1. 문제 링크
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/5213
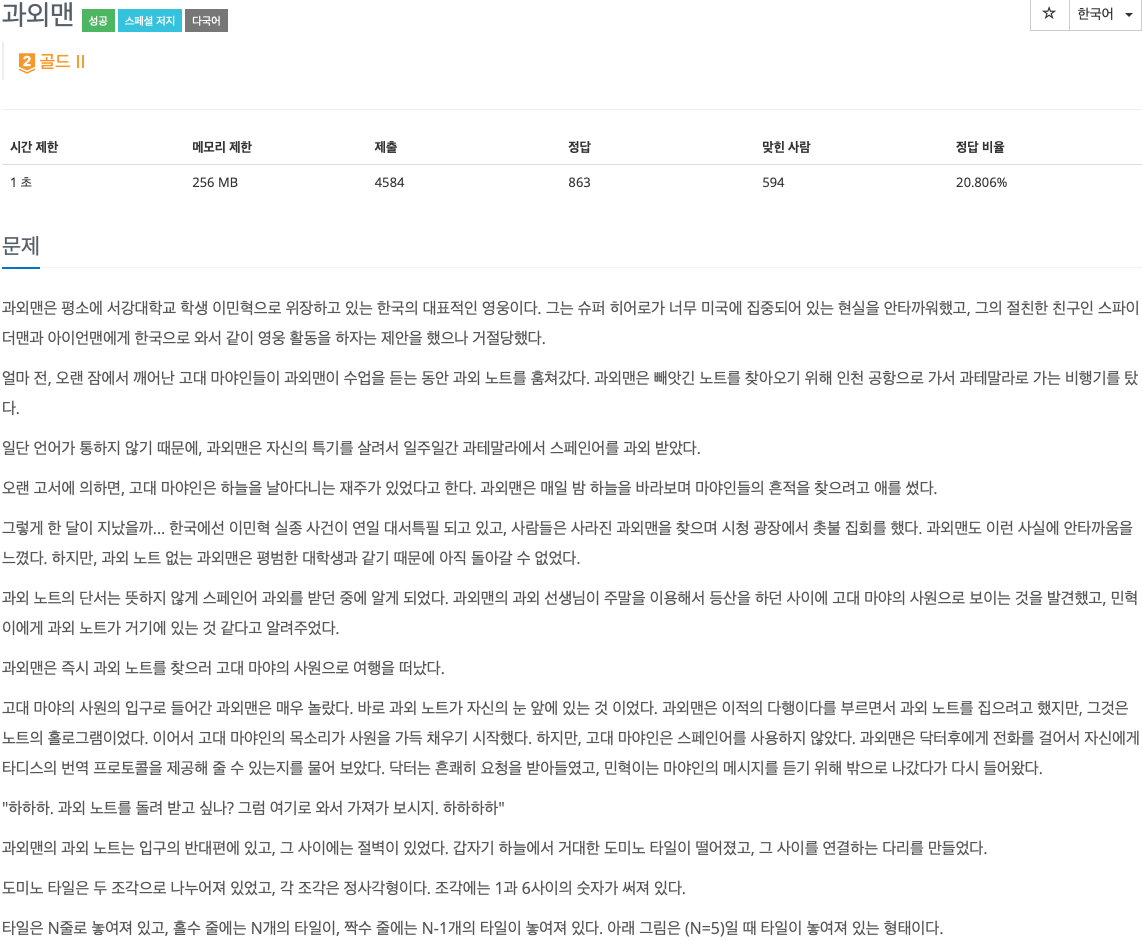
2. 문제



3. 소스코드
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
static int size;
static int[][] tiles;
static int[][] tileNumbers;
static int[] dx = {-1, 0, 1, 0};
static int[] dy = {0, -1, 0, 1};
static void input() {
Reader scanner = new Reader();
size = scanner.nextInt();
tiles = new int[size][size * 2];
tileNumbers = new int[size][size * 2];
int tileNum = 1;
for (int row = 0; row < size; row++) {
for (int col = row % 2 == 0 ? 0 : 1; col < (row % 2 == 0 ? tiles[row].length : tiles[row].length - 1);
col += 2) {
int left = scanner.nextInt();
int right = scanner.nextInt();
tiles[row][col] = left;
tiles[row][col + 1] = right;
tileNumbers[row][col] = tileNumbers[row][col + 1] = tileNum++;
}
}
}
/*
* 도미노 타일 하나가 두 조각으로 나누어져 있기 때문에 각 조각이 아닌 각 도미노 타일 단위로 BFS를 진행하여 가장 짧은 경로의 길이를 구한다
* BFS를 시작할 때에는 1번 타일(가장 왼쪽 위 타일)부터 시작하기 때문에 1번 타일에 해당하는 두 조각을 Queue에 넣고 시작한다
* 한 타일을 기준으로 이동할 수 있는 곳은 상하좌우이기 때문에 Queue에 있는 각 조각을 기준으로 상하좌우로 이동해본다
* 가장 짧은 경로로 가기 위해서는 방문한 곳을 다시 방문하여서는 안되기 때문에 이동한 위치가 방문하지 않은 곳인지 먼저 확인한다
* 방문하지 않은 곳이라면 조각에 쓰여있는 숫자가 같은 곳으로만 이동이 가능하기 때문에 쓰여있는 숫자가 일치하는지 확인한다
* 일치한다면 해당 위치로 이동이 가능하다는 뜻이므로 방문 체크 및 이동 타일 번호를 갱신하고 다음 탐색에 활용하기 위해 Queue에 넣는다
* 또한 어떠한 조각으로 이동했다면 그 조각이 포함되는 타일을 방문했다고 볼 수 있으니 방문한 타일의 다른 조각 역시 방문 체크 및 다음 탐색에 활용하기 위해 Queue에 넣는다
* 이를 반복해서 BFS 로직을 돌리며 이동 경로를 파악한다.
*/
static void solution() {
List<Integer> answer = bfs();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(answer.size()).append('\n');
answer.stream().forEach(tileNum -> sb.append(tileNum).append(' '));
System.out.println(sb);
}
static List<Integer> bfs() {
Queue<Loc> queue = new LinkedList<>();
List<Integer> paths = new ArrayList<>(List.of(1));
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[size][size * 2];
queue.offer(new Loc(0, 0, paths));
queue.offer(new Loc(0, 1, paths));
visited[0][0] = visited[0][1] = true;
int maxTileNumber = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
Loc answer = null;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Loc cur = queue.poll();
if (tileNumbers[cur.x][cur.y] > maxTileNumber) {
maxTileNumber = tileNumbers[cur.x][cur.y];
answer = cur;
}
for (int dir = 0; dir < dx.length; dir++) {
int cx = cur.x + dx[dir];
int cy = cur.y + dy[dir];
if (isInMap(cx, cy) && !visited[cx][cy]) {
if (tiles[cur.x][cur.y] == tiles[cx][cy]) {
visited[cx][cy] = true;
List<Integer> nextPaths = new ArrayList<>(cur.paths);
nextPaths.add(tileNumbers[cx][cy]);
queue.offer(new Loc(cx, cy, nextPaths));
if (tileNumbers[cx][cy] == tileNumbers[cx][cy + 1]) {
visited[cx][cy + 1] = true;
queue.offer(new Loc(cx, cy + 1, nextPaths));
continue;
}
if (tileNumbers[cx][cy] == tileNumbers[cx][cy - 1]) {
visited[cx][cy - 1] = true;
queue.offer(new Loc(cx, cy - 1, nextPaths));
}
}
}
}
}
return answer.paths;
}
static boolean isInMap(int x, int y) {
return 0 <= x && x < size && 0 <= y && y < size * 2;
}
static class Loc {
int x;
int y;
List<Integer> paths;
public Loc(int x, int y, List<Integer> paths) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.paths = paths;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
input();
solution();
}
static class Reader {
BufferedReader br;
StringTokenizer st;
public Reader() {
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
}
String next() {
while (st == null || !st.hasMoreElements()) {
try {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return st.nextToken();
}
int nextInt() {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
}
}
