문하지 않은 역들로 이동
* - 이때, 현재 위치한 노선과 같은 노선으로 이동하는 것이라면 환승 횟수를 늘리지 않고
* - 현재 위치한 노선과 다른 노선으로 이동하는 것이라면 환승 횟수를 1 늘린다
* - 처음 출발지 역을 Queue에 넣을 때, 노선 번호를 0으로 넣어놨기 때문에, 노선 번호가 0이라면 환승 횟수는 항상 0으로 두고 다음 역으로 이동한다
* - 위와 같은 방식으로 탐색을 진행하다 처음 목적지 역에 도착했다면 그때까지의 환승 횟수가 최소 환승 횟수이므로 이를 출력한다
*/
static int bfs(int startStation, int endStation) {
Queue<Station> stationQueue = new PriorityQueue<>();
boolean[] lineVisited = new boolean[lineCount + 1];
boolean[] stationVisited = new boolean[stationCount + 1];
stationQueue.offer(new Station(startStation, 0, 0));
stationVisited[startStation] = true;
int minChangeCount = -1;
while (!stationQueue.isEmpty()) {
Station cur = stationQueue.poll();
if (cur.stationNumber == endStation) {
minChangeCount = cur.changeCount;
break;
}
for (int lineNumber : stations.get(cur.stationNumber)) {
if (lineVisited[lineNumber]) {
continue;
}
lineVisited[lineNumber] = true;
int nextChangeCount = cur.changeCount;
nextChangeCount += cur.lineNumber == lineNumber ? 0 : 1;
if (cur.lineNumber == 0) {
nextChangeCount = 0;
}
for (int stationNumber : lines.get(lineNumber)) {
if (stationVisited[stationNumber]) {
continue;
}
stationVisited[stationNumber] = true;
stationQueue.offer(new Station(stationNumber, lineNumber, nextChangeCount));
}
}
}
return minChangeCount;
}
static class Station implements Comparable<Station> {
int stationNumber;
int lineNumber;
int changeCount;
public Station(int stationNumber, int lineNumber, int changeCount) {
this.stationNumber = stationNumber;
this.lineNumber = lineNumber;
this.changeCount = changeCount;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Station o) {
return changeCount - o.changeCount;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
input();
solution();
}
static class Reader {
BufferedReader br;
StringTokenizer st;
public Reader() {
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
}
String next() {
while (st == null || !st.hasMoreElements()) {
try {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return st.nextToken();
}
int nextInt() {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
}
}
